1, JSP:
1. Instruction
(1) function:
Used to configure JSP pages and import resource files
(2) format:
<% @ instruction name attribute name 1 = attribute value 1 attribute name 2 = attribute value 2...% >
(3) classification:
① page: configure the of JSP pages
- contentType: equivalent to response.setContentType()
1. Set the mime type and character set of the response body
2. Set the encoding of the current jsp page (only high-level IDE can take effect. If low-level tools are used, you need to set pageEncoding property and set the character set of the current page) - Import: import package
- errorPage: after an exception occurs on the current page, it will automatically jump to the specified error page
- isErrorPage: identifies whether the current page is an error page.
*true: Yes, you can use the built-in object exception
*false: No. Default value. The built-in object exception cannot be used
For example:
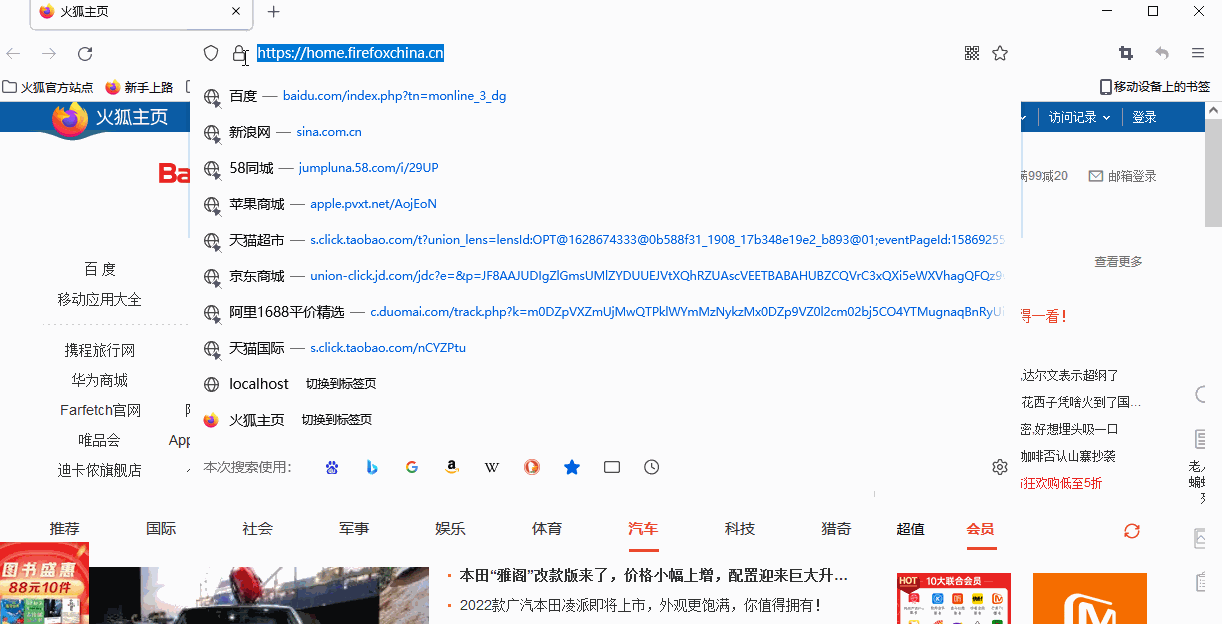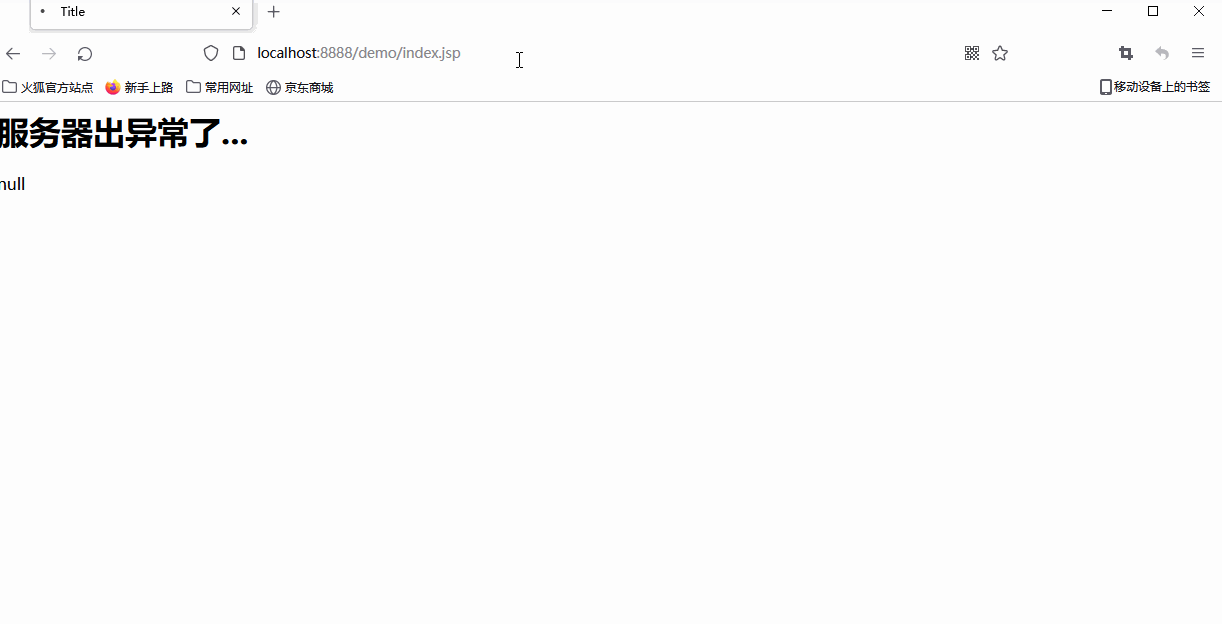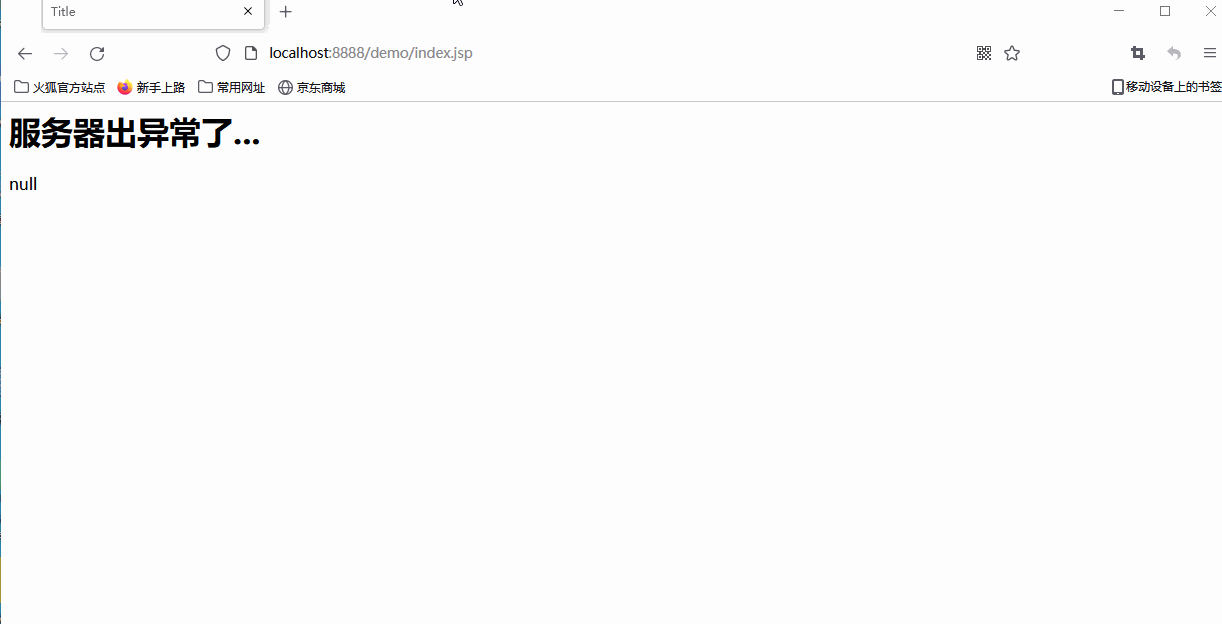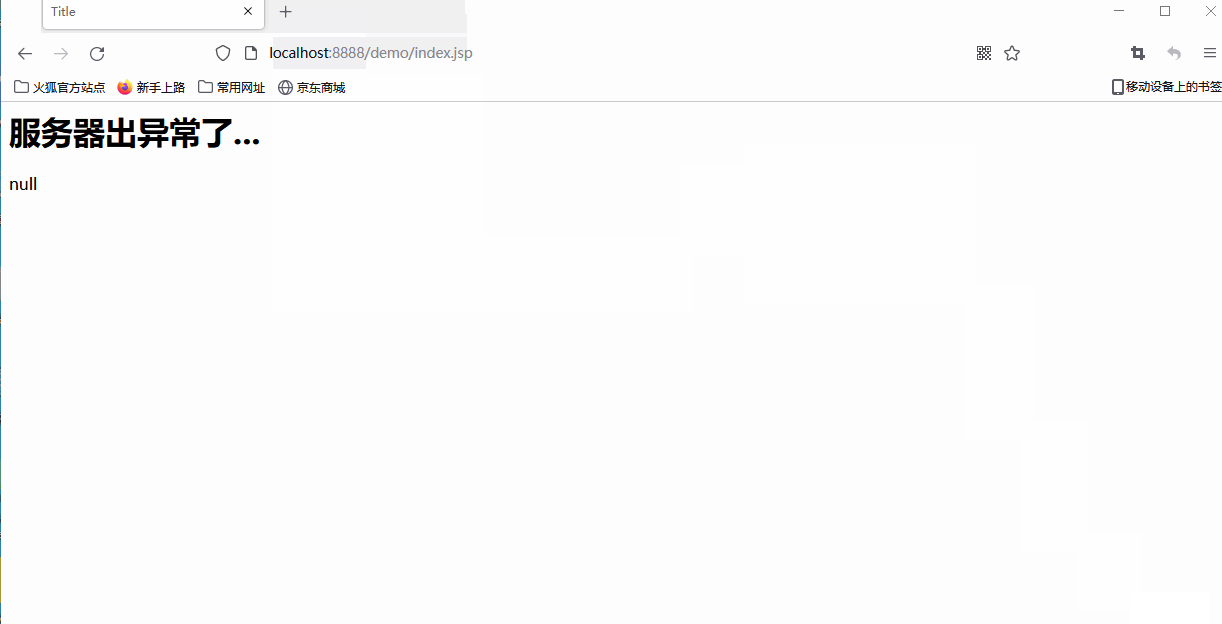
Exception page 500.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" isErrorPage="true" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Something went wrong with the server...</h1>
<%
String message = exception.getMessage();
out.print(message);
%>
</body>
</html>
Main page index.jsp
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" errorPage="500.jsp" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
List<String> lists = null;
out.write(lists.size());
%>
</body>
</html>
The effect is as follows
② include: the page contains.
Import the resource file for the page
<%@include file="top.jsp"%>
For example:
Public resource page top.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Public page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Copyright belongs to detective WeChat official account.</h1>
</body>
</html>
Home page index.jsp
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<%@ include file="top.jsp"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to corky's official website</h1>
</body>
</html>
The effects are as follows:
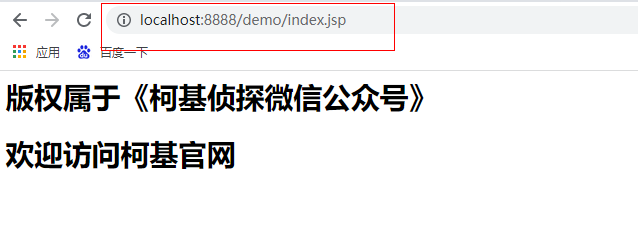
③ taglib: import resources (generally used to import label libraries)
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
Prefix: prefix, customized
This part will not be explained first, but will be introduced later
2. Notes:
- html comments:
<!-- -->: Only html snippets can be annotated - jsp comments: Recommended
<% ---% >: all comments can be made
3. Built in objects
In the jsp page, there are 9 objects that do not need to be created directly:
| Variable name | Real type | effect |
|---|---|---|
| pageContext | PageContext | The current page shares data, and eight other built-in objects can be obtained |
| request | HttpServletRequest | Multiple resources requested at one time (forwarding) |
| session | HttpSession | Between multiple requests in a session |
| application | ServletContext | Share data among all users |
| response | HttpServletResponse | Response object |
| page | Object | this object of the current page (Servlet) |
| out | JspWriter | Output object, data output to page |
| config | ServletConfig | Configuration object of Servlet |
| exception | Throwable | Exception object |
2, MVC
1.jsp evolution history
- In the early days, there were only servlet s, and only response was used to output tag data, which was very troublesome
- Later, there was jsp, which simplified the development of Servlet. If jsp is used excessively, it will write a lot of java code and html in jsp, which makes it difficult to maintain and cooperate
- Later, the web development of java draws lessons from the mvc development mode to make the program design more reasonable
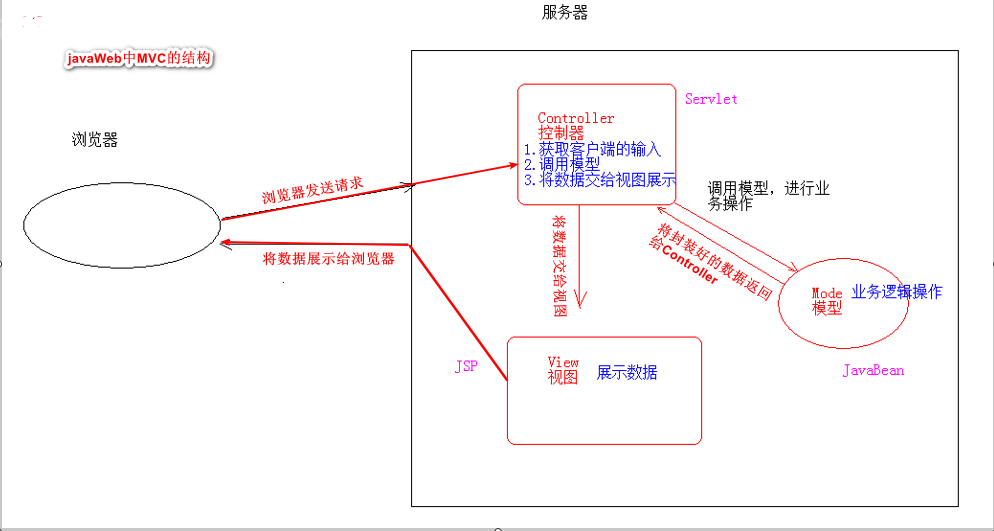
2. MVC in JavaWeb:
1. M: Model. JavaBean
Complete specific business operations, such as querying the database and encapsulating objects
2. V: View. JSP
Display data
3. C: Controller. Servlet
- Get user input
- Call model
- Give the data to the view for presentation
As shown in the figure
3. Advantages and disadvantages:
(1) advantages:
- Low coupling, easy maintenance, can be conducive to division of labor and cooperation
- High reusability
(2) disadvantages:
- It makes the project architecture complex and requires high developers
3, EL expression
1. Concept:
Expression Language
2. Function:
Replace and simplify the writing of java code in jsp pages
3. Syntax:
${expression}
For example:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>EL expression</title>
</head>
<body>
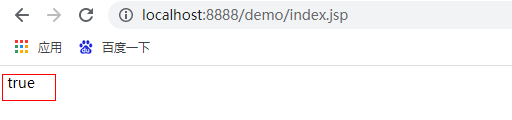
${4 > 1 }
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
4 note:
jsp supports el expressions by default. If you want to ignore the el expression
1. Set the page instruction in jsp: isELIgnored="true" ignore all el expressions in the current JSP page
For example:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" isELIgnored="true" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>EL expression</title>
</head>
<body>
${4 > 1 }
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
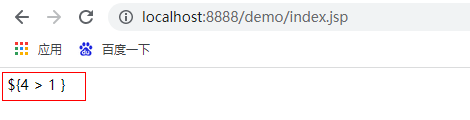
2. \ ${expression}: ignore the current el expression
For example:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>EL expression</title>
</head>
<body>
${4 > 1 }
<hr>
\${4>1}
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
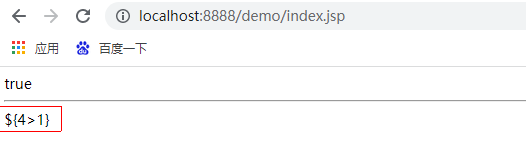
5 usage scenario:
(1) calculation:
① Operator:
- Arithmetic operator: + - * / (DIV)% (MOD)
- Comparison operator: > < > = < = ==
- Logical operator: & & (and) | (or)! (not)
- Air transport operator: empty
*Function: used to judge whether string, collection and array objects are null or length is 0
* ${empty list}: judge whether the string, collection and array objects are null or have a length of 0
* ${not empty str}: indicates whether the string, collection and array objects are not null and the length is > 0
For example:
<%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>EL expression</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Arithmetic operator </h3>
${3 + 4}<br>
${3 / 4}<br>
${3 div 4}<br>
${3 % 4}<br>
${3 mod 4}<br>
<h3>Comparison operator</h3>
${3 == 4}<br>
<h3>Logical operator</h3>
${3 > 4 && 3 < 4}<br>
${3 > 4 and 3 < 4}<br>
<h4>empty operator</h4>
<%
String str = "";
request.setAttribute("str",str);
List list = new ArrayList();
request.setAttribute("list",list);
%>
${not empty str}
${empty list}
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
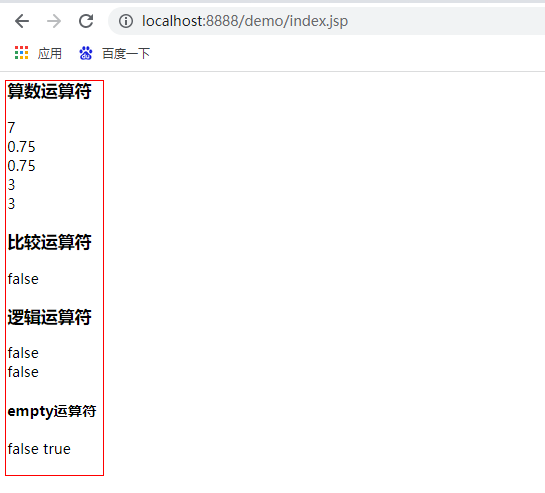
(2) get value
1. El expressions can only get values from domain objects
II. Syntax:
① ${field name. Key name}: gets the value of the specified key from the specified field
Domain name: (scope from small to large)
- pageScope --> pageContext
- requestScope --> request
- sessionScope --> session
- applicationScope --> application(ServletContext)
② ${key name}: indicates whether there is a value corresponding to the key from the smallest field until it is found.
For example:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>el Get data in domain</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
//Storing data in a domain
session.setAttribute("name","Li Si");
request.setAttribute("name","Zhang San");
session.setAttribute("age","23");
request.setAttribute("str","");
%>
<h3>el Get value</h3>
${requestScope.name}
${sessionScope.age}
<%-- If the obtained value does not exist; otherwise null,And not displayed on the page--%>
${sessionScope.haha}
${name}
${sessionScope.name}
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
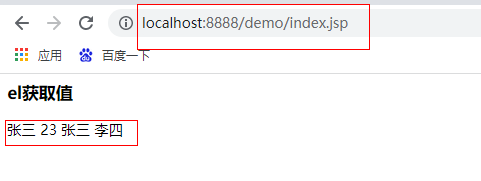
③ Get the values of object, List collection and Map collection
1. Object: ${domain name. Key name. Attribute name}
In essence, it will call the getter method of the object
For example:
User.java class
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public User(String name, int age, Date birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public User() {
}
/**
* Logical view
* @return
*/
public String getBirStr(){
if(birthday != null){
//1. Format date object
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//2. Just return the string
return sdf.format(birthday);
}else{
return "";
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
index.jsp page
<%@ page import="com.kejizhentan.bean.User" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.Date" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>el Get data in domain</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
User user = new User();
user.setName("Zhang San");
user.setAge(23);
user.setBirthday(new Date());
request.setAttribute("u",user);
%>
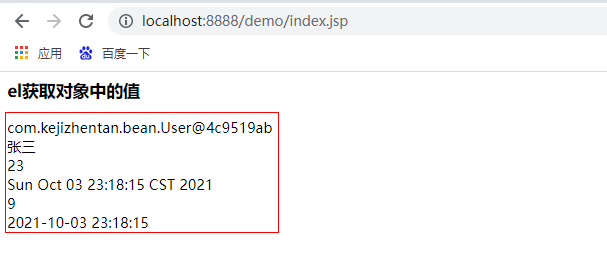
<h3>el Gets the value in the object</h3>
${requestScope.u}<br>
<%--
* It is obtained through the properties of the object
* setter or getter Method, remove set or get,In the rest of the, the first letter becomes lowercase.
* setName --> Name --> name
--%>
${requestScope.u.name}<br>
${u.age}<br>
${u.birthday}<br>
<%-- Date Object month It starts from scratch--%>
${u.birthday.month}<br>
${u.birStr}<br>
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
2. List set: ${field name. Key name [index]}
For example:
User.java class
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public User(String name, int age, Date birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public User() {
}
/**
* Logical view
* @return
*/
public String getBirStr(){
if(birthday != null){
//1. Format date object
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//2. Just return the string
return sdf.format(birthday);
}else{
return "";
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
index.jsp page
<%@ page import="com.kejizhentan.bean.User" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.Date" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>el Get data in domain</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
User user = new User();
user.setName("Zhang San");
user.setAge(23);
user.setBirthday(new Date());
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add(user);
request.setAttribute("list",list);
%>
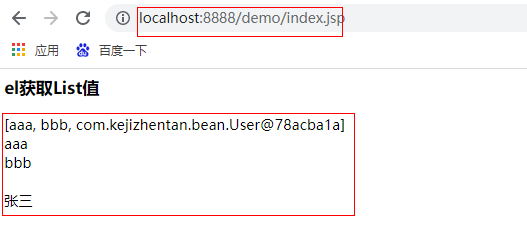
<h3>el obtain List value</h3>
${list}<br>
${list[0]}<br>
${list[1]}<br>
${list[10]}<br>
${list[2].name}
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
3. Map set:
- ${field name. key name. key name}
- ${domain name. Key name ["key name"]}
For example:
User.java class
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public User(String name, int age, Date birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public User() {
}
/**
* Logical view
* @return
*/
public String getBirStr(){
if(birthday != null){
//1. Format date object
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//2. Just return the string
return sdf.format(birthday);
}else{
return "";
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
index.jsp page
<%@ page import="com.kejizhentan.bean.User" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.*" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>el Get data in domain</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
User user = new User();
user.setName("Zhang San");
user.setAge(23);
user.setBirthday(new Date());
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("sname","Li Si");
map.put("gender","male");
map.put("student",user);
request.setAttribute("map",map);
%>
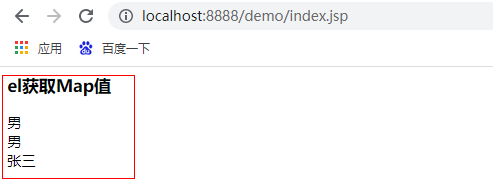
<h3>el obtain Map value</h3>
${map.gender}<br>
${map["gender"]}<br>
${map.student.name}
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
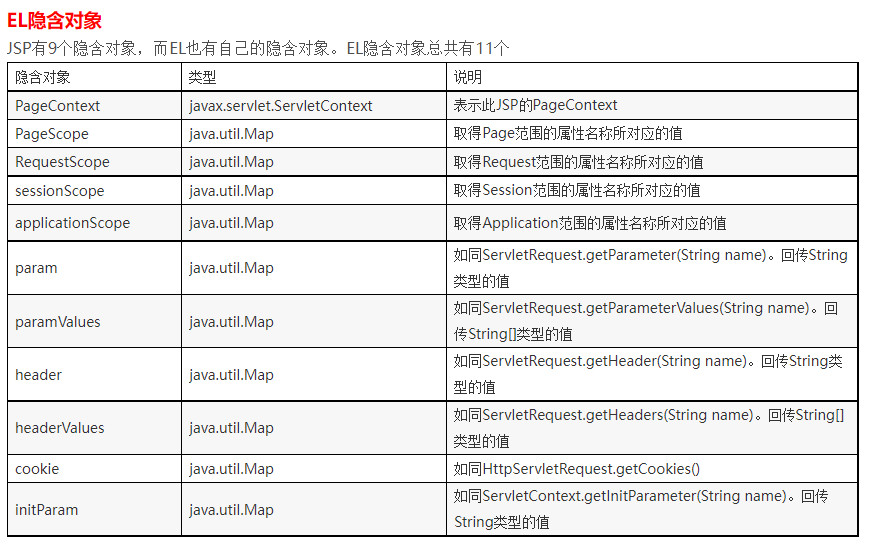
6 implicit objects:
There are 11 implicit objects in the el expression
pageContext uses the most:
effect:
1. Get the other eight built-in objects of jsp
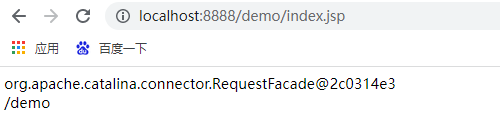
2${pageContext.request.contextPath}: get virtual directory dynamically
For example:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>el Get data in domain</title>
</head>
<body>
<%-- obtain jsp Eight other built-in objects--%>
${pageContext.request}<br>
<%--Get virtual path--%>
${pageContext.request.contextPath}
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
4, JSTL tag library
1. Concept: JavaServer Pages Tag Library JSP standard tag library
