structural morphology
Why does struct exist?
Computer is to solve people's problems. People know the natural world through "attributes".
The attribute set abstracted from anything can be used to represent a class of things and types. In this work, c, struct.
Declaration of structure type
struct tag
{
member_list;
}variable_list;Special declaration (incomplete declaration is allowed when declaring the structure)
For example:
//Anonymous structure type
struct
{
int a;
char b;
float c;
}x;
struct
{
int a;
char b;
float c;
}a[20],*p;//Based on the above code, the following code is illegal p=&x;
Warning: the compiler will treat the above two declarations as two completely different types. So it's illegal.
(as long as there are two structure types, even if the internal elements are the same, they are also different types.)
Self reference of structure (completed by pointer)
Why is there self reference? Variables should form a relationship.
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};Definition and initialization of structure variables:
struct Point
{
int x;
int y; }p1; //Define the variable p1 while declaring the type
struct Point p2; //Define structure variable p2
//Initialization: define variables and assign initial values at the same time.
struct Point p3 = {x, y};
struct Stu //Type declaration
{
char name[15];//name
int age; //Age
};
struct Stu s = {"zhangsan", 20};//initialization
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Point p;
struct Node* next;
}n1 = {10, {4,5}, NULL}; //Structure nesting initialization
struct Node n2 = {20, {5, 6}, NULL};//Structure nesting initializationStructure memory alignment
Test site: how to calculate the size of the structure? First, you have to master the alignment rules of the structure
1. The address of the first member at the structure variable offset of 0.
(why doesn't the first member consider alignment? 0 / any number can be divided)
2. Other member variables except the first member shall be aligned to the address of the minimum integer multiple of a number (alignment number).
Number of alignments: its own size.
Minimum integer multiple = starting offset / number of alignments.
3. The total size of the structure is the minimum integer multiple of the maximum alignment number (each member has an alignment number).
Note: Although the first member does not participate in the alignment, he should participate in the comparison of the maximum alignment number.
4. If the structure contains a structure, the alignment number of the internal structure is its maximum alignment number;
If the structure contains an array, the first element is aligned and the other elements are aligned.
Why is there memory alignment?
Bit segment
What is a bit segment?
struct A {
int _a:2;
int _b:5;
int _c:10;
int _d:30;
};//An example
struct S {
char a:3;
char b:4;
char c:5;
char d:4;
};
struct S s = {0};
s.a = 10;//01010
s.b = 12; //01100
s.c = 3; //00011
s.d = 4;//00100
//How is space opened up?
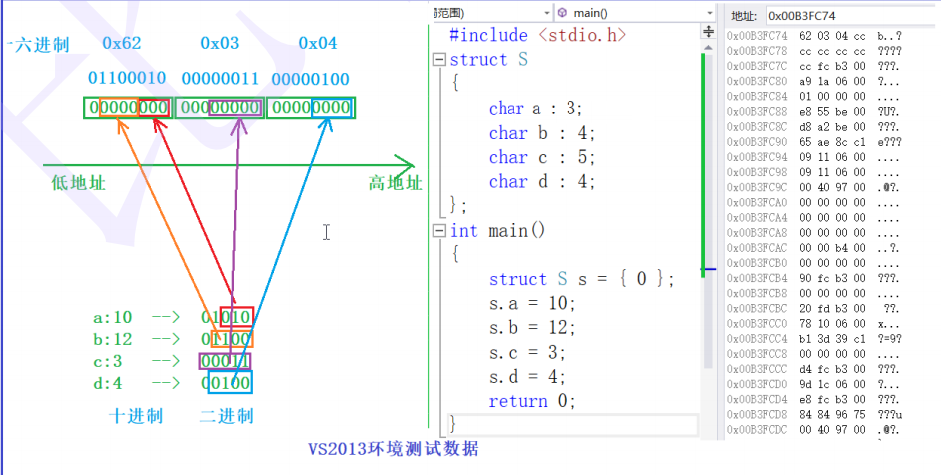
As can be seen from the test results above, truncation occurs if the size of the binary storage exceeds the size assigned to you by the bit segment.
enumeration
Definition of enumeration type
emun Day//week
{
Mon,
Tues,
Wed,
Thur,
Fri,
Sat,
Sun
};
enum Color//colour
{
RED=1,
GREEN=2,
BLUE=4
};
enum Color clr = GREEN;//You can only assign values to enumeration variables with enumeration constants, so that there will be no type difference.
clr = 5; //OK?? OK!!! Enumeration is essentially an integer
Consortium
//Declaration of union type
union Un
{
char c;
int i;
};
//Definition of joint variables
union Un un;
//Calculate the size of multiple variables
printf("%d\n", sizeof(un));Characteristics of the joint:
union Un
{
int i;
char c;
};
union Un un;
// Are the output results the same? The same!!!!
printf("%p\n",&un);
printf("%d\n", &(un.i));
printf("%d\n", &(un.c));
//What is the output below?
un.i = 0x11223344;
un.c = 0x55;
printf("%x\n", un.i);Interview questions:
Determine the size of the current computer:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
union Un{
int i;
char c;
};
int main()
{
union Un un;
un.i = 0x33221100;
if (un.c ){
printf("Big end\n");
}
else
printf("Small end\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}Calculation of consortium size: (the third point of memory alignment shall be considered)
The size of the consortium is at least the size of the largest member
When the maximum member size is not an integer multiple of the maximum alignment number, it should be aligned to an integer multiple of the maximum alignment number.
union Un1
{
char c[5];
int i;
};
union Un2
{
short c[7];
int i;
};
//What is the output below?
printf("%d\n", sizeof(union Un1));//8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(union Un2));//16