1. Introduction to database
Baidu's definition of database is: "database is" a warehouse for organizing, storing and managing data according to data structure ". It is a collection of large amounts of data stored in computers for a long time, organized, shareable and uniformly managed."
In short, a database is a collection of data stored, maintained and managed. In computer learning, the database is a very important process from children's house to daily use, which means that the program is not entertaining itself. By accessing the database, the data can be shared, exchanged and saved with others.
1.1 three paradigms of relational database
Database is divided into non relational database and relational database. This paper focuses on MySQL, so it focuses on the three paradigms of relational database.
Relational database: refers to a database that uses a relational model to organize data. It stores data in the form of rows and columns to facilitate user understanding. A series of rows and columns in a relational database are called tables, and a group of tables form a database. The user retrieves the data in the database through a query, which is an executive code used to limit some areas in the database. Relational model can be simply understood as two-dimensional table model, and a relational database is a data organization composed of two-dimensional tables and their relationships.
The figure above is easy to understand:
The three paradigms are actually the three basic specifications of relational database, which are simply divided into: 1. No duplicate columns 2. Each instance or row in the database table must be uniquely distinguished (rows cannot be repeated) 3. It is required that one database table does not contain non keyword information already contained in other tables (concise)
2. MySQL (relational database management system)
2.1. Introduction
Developed by Swedish MySQL AB company, it is a product of Oracle. The SQL language used by MySQL is the most commonly used standardized language for accessing databases. Because of its small size, fast speed and low overall cost of ownership, especially the characteristics of open source, MySQL is generally selected as the website database for the development of small and medium-sized websites. Therefore, learning MySQL well is a very effective way to contact database learning.
2.2 MySQL installation and uninstallation
-
Download the compressed package (. zip) instead of (. exe) on the official website. Remember to register the Oracle account
Tucao run away, or else it will make complaints about bushi.
-
Load the path of the extracted folder bin into the path environment variable
-
Create a new my.ini configuration file in the folder
-
Edit
[mysqld] #Set 3306 interface port = 3306 #Set the installation directory of mysqld (this is different for everyone, subject to their own installation path) basedir = D:\Program Files\mysql #Set the data storage directory of mysql database (it can not be in the folder, and do not create it yourself) datadir = D:\Program Files\mysql\data #Maximum number of connections allowed (prevent server overload) max_connections = 200 #Number of failures allowed (preventing attacks on the database system from the host) max_connect_errors = 10 #The character set used by the server is utf8 by default character-set-server = utf8 #The default storage engine that will be used when creating new tables default-storage-engine = INNODB #The "mysql_native_password" plug-in authentication is used by default default_authentication_plugin = mysql_native_password [mysql] #Set the default character set of mysql client default-charcater-set = utf8 [client] #client port = 3306 default-charcater-set = utf8
-
Install mysql
In the mysql installation directory, open the bin folder and run the cmd window (you can use the windows key + r to open it)
Execute instructions:
mysqld --initialize --console
If the display is successful, the installation is successful. If it fails, check the preceding steps
Also remember the password assigned by the system, root@localhost The following is the password:
No matter how strange, mine is mAuyXXqV(0)c
-
Installation services
mysqld --install (service name)(default mysql,You can define it yourself) There are other instructions: net start Service name start service net start Service name shutdown service mysql -u root -p Login instruction Enter password:Password (input) Modify account password alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified with mysqld_native_password BY 'password'; quit Exit Service
-
Uninstall MySQL
-
Run CMD net stop mysql8 as administrator (service name)
-
Delete MySQL service sc delete mysql8
-
Delete mysqlDB directory file mysqld remove mysqld8 (the specified directory of my.ini)
-
3. SQL language (Structured Query Language)
Allow C (create) R (read) U (update) D (delete) to add, delete, modify and query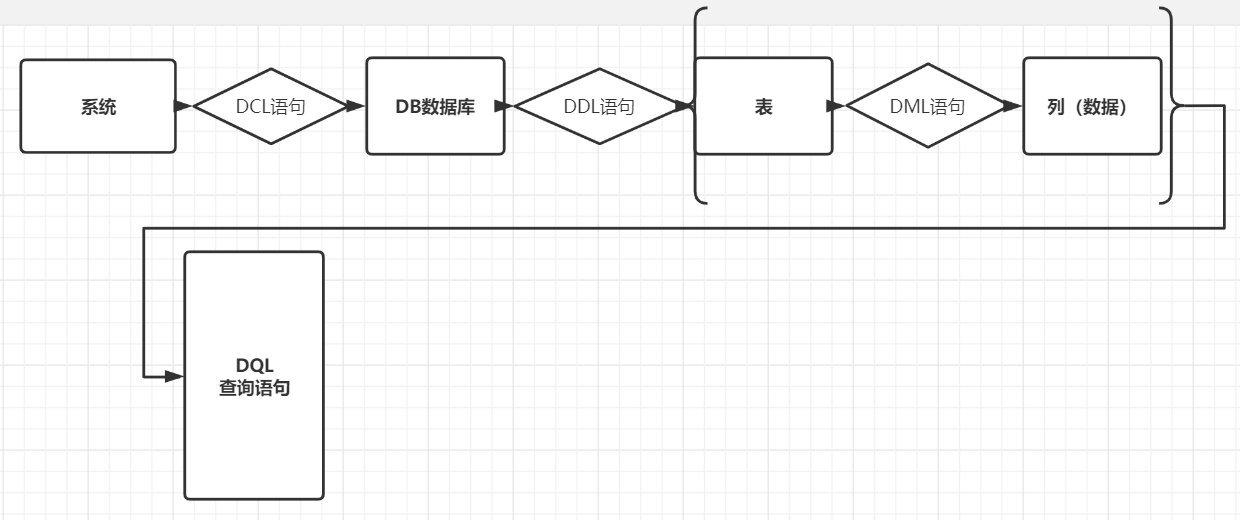
--Figure 1-1: relationship between sql statement and database
1.sql statement ends with; 2.mysql keyword is not case sensitive
3.1 DDL(Definition)
Data definition language, defining database objects
3.1.1 operations related to database tables
create database Database name; //establish show databases; //Check all databases of the server alter database Database name character set Coding mode; //Modify coding method drop database Database name; select database(); //View connected databases use Database name; //Connect to database
3.1.2 DDL operation table (create table)
create table Database name ( Column name 1 data type [constraint(not essential)], Column name 2 data type [constraint(not essential)], Column name 3 data type [constraint(not essential)] (The last column is not comma marked)al ); Available data types: int double char varchar text blob date time timetamp datetime
3.1.3 other table operations
Check: show tables; (All tables) desc Table name; (Field information of lookup table) show create table Table name; (View table creation details) Delete: drop table Table name; (Delete table) Change: alter table Table name add; New column name new data type (New column) alter table Table name change; Old column name new column name new data type (Modify column) alter table Table name drop; Column name (delete column) alter table Old table name rename; New table name (change table name))
3.2 DML(Manipulation)
The data operation language defines the database record data, such as adding, deleting and changing, that is, adding, deleting and changing the data in the table
Note that in mysql, string types and date types are enclosed in single parentheses
3.2.1 insertion
insert into Table name (column name) values(Data value);
eg: insert into stu(name,id) values('zhangSan',18);
Note: 1. Multiple columns and values are separated by commas. 2. Column names correspond to values one by one. 3. Column values that are not data use single quotation marks
4. Add multiple lines at the same time, separated by commas
There is a way to add data by omitting column names - add data to all columns (column values should be in the order in the table)
3.2.2 modification
Operators in sql
1.Arithmetic operator : + - * / % 2.Assignment Operators : = 3.Logical operator : and or not 4.Relational operator : > < >= <= != = All data query syntax: select *(This is a query that represents all columns) from Table name Modify the data syntax of the inserted row: update Table name set Column name 1=Column value 1, ... where Listing=value;
Note that there are two cases of null values. If you want to filter where, you need to connect the two conditions with and
where column name is null and column name = ''
3.2.3 deletion
Syntax for deleting a row of stored data: delete from Table name where Listing=value; or truncate table Table name;
Differences between the two Grammars:
delete deletes the data. The table structure is still. After deletion, the data can still be retrieved