It is an open source free jsp tag < tag > provided by Apache organization
2. Function:
Used to simplify and replace java code on jsp pages
3. Use steps:
- Import jstl related jar packages
Click to download the jar package required for jstl - Import tag library: taglib instruction: <% @ taglib% >
- Use label
4. Common JSTL Tags
(1) if: equivalent to if statement of java code
1. Properties:
- test must be an attribute and accept a boolean expression
*If the expression is true, the if label body content is displayed; if false, the label body content is not displayed
*In general, the test attribute value is used in conjunction with el expressions
be careful:
c: The if tag does not have else. If you want else, you can define a c:if tag
For example:
Project structure:
index.jsp page
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>jstl Label library presentation</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--
c:if label
1. Properties:
* test Attribute required, accepted boolean expression
* If the expression is true,Then display if Label body content, if false,The label body content is not displayed
* Normally, test Attribute values are combined el Use with expressions
2. be careful: c:if No label else Situation, want else In this case, you can define a c:if label
--%>
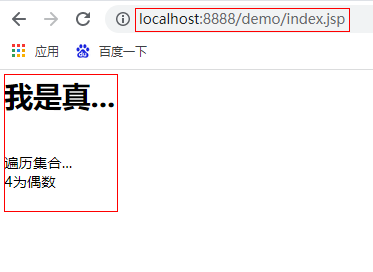
<c:if test="true">
<h1>I'm serious...</h1>
</c:if>
<br>
<%
//Judge whether a list collection in the request field is empty. If it is not null, the traversal collection will be displayed
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("aaaa");
request.setAttribute("list",list);
request.setAttribute("number",4);
%>
<c:if test="${not empty list}">
Traversal set...
</c:if>
<br>
<c:if test="${number % 2 != 0}">
${number}Odd number
</c:if>
<c:if test="${number % 2 == 0}">
${number}Even number
</c:if>
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
(2) choose: the switch statement equivalent to java code
- Using the choose tag to declare is equivalent to the switch declaration
- Use the when tag for judgment equivalent to case
- Using the otherwise tag to declare other situations is equivalent to default
For example:
Project structure:

index.jsp page
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>jstl Label library presentation</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--
The completion number corresponds to the day of the week case
1.Store a number in the field
2.use choose Label extraction number amount to switch statement
3.use when Digital judgment of labels amount to case
4.otherwise The label makes a statement in other cases, which is equivalent to default
--%>
<%
request.setAttribute("number",51);
%>
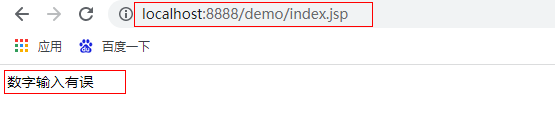
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${number == 1}">Monday</c:when>
<c:when test="${number == 2}">Tuesday</c:when>
<c:when test="${number == 3}">Wednesday</c:when>
<c:when test="${number == 4}">Thursday</c:when>
<c:when test="${number == 5}">Friday</c:when>
<c:when test="${number == 6}">Saturday</c:when>
<c:when test="${number == 7}">Sunday</c:when>
<c:otherwise>Digital input error</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</body>
</html>
The effects are as follows:
(3) foreach: equivalent to the for statement of java code
For example:
Project structure:

index.jsp page
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Array" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>jstl Label library presentation</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--
foreach:amount to java Coded for sentence
1. Repeat operation completed
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++){
}
* Properties:
begin: Start value
end: End value
var: Temporary variable
step: step
varStatus:Loop state object
index:The index of the element in the container, starting from 0
count:Number of cycles, starting from 1
2. Traversal container
List<User> list;
for(User user : list){
}
* Properties:
items:Container object
var:Temporary variable for element in container
varStatus:Loop state object
index:The index of the element in the container, starting from 0
count:Number of cycles, starting from 1
--%>
<c:forEach begin="1" end="10" var="i" step="2" varStatus="s" >
Value of temporary variable: ${i},Index of elements in container: ${s.index},Number of cycles: ${s.count}<br>
</c:forEach>
<hr>
<%
ArrayList<String> lists = new ArrayList<>();
lists.add("aaaa");
lists.add("bbbb");
lists.add("cccc");
request.setAttribute("lists",lists);
%>
<c:forEach items="${lists}" var="str" varStatus="s">
Elements in collection: ${str} , Index of element: ${s.index},Number of collection cycles: ${s.count}<br>
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows:
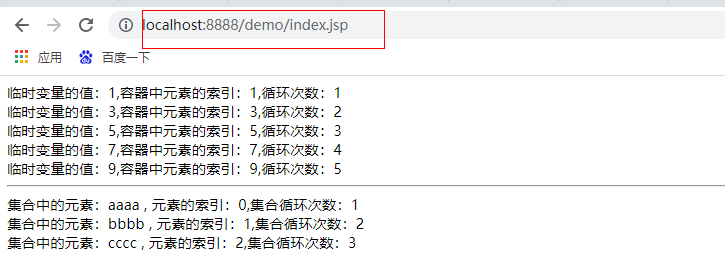
(4) comprehensive exercise of jstl tag library:
Requirement: there is a list collection containing User objects in the request field. You need to use jstl+el to display the list set data in the table of the jsp page
The project structure is as follows:
User.java entity class
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public User(String name, int age, Date birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public User() {
}
/**
* Logical view
* @return
*/
public String getBirStr(){
if(birthday != null){
//1. Format date object
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//2. Just return the string
return sdf.format(birthday);
}else{
return "";
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
index.jsp page
<%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %>
<%@ page import="com.kejizhentan.bean.User" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.Date" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>jstl Label library presentation</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new User("zhangsan",21,new Date()));
list.add(new User("lisi",22,new Date()));
list.add(new User("wangwu",23,new Date()));
request.setAttribute("lists",list);
%>
<table border="1" width="500" align="center">
<tr>
<th>number</th>
<th>full name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>date of birth</th>
</tr>
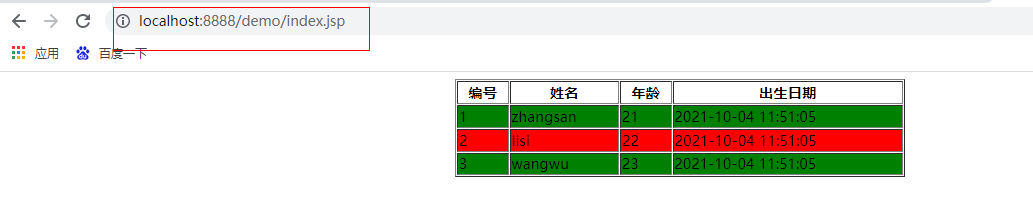
<c:forEach items="${lists}" varStatus="s" var="user">
<c:if test="${s.count % 2 == 0}">
<tr bgcolor="red">
<td>${s.count}</td>
<td>${user.name}</td>
<td>${user.age}</td>
<td>${user.birStr}</td>
</tr>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${s.count % 2 != 0}">
<tr bgcolor="green">
<td>${s.count}</td>
<td>${user.name}</td>
<td>${user.age}</td>
<td>${user.birStr}</td>
</tr>
</c:if>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html>
The results are as follows: