@Concepts, differences and execution order of PostConstruct, @ PreDestroy and initMethod, destroyMethod, InitializingBean and DisposableBean
@PostConstruct
Definition related
- This annotation is added to the Java EE5 specification, not spring. Spring means that it follows this specification and plays a certain role in the Servlet life cycle. It is usually some initialization operations, but initialization may depend on other injected components, so it should be executed after all dependencies are loaded
- @The PostConstruct annotation is used for methods executed after dependency injection is complete
- The method may be modified with final
usage
Declaring a void method in a class, of course, can be of other types, but it has no practical significance. It is generally a non static void method
@PostConstruct
public final void initForPostConstruct(){
System.out.println("initForPostConstruct Method executed!");
}
@PreDestroy
Definition related
- This annotation is also added to the Java EE5 specification, not spring. Spring means that it follows this specification and plays a certain role in the Servlet life cycle. It is usually some operations before destruction.
- @The PreDestroy annotation is used as a callback notification on the method to indicate that the instance is being deleted by the container
- Methods annotated with @ PreDestroy are usually used to release resources it has always held, or for garbage collection
- The method may be modified with final
usage
Like @ PostConstruct, declaring a void method in a class can of course be of other types, but it has no practical significance. It is generally a non-static void method
@PreDestroy
public void destroyForPreDestroy(){
System.out.println("destroyForPreDestroy Method executed!");
}
initMethod and destroyMethod
Definition related
After initializing an object (bean), initialize and load some data immediately, and do some resource release and garbage collection operations before destroying the object
usage
xml, define init and destroy methods in the corresponding class of the bean, and use init method and destroy method Association in xml
public void initForInitMethod (){
System.out.println("initForInitMethod Method executed!");
}
public void destroyFordestroyMethod(){
System.out.println("destroyFordestroyMethod Method executed!");
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="initOrDestroyTest" class="com.cyyit.bean.TestBean" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
</bean>
</beans>
javaConfig mode, the effect is equivalent to xml mode
@Configuration
public class config {
@Bean(initMethod = "initForInitMethod",destroyMethod ="destroyFordestroyMethod")
public TestBean testBean(){
return new TestBean();
}
}
InitializingBean
The IinitializingBean interface provides a way for beans to initialize methods. It only includes the afterpropertieset method. All classes that inherit this interface will execute this method when initializing beans.
DisposableBean
The DisposableBean interface provides a way for beans to destroy bean methods. It only includes the destroy method. All classes that inherit this interface will execute this method when destroying beans.
Execution sequence
Test: define a TestBean as follows
public class TestBean implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Autowired
private TestBean1 testBean1;
@PostConstruct
public final void initForPostConstruct(){
System.out.println("initForPostConstruct Method executed!");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroyForPreDestroy(){
System.out.println("destroyForPreDestroy Method executed!");
}
public void initForInitMethod (){
System.out.println("initForInitMethod Method executed!");
}
public void destroyFordestroyMethod(){
System.out.println("destroyFordestroyMethod Method executed!");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("destroy Method executed!");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet Method executed!");
}
}
Execution result of main function:
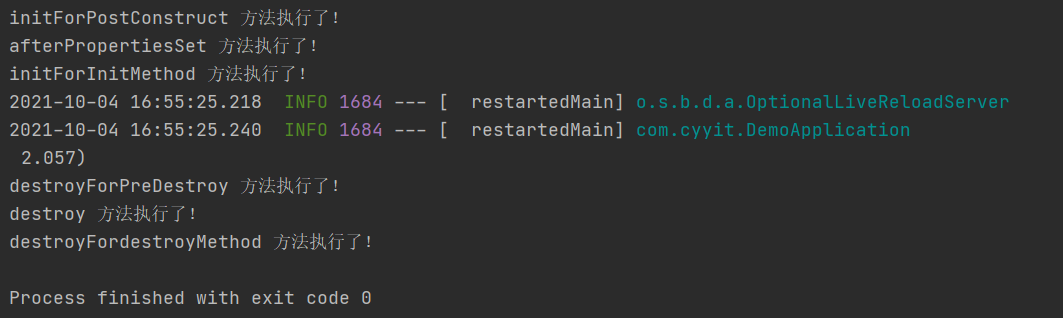
Conclusion: it can be seen from the above that in fact, the three methods are all used to do some related operations in the initialization and destruction stages of the springBean life cycle. In fact, one of the three methods can be used, which can be configured according to needs. In addition, @ PostConstruct and @ PreDestroy are java's own annotations, not spring's. spring just follows such a specification. The three execution sequences are:
Initialization: @ postconstruct > initializingbean > initmethod
Destroy: @ predestroy > disposablebean > destroymethod