truncate deletion is to DROP the table and create a new table. The data cannot be retrieved and the speed is faster
3.3 DCL(control) data control language
Used to define access rights and security levels
3.3.1 create user
create user user name@appoint ip identified by password; create user user name@client ip identified by password; appoint ip To log in create user user name@'%' identified by password; arbitrarily ip Also
3.3.2 user authorization
1.grant grant Permission 1, permission 2,...,jurisdiction n on Database name.* to 'user name'@'ip'; Assign database permissions to the specified user grant all on *.* to 'user name'@'ip'; Give all database permissions to the specified user 2.query show grants for 'user name'@'ip'; 3.revoke remove Permission 1, permission 2,...,jurisdiction n on Database name.* to 'user name'@'ip'; The syntax is almost consistent with authorization 4.delete drop user 'user name'@'ip';
3.4 DQL(Query) data query language (absolute focus)
It is used to query records (data) and return virtual tables without affecting database data
Basic syntax: select Listing from Table name where -> group by -> having -> order by

3.4.1 simple query
-
Query all columns select * from table names;
-
Query partial column select partial column name from table name;
3.4.2 query criteria (where)
The following operators and keywords can be used in the where clause
= != <> (not equal to) < < = > > = between.. and in (set) is null and or not
Listing in (Column value 1, column value 2) in:In what range, parentheses cannot be omitted. Note that only strings can be used not in (...) Out of range between 20 and 40; Indicates the middle of the value, including the critical value. Note that only numbers can be used eg: select name from stu where name='zhangSan';
3.4.3 fuzzy query
Syntax:
Listing like 'expression'; //The expression must be a string wildcard: _(Underline):Any character % : Any 0~n Characters The second letter of the query is a Name of student: select name from stu where name like '_a%';
3.4.4 field control query
Remove duplicate data (of columns):
1).select distinct column name from table name;
2).select *, column name + isfull (comn, 0) (this is an aggregate function, which means adding two columns of data and changing the null value of comn column to 0) from table name;
3) . alias the column (optimize display) select *, column name + isfull (CoMn), 0) as (replace with spaces) new name from table name;
3.4.5 sorting
Syntax: order by column name ASC (default, ascending) / desc (descending)
select * from Table name order by Column name 1 desc,Column name 2 desc; (Query, sort by the first column. If the query is the same, sort by the second column)
3.4.6 aggregate function (function used for vertical operation)
Count (column name): counts the number of records whose column is not null
Sum (column name): the sum of statistical columns
AVG (column name): Statistics column average
Max (column name): max min (column name): Min
3.4.7 group query
If there are grouping operations in the query, only aggregate functions and grouped column names can be added after select
select Column name 1,sum(Column name 2) from Table name group by Column name 1; Grouping column names, aggregate functions
3.4.8 Having clause
Condition screening after grouping
The difference between having and where
-
having is to filter the data after grouping, and where is to filter the data before grouping
-
Grouping functions (statistical functions) can be used after having, but not after where
3.4.9 limit
Limit is used to limit the number of starting rows and total rows of query results
limit starts subscript and displays the number of entries// Start subscript, starting from 0
limit displays the number of entries// The default starts at 0
Pagination query pageIndex page number value pageSize number displayed per page
limit (pageIndex - 1)*pageSize,pageSize; Variable replacement
The above is the basic sql statement.