🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷
🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷🐷
💚 BC23. Time conversion
Description:
Given number of seconds seconds (0< seconds < 100,000,000),Convert seconds into hours, minutes, and seconds
Enter Description:
One line, including an integer, that is, the given number of seconds
Output Description:
One line, including three integers, which are the hours, minutes and seconds (possibly zero) corresponding to the input integers, separated by a space
Example:
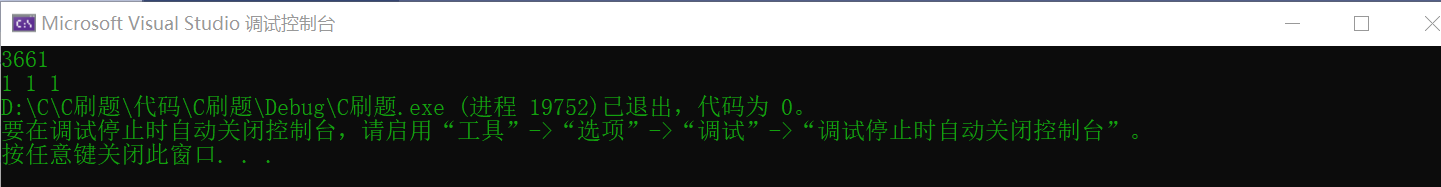
Input: 3661 Output: 1 1 1
code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
int second = 0;
scanf("%d", &second);
int h = 0;
int m = 0;
int s = 0;
//calculation
h = second / 60 / 60;
m = second % 3600 / 60;
s = second % 60;
//output
printf("%d %d %d", h, m, s);
return 0;
}
result:
Extension:
Under VS2019 compiler
int indicates that the integer range is: - 231 ~ 231-1 (- 2147483648 ~ 2147483647)
Unsigned int indicates that the integer range is 0 ~ 2 ^ 32-1 (0 ~ 4294967295)
long indicates that the integer range is: - 231 ~ 231-1 (- 2147483648 ~ 2147483647)
Unsigned long indicates that the integer range is 0 ~ 2 ^ 32-1 (0 ~ 4294967295)
long long indicates that the integer range is: - 263 ~ 263-1 (- 9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807)
Unsigned long long indicates that the integer range is 02 ^ 64-1 (018446744073709551615)
🧡 BC24. Calculation of total score and average score
Description:
Input the scores of three subjects of a student in turn, and output the total score and average score of the student on the screen
Enter Description:
One line, 3 grades, separated by a space
Output Description:
One line, total score and average score (two decimal places), separated by a space
Example:
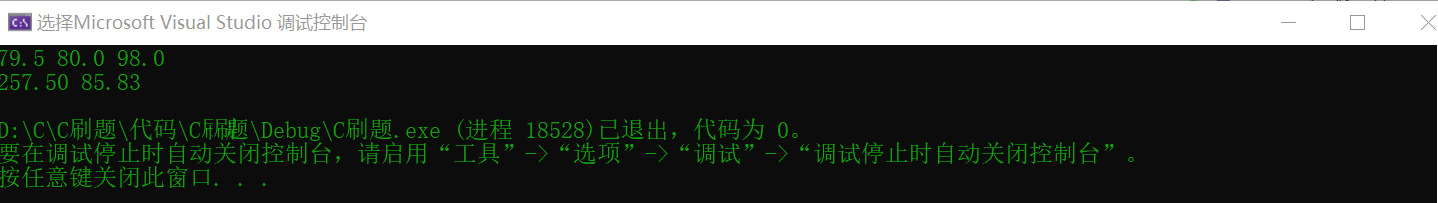
Input: 79.5 80.0 98.0 Output: 257.50 85.83
code:
//Method 1: create 3 variables
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
double chinese = 0.0;
double math = 0.0;
double english = 0.0;
scanf("%lf %lf %lf", &chinese, &math, &english);
//calculation
float sum = chinese + math + english;
float average = sum / 3.0;
//output
printf("%.2lf %.2lf\n", sum, average);
return 0;
}
//Method 2: create variables with arrays
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
double score[3] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
scanf("%lf", &score[i]);
}
//calculation
double sum = score[0] + score[1] + score[2];
double average = sum / 3.0;
//output
printf("%.2lf %.2lf\n", sum, average);
return 0;
}
//Method 3: input and calculate
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double score = 0.0;
double sum = 0.0;
int i = 0;
//Enter and calculate
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
scanf("%lf", &score);
sum += score;
}
//output
printf("%.2lf %.2lf\n", sum, sum / 3.0);
return 0;
}
result:
💛 BC30, kiki and yogurt
Description:
BoBo Bought a box of yogurt with n A box of unopened yogurt, KiKi I like to drink yogurt. I found yogurt for the first time. KiKi each h You can drink up a box of yogurt in minutes, and KiKi If you don't drink another box of yogurt before you drink it up, then m How many boxes of unopened yogurt are there in minutes
Enter Description:
Multiple sets of inputs with only one line per set, including n,h and m(Are integers). Input data assurance m <= n * h
Output Description:
For each group of input, the output is only one line, and the number of unopened yogurt boxes remains
Example:
Input: 8 5 16 Output: 4
code:
//Single group input
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
int n = 0;
int h = 0;
int m = 0;
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &h, &m);
//Calculation and output
if (m % h)
{
printf("%d\n", n - m / h - 1);
}
else
{
printf("%d\n", n - m / h);
}
return 0;
}
//Multi group input
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 0;
int h = 0;
int m = 0;
while(scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &h, &m) != EOF)
{
if(m%h>0)
printf("%d\n", n-m/h-1);
else
printf("%d\n", n-m/h);
}
return 0;
}
result:

💙 BC31. Press conference information
Description:
Your mobile phone is lost. Output information on the screen to tell everyone
Enter Description:
nothing
Output Description:
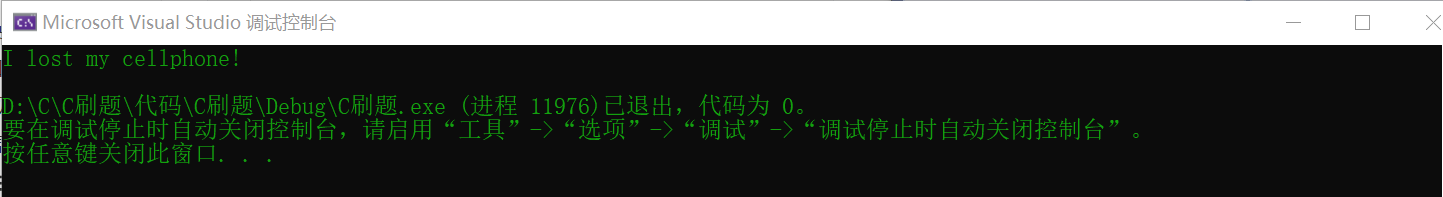
I lost my cellphone!
code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("I lost my cellphone!\n");
return 0;
}
result:
💜 BC32. Output student information
Description:
Student information management system is an important tool for school teaching management. The basic information of a student is as follows: name-Jack,Age-18,Gender-Man,Please output the student's information in the format of the output sample
Enter Description:
nothing
Output Description:
The output is divided into three lines: title line, separated line and information line. The first line is the title line, with 4 spaces between each title. The second line, separate lines, has 21 minus signs"-". The third row, the information row, aligns the output information of each column with the first letter of the title. The output example is as follows: Name Age Gender --------------------- Jack 18 man
code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Name Age Gender\n");
printf("---------------------\n");
printf("Jack 18 man\n");
return 0;
}
result:
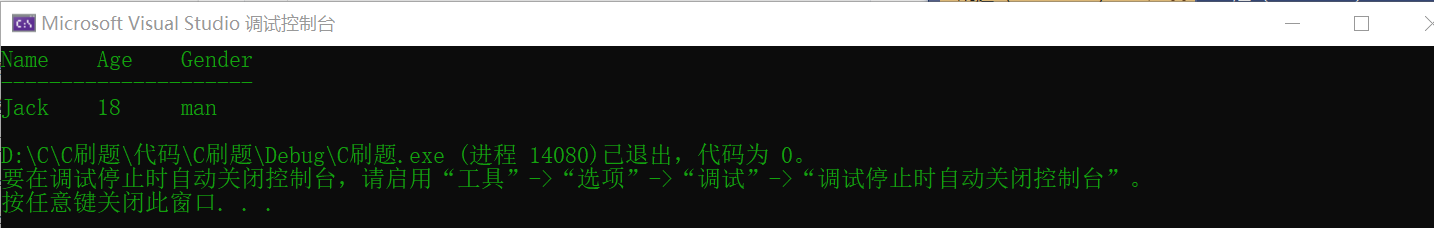
🤎 BC33. Calculate average score
Description:
Enter the scores (integers) of 5 students from the keyboard to find their average score (floating point number, keep one decimal place)
Enter Description:
Enter 5 integers in a row (range 0~100),Separated by spaces
Output Description:
One line, output the average of 5 numbers (keep one decimal place)
Example:
Input: 75 80 43 67 96 Output: 72.2
code:
//Method 1: use the array to input 5 scores
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
int score[5] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &score[i]);
}
//calculation
double average = (score[0] + score[1] + score[2] + score[3] + score[4])/5.0;
//output
printf("%.1lf\n", average);
return 0;
}
//Method 2: input and calculate
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int score = 0;
double sum = 0.0;
int i = 0;
//Enter and calculate
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &score);
sum += score;
}
//output
printf("%.1lf\n", sum / 5.0);
return 0;
}
result:

🖤 BC34, binary A+B
Description:
Enter a hexadecimal number a,And an octal number b,output a+b Decimal result of (range)-2^31~2^31-1)
Enter Description:
One line, one hexadecimal number a,And an octal number b,One space in between
Output Description:
a line, a+b Decimal result of
Example:
Input: 0x12 05 Output: 23
remarks:
hexadecimal Hexadecimal Generally 0 x Start, e.g. 0 xFF. octal number system Octal,It usually starts with 0, such as 07
code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//Whether octal or decimal, hexadecimal is stored in the computer, which is binary
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
//%x is the hexadecimal data format%o is the octal data format
//0x is a hexadecimal prefix and 0 is an octal prefix
scanf("%x %o", &a, &b);
int sum = a + b;
printf("%d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
result:
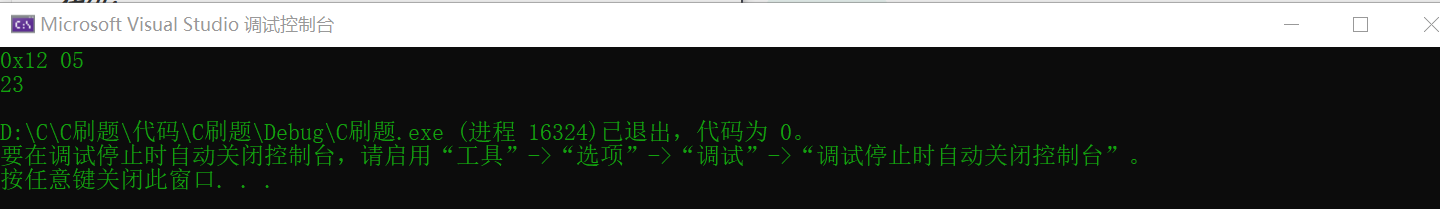
Extension:
- Decimal, hexadecimal and octal are just the representation of data, not the storage form of data
- %x is hexadecimal format,% o is octal format and% d is decimal format
- 0x is a hexadecimal prefix and 0 is an octal prefix
- The data of different hexadecimals are stored in shaping variables. They are all shaping values. They can be calculated directly and handed over to the computer
💚 BC37. Online shopping
Description:
KiKi He likes online shopping very much. In a shop, he took a fancy to a dress. He learned that if today is "double 11" (November 11), the dress will be 20% off, and "double 12" (December 12), the dress will be 20% off. If there is a coupon, an additional 50 yuan can be reduced (the coupon can only be used on double 11 or double 12). Please KiKi The final amount of money spent
Enter Description:
There are four numbers in a row. The first number represents Xiao Ming's favorite clothing price, the second and third integers represent the month and date of the day, and the fourth integer represents whether there is a coupon (1 for coupons and 0 for no coupons)
Output Description:
One line, the amount of money actually spent by Xiao Ming (keep two decimal places). (tip: don't expect the merchant to give you money back
Example:
Input:
1000.0 11 11 1
Output:
650.00
Input:
999.8 12 12 0
Output:
799.84
Input:
66.6 11 11 1
Output:
0.00
code:
//Although feasible, there are many duplicate codes
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
double price = 0.0;
double last_price = 0.0;
int month = 0;
int date = 0;
int flag = 0;
double cut = 0.0;
scanf("%lf %d %d %d", &price, &month, &date, &flag);
//calculation
if (month == 11 && date == 11)
{
cut = 0.7;
if (flag == 1)
{
last_price = price * cut - 50;
}
else
{
last_price = price * cut;
}
}
else if (month == 12 && date == 12)
{
cut = 0.8;
if (flag == 1)
{
last_price = price * cut - 50;
}
else
{
last_price = price * cut;
}
}
else
{
last_price = price;
}
if (last_price < 0.0)
{
printf("%.2lf\n", 0.0);
}
else
{
printf("%.2lf\n", last_price);
}
return 0;
}
//Simplified code
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
double price = 0.0;
double last_price = 0.0;
int month = 0;
int date = 0;
int flag = 0;
double cut = 1.0;
scanf("%lf %d %d %d", &price, &month, &date, &flag);
//calculation
if (month == 11 && date == 11)
{
cut = 0.7;
}
else if (month == 12 && date == 12)
{
cut = 0.8;
}
last_price = cut * price - flag * 50;
if (last_price < 0.0)
{
printf("%.2lf\n", 0.0);
}
else
{
printf("%.2lf\n", last_price);
}
return 0;
}
result:

🧡 BC39. Compete for the top five
Description:
The mid-term exam begins. Everyone wants to get good grades and compete for the top five. Enter from the keyboard n Students' scores (no more than 40) and output the top five scores of each group
Enter Description:
Two lines. In the first line, enter an integer to represent n Students(>=5),Second line input n Student grades (expressed as integers, range 0)~100),Separated by spaces
Output Description:
One line, output the top five with the highest scores, separated by spaces
Example:
Input: 6 99 45 78 67 72 88 Output: 99 88 78 72 67
code:
//Sort by yourself
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
int n = 0;//Enter the number of students
int score[40] = { 0 };//Enter grade
scanf("%d", &n);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &score[i]);
}
//Sorting (self implemented sorting: bubble sorting)
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
//Sorting of each trip
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (score[j] > score[j + 1])
{
int tmp = 0;
tmp = score[j];
score[j] = score[j + 1];
score[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
for (i = n - 1; i > n - 6; i--)
{
printf("%d ", score[i]);
}
return 0;
}
//Using library functions
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return *(int*)e2 - *(int*)e1;
}
int main()
{
//input
int n = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
int score[40] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &score[i]);
}
//Calculation (using library functions)
qsort(score, n, 4, cmp_int);
//output
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%d ", score[i]);
}
return 0;
}
result:
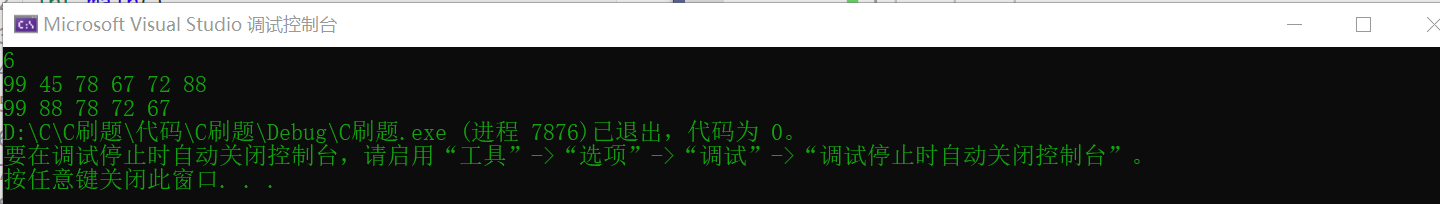
Extension:
- Bubble sorting idea:
