Environmental description:
Centos 7.9 x86_64
The command is executed under root
#1 download the installation package of Prometheus
website: https://prometheus.io/download/
The page is as follows:
Select the corresponding version and download it. At present, it seems that there is no rpm package deployed on Centos, so we need to manually configure some user permissions.
The compressed package can be downloaded directly on the page or wget on Centos:
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.30.0/prometheus-2.30.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Note here that the installation package is on github. If you are hit by a wall, you need to get a ladder.
#2. Unzip - put it into the corresponding folder
After downloading, extract tar xvf prometheus-2.30.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz, and the following files are in the folder:
It's OK to put it in any folder. It's recommended to put it here
/Under usr/local folder, and change the folder of prometheus to prometheus. The complete directory is as follows:
/usr/local/prometheus
# 3 add the account running Prometheus and modify the folder permissions
groupadd prometheus # add group useradd -g prometheus -s /sbin/nologin prometheus # Add a prometheus account and set it to no login chown -R prometheus: prometheus /usr/local/prometheus # Modify the folder permissions so that the prometheus user has permission to execute the files in the directory
Note: the permissions of prometheus and promtool in the folder are 755, which is normal. If the permissions are not modified
chmod 755 prometheus promtool # is executed in the / usr/local/prometheus directory
#4 start prometheus
Simple method, directly execute. / prometheus in bash.
Yes, prometheus.yml can be configured without any configuration. In other words, prometheus.yml looks like the bottom. If you want to start the prometheus server, it's OK not to configure the YML file first.

Another method is to write a service to let the prometheus server follow the system startup, and configure some other parameters:
vim /lib/systemd/system/prometheus.service
The contents of prometheus.service file are as follows:
[Unit] Description=prometheus After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=prometheus ExecStart=/usr/local/prometheus/prometheus --config.file=/usr/local/prometheus/prometheus.yml --storage.tsdb.path=/var/prometheus [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Note that there are two parameters in the parameters of ExecStart, one is config.file, which can point to the yml file. One is tsdb (time series database) used in the background of prometheus server. Here we put it in the / var/prometheus directory (this directory can be modified according to the actual situation), so we need to give this directory permission.
mkdir -p /var/prometheus # Create the folder first chown -R prometheus: prometheus /var/prometheus # Set permissions
Note: the tsdb directory contains the database of prometheus server, which is roughly as follows:
After the prometheus.service is written, you can use systemd to configure the service:
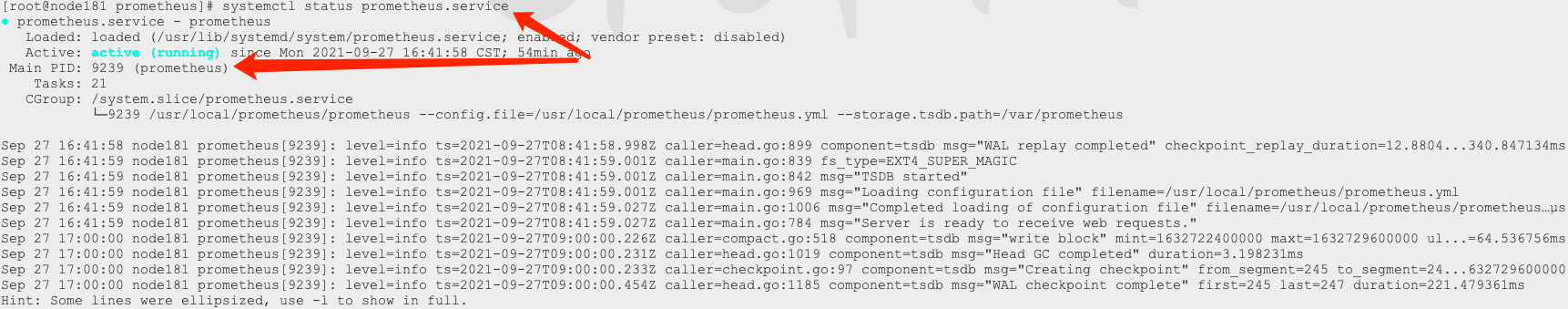
systemctl enable prometheus.service # Set prometheus service startup systemctl start prometheus.service # Start service systemctl status prometheus.service # Confirm status
If the configuration is normal, you should see that the prometheus server starts normally:
#5 configure Host Firewall - firewalld
The default port of prometheus server is TCP 9090 (I can't find where to modify it)
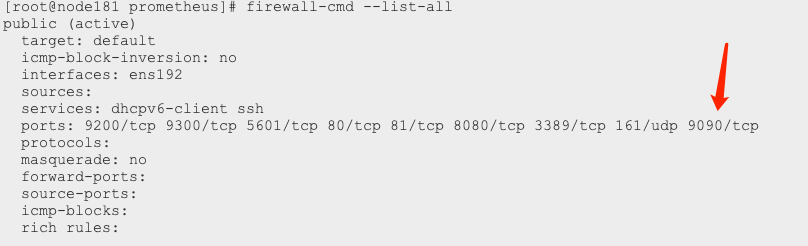
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9090/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload firewall-cmd --list
Confirm that the firewall policy is configured correctly
#6. Access the built-in management interface
http://[your-host-ip-or-name]:9090
If you are not surprised, you can see the following interface: