catalogue
1, js inheritance mode and its characteristics
1. Prototype chain inheritance
2. Classic inheritance (constructor)
3. Combination function inheritance (prototype chain + Classic)
2.Math object (math built-in object)
3.Date object (method of date built-in object)
1. System library (basic application)
2. Third party Library (advanced application)
1, js inheritance mode and its characteristics
Principle of inheritance: standing on the shoulders of giants, parent-child relationship (type relationship)
1. Prototype chain inheritance
Each constructor has a prototype object. The prototype object contains a pointer to the constructor, and the instance contains an internal pointer to the prototype object. When the prototype object is equal to an instance of another type, it inherits.
Disadvantages: if a constructor instance object modifies the property values and methods on the prototype object, it will also affect other instance objects. And the property cannot be set.
//Prototype chain inheritance
function Animal(){}
//All instance objects share the properties and methods defined in prototype
Animal.prototype.name = 'xb';
Animal.prototype.age = 2;
Animal.prototype.sayName = function(){
console.log(this.name);
}
function Dog(){}
Dog.prototype=new Animal;//Completed a prototype chain inheritance
Dog.prototype.constructor = Dog;//Reassign the constructor
var d1 = new Dog();
console.log(d1);//Dog {}
console.log(d1.name);//xb
d1.sayName();//xb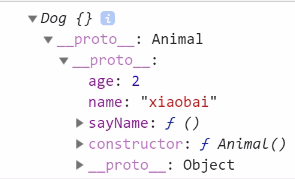
After reassigning the constructor, it may be ambiguous not to specify it (the successor's grandmother becomes the mother)
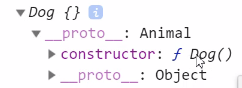
2. Classic inheritance (constructor)
Also known as "fake object" or "borrow constructor", call the supertype constructor inside the subtype constructor. A function is just an object that executes code in a specific environment, so it can be (in the future) through the apply(),call() method Execute the constructor on the new object, that is, execute the initialization code of all objects defined in the parent type function on the subtype object. As a result, each subclass instance has the properties and methods in the parent type, which is not inheritance, but relative to calling
Disadvantages: pseudo inheritance, no prototype, reuse is impossible
//Classic inheritance (pseudo inheritance)
function Animal(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.name = age;
}
function Dog(name,age,color){
Animal.call(this,name,age);//In the subclass, the parent class constructor animal is called, and the method of the parent class is executed once.
this.color = color;
}
var d1 = new Dog('xb',2,'white');
console.log(d1);//Dog { name: 2, color: 'white' }3. Combination function inheritance (prototype chain + Classic)
Prototype chain + pattern of borrowing constructor
Prototype chain inherits prototype properties and methods, and inherits instance properties by borrowing constructors
//Prototype chain + borrowing constructor
function Animal(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.name = age;
}//attribute
Animal.prototype.sayName = function(){
console.log(this.name);
}//method
function Dog(name,age,color){
Animal.call(this,name,age);//Calling parent class properties
this.color = color;
}//Cannot inherit parent method
Dog.prototype =new Animal;//Prototype chain inherits parent method
Dog.prototype.constructor = Dog;//Set the constructor back
Dog.prototype.sayColor = function(){
console.log(this.color);
}//Define your own method
var d1 = new Dog('xb',2,'white');
d1.sayName();//2 call method
d1.sayColor();//white2, Built in object
1. String object method in JS
var str = 'xiaomiang';
console.log(str.length);//Gets the length of the string
console.log(str.charAt(2));//Returns the character at the given position
console.log(str.charCodeAt(2)); //Returns the character encoding of the given position
console.log(str.indexOf('a'));//Returns the position of the given character
console.log(str.lastIndexOf('a'));//Returns the position of the given character (reverse lookup)
console.log(str.concat('xiaohong'));//String splicing to return a new string
console.log(str.slice(2,4));//String interception ao(start_index,end_index);
console.log(str.substr(2,4));//String interception ao(start_index,length);
console.log(str.substring(2,4));//String interception ao(start_index,end_index);
console.log(str.trim());//Remove spaces on both sides of a string
console.log(str.toLowerCase());//Converts the letters of a string to lowercase
console.log(str.toUpperCase());//Converts the letters of a string to uppercase
var str1 = 'xiaoxing';//js Chinese characters are also a character
var str2 = String('x m ');//Using wrapper
var str3 = new String('xm');//Object type string, which makes no difference in use
console.log(str1.length);//String length
console.log(str1.charAt(0));//Returns the character x of index 0
console.log(str1.charCodeAt(0));//Returns the character encoding 120 of the character with index 0
console.log(str1.indexOf('x'));//Returns the index position 0 of the character
console.log(str1.lastIndexOf('x'));//Find back and forward returns the index position 4 of the character
console.log(str1.concat('hhh'));//String splicing
console.log(str1.slice(2,4));//Return the intercepted character Ao (start_index, end_index);
console.log(str1.substr(2,4));//String interception Aoxi (start_index, length);
console.log(str1.substring(2,4));//String interception ao
console.log(str2.trim());//Remove spaces on both sides of the string
console.log(str2.toUpperCase());//Convert string to uppercase X M
console.log(str2.toLowerCase());//Convert string to lowercase x m
//Count the number of characters in a string
var obj = {};
for (var i=0;i<str1.length;i++){//How do I know if the character is in the above object
if (str1.charAt(i) in obj){
obj[str1.charAt(i)]++;
}else{
obj[str1.charAt(i)]=1;
}
}
console.log(obj);//{ x: 1, m: 1 }2.Math object (math built-in object)
console.log(Math.min(2,4,6,2,1,7));//The smallest of them console.log(Math.max(2,4,6,2,1,7));//The largest one var num = 10.41; console.log(Math.ceil(num));//Up trade-offs 11 console.log(Math.floor(num));//Downward trade-offs 10 console.log(Math.round(num));//Round to 10 console.log(parseInt(num));//10 console.log(Math.random());//Get a random number from 0 to 1 console.log(Math.ceil(Math.random()*100));//1-100 console.log(Math.PI);//PI
//Math math built-in object //Find the maximum and minimum value var arr = [2,3,6,8,4,55,7,88,2]; console.log(Math.max(...arr));//Return maximum 88 console.log(Math.min(...arr));//Return minimum 2 console.log(Math.max(2,3,6,8,4,55,7,88,2));//Ibid. 88 console.log(Math.min(2,3,6,8,4,55,7,88,2));//Ibid. 2 //Decimal point processing var num = 12.4; console.log(Math.ceil(num));//Add one up 13 console.log(Math.floor(num));//Discard down 12 console.log(Math.round(num));//Round to 12 console.log(parseInt(num));//Discard down 12 console.log(parseFloat(num)); //Keep floating point 12.4 //random number console.log(Math.random());//Give a random number from 0 to 9 console.log(Math.random()*100)//Find 1-100 * 100; console.log(Math.ceil(Math.random()*100))//The decimal places can be removed by wrapping with math.ceil //PI Pi console.log(Math.PI);//3.141592653589793 //absolute value console.log(Math.abs());
3.Date object (method of date built-in object)
var date = new Date(); console.log(date.getFullYear()); //Back to 202020 console.log(date.getMonth()); //Month 0-11 console.log(date.getDate()); //Return day 1-31 console.log(date.getHours()); //Return hours 0-23 console.log(date.getMinutes()); //Minutes 0-59 console.log(date.getSeconds()); //Seconds 0-59 console.log(date.getDay()); //3 Wednesday console.log(date.getMilliseconds());//millisecond console.log(date.getTime()); //time stamp
//Date time built-in object var str = "2021/09/09 10:12:12" //If the above string is passed in, the date time will be set to the above time. If not, the system time will be obtained var date = new Date(str);//2021-09-09T02:12:12.000Z console.log(date); //You can also pass in a timestamp to return the time set by the timestamp var date = new Date();//2021-09-09T02:15:40.750Z console.log(date); console.log(date.getFullYear()); //Return to 2021 console.log(date.getMonth()); //Month 0-11 8 (September) console.log(date.getDate()); //Return day nine console.log(date.getHours()); //Return hours 0-23 10 console.log(date.getMinutes()); //Minutes 0-59 19 console.log(date.getSeconds()); //9 seconds 0-59 console.log(date.getDay()); //Monday - July 4 console.log(date.getMilliseconds());//millisecond console.log(date.getTime()); //Timestamp 163115477745 console.log(Date.now());//Timestamp 163115477748 console.log(date.toString());//Return to all Thu Sep 09 2021 10:30:24 GMT+0800 (China standard time) console.log(date.toDateString());//Date section Thu Sep 09 2021 console.log(date.toTimeString());//Return time section 10:30:24 GMT+0800 (China standard time) console.log(date.toISOString());//Return international time string 2021-09-09T02:30:24.118Z
3, Extension library
1. System library (basic application)
Functions defined in objects: Math
The function is defined in the constructor prototype: Object/Array/RegExp/Date
2. Third party Library (advanced application)
Bootcdn moment.js lodash.js
BootCDN - Bootstrap Chinese open source project free CDN acceleration service
Moment.js
Is a JavaScript date processing class library for parsing, checking, operating, and displaying dates.
moment.js (v2.29.1) - Moment.js is a JavaScript date processing class library for parsing, verifying, operating, and displaying dates. | BootCDN - Bootstrap Chinese open source project free CDN acceleration service The reference manual roughly teaches students how to quickly read and learn
usage method:
1: Click download to pop up the following interface. Copy the content and put it into a new file

2. Use after importing directly in HTML file
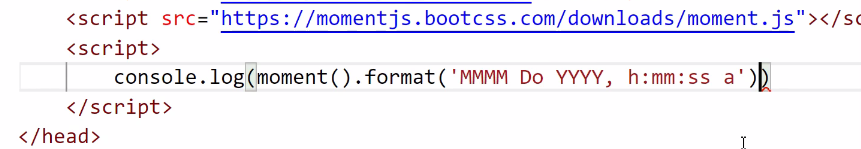
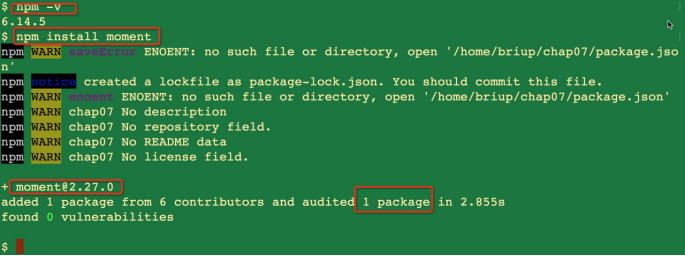
3. Download directly from node.js
Lodash.js
Lodash is a JavaScript tool library with consistent interface, modularity and high performance
Lodash makes JavaScript easier by reducing the difficulty of using array, number, objects and string.
Chinese documents: Lodash introduction | lodash Chinese document | lodash Chinese website
QS Chinese document