1. Case realization
Enter the student's information on the keyboard and store the data in the txt file
Then we read the data in the bar txt file, convert it into a student object, and add it to the treeset set. The elements in the treeset set are sorted and stored according to the total score.
Here I mainly want to explain the TreeSet set
2. Set structure
Compared with an array, the length of a set is not fixed. There is no need to set the length of the set in advance. The structure of the set is as follows
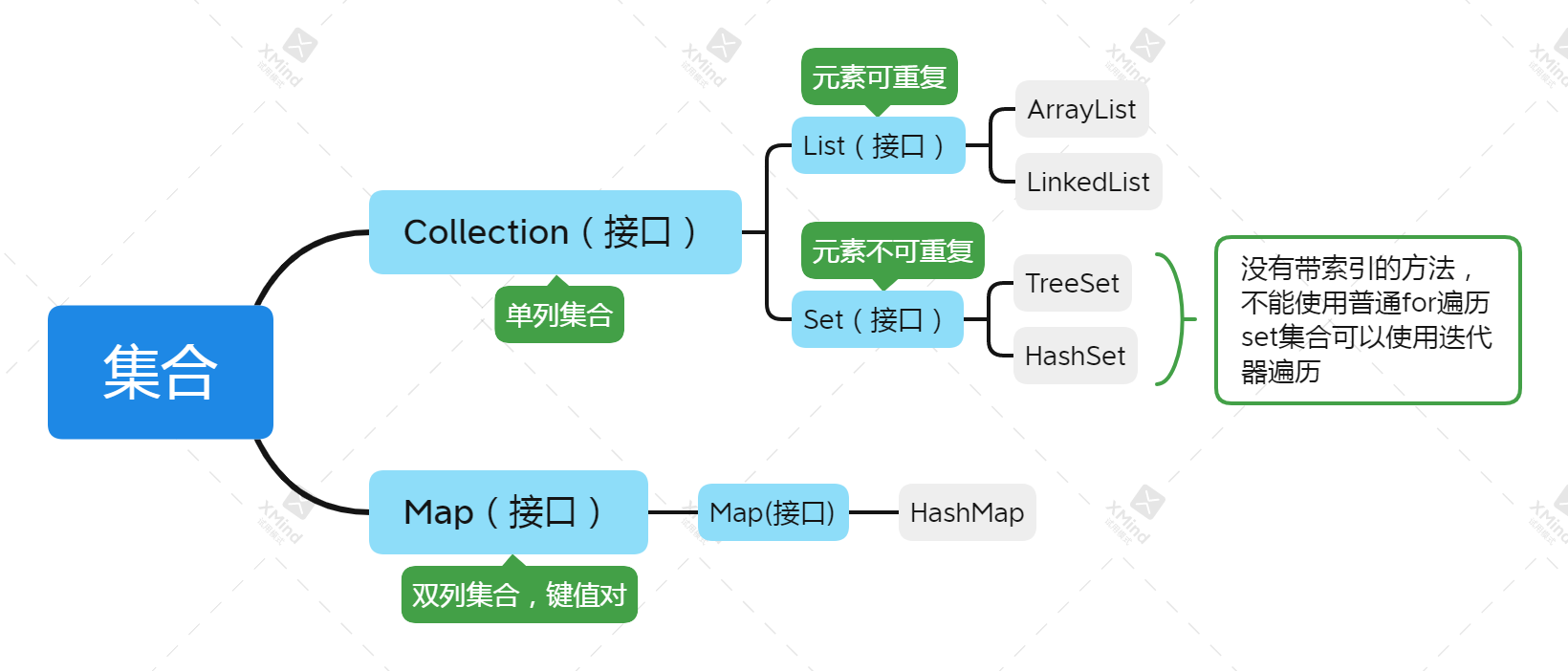
ArrayList, TreeSet and HashMap are commonly used
The elements of TreeSet are not repeated, and comparator sorting can be realized. You can sort according to your own defined methods or natural sorting
HashMap combination stores data according to key value pairs. We have several methods when traversing
1. Get the key set of the set, get the value according to the key set, and traverse
2. Obtain the key value of the set, and then traverse the set of objects after obtaining the key and value respectively
3. Explanation of TreeSet comparator sorting
Construction method of Treeset
TreeSet() {} / / sort by nature
TreeSet (comparator) {} / / sort by user-defined comparator
When customizing the comparator, because the parameter is an interface, we need to use the specific implementation class of the interface. Here, anonymous inner classes are used
//Create a collection to store the data read from the file and set a comparator for it
TreeSet<Student> treeSet =new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
//From front to back
//Pay attention to the primary and secondary conditions
//Sort by total score first
int res1 = s2.getSum()-s1.getSum();
//If the total score is the same, compare it according to the Chinese score
int res2 = res1 == 0 ? s2.getChinese()-s1.getChinese() : res1;
//If the total score is the same and the Chinese score is the same, compare it according to the math score
int res3 = res2==0? s2.getMath()- s1.getMath() : res2;
//If the total score is the same, the Chinese score is the same, and the math score is the same, then compare it according to the English score
int res4 = res3==0 ? s2.getEnglish()- s2.getEnglish() : res3;
//If the scores are all the same outside the number of words, they are sorted from a-z according to their initials
int res5 = res4==0? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : res4;
return res5;
}
});
Inside the code
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2), student is the student object,
Before subtraction, the int data implementation is added to the combination from small to large, and the String implementation is added to the collection from a-z
Before subtraction, add from large to small to combination for int data implementation, and add from z-a to collection for String implementation
//When we add the last data to the set, the set has been sorted,
Note how the comparator compares String data
//If the scores are all the same outside the number of words, they are sorted from a-z according to their initials
int res5 = res4==0? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : res4;
4. Complete project code:
Student object**
package package03_getFiletoStudentAndPaiXu;
public class Student {
private String name ;
private int chinese ;
private int math;
private int english;
private int sum;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english) {
this.name = name;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getChinese() {
return chinese;
}
public void setChinese(int chinese) {
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public int getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
this.math = math;
}
public int getEnglish() {
return english;
}
public void setEnglish(int english) {
this.english = english;
}
public int getSum() {
return sum = chinese+english+math;
}
}
main program
package package03_getFiletoStudentAndPaiXu;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class demo1 {
/*
Realize the keyboard to input the information of 5 students
Format this information and store it in a file
Then convert the data in the file into student objects
These student objects are stored in the collection
When the output set is required, it is sorted from high to low according to the total score of students
Because several are to be sorted, the Treeset collection is used and the comparator is used to sort
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Create character input stream
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\IdeaProjects\\Day07\\a.txt");
//Character output buffer stream
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
//Keyboard input data
System.out.println("How many students do you want to enter?");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
//Start entering student information
Scanner sc_data = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0 ; i< num ;i++){
System.out.println("Please enter page"+(i+1)+"Student information");
System.out.println("full name");
String name = sc_data.nextLine();
System.out.println("grade scores of Chinese");
String chinese = sc_data.nextLine();
System.out.println("Mathematics achievement");
String math =sc_data.nextLine();
System.out.println("English achievement");
String english = sc_data.nextLine();
String s = name+","+chinese+","+math+","+english;
System.out.println(s);
//Line by line storage into the file
bw.write(s);
//Line feed
bw.newLine();
//Refresh
bw.flush();
}
//Release resources at the end of storage
bw.close();
//Start reading data from the file
FileReader fr = new FileReader("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\IdeaProjects\\Day07\\a.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
//Create a collection to store the data read from the file and set a comparator for it
TreeSet<Student> treeSet =new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
//From front to back
//Pay attention to the primary and secondary conditions
//Sort by total score first
int res1 = s2.getSum()-s1.getSum();
//If the total score is the same, compare it according to the Chinese score
int res2 = res1 == 0 ? s2.getChinese()-s1.getChinese() : res1;
//If the total score is the same and the Chinese score is the same, compare it according to the math score
int res3 = res2==0? s2.getMath()- s1.getMath() : res2;
//If the total score is the same, the Chinese score is the same, and the math score is the same, then compare it according to the English score
int res4 = res3==0 ? s2.getEnglish()- s2.getEnglish() : res3;
//If the scores are all the same outside the number of words, they are sorted from a-z according to their initials
int res5 = res4==0? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : res4;
return res5;
}
});
String dataFromFile ;
while ((dataFromFile = br.readLine()) != null){
//Start splitting data
String split_res[] = dataFromFile.split(",");
//Get every data
String name = split_res[0];
int chinese = Integer.parseInt(split_res[1]);
int math = Integer.parseInt(split_res[2]);
int english = Integer.parseInt(split_res[3]);
//Create student object
Student student = new Student(name,chinese,math,english);
//Add to collection
treeSet.add(student);
}
//Start traversing the collection
for (Student student : treeSet){
System.out.println(student.getName()+"--"+student.getChinese()+"--"
+student.getMath()+"--"+student.getEnglish()+"--"+student.getSum());
}
}
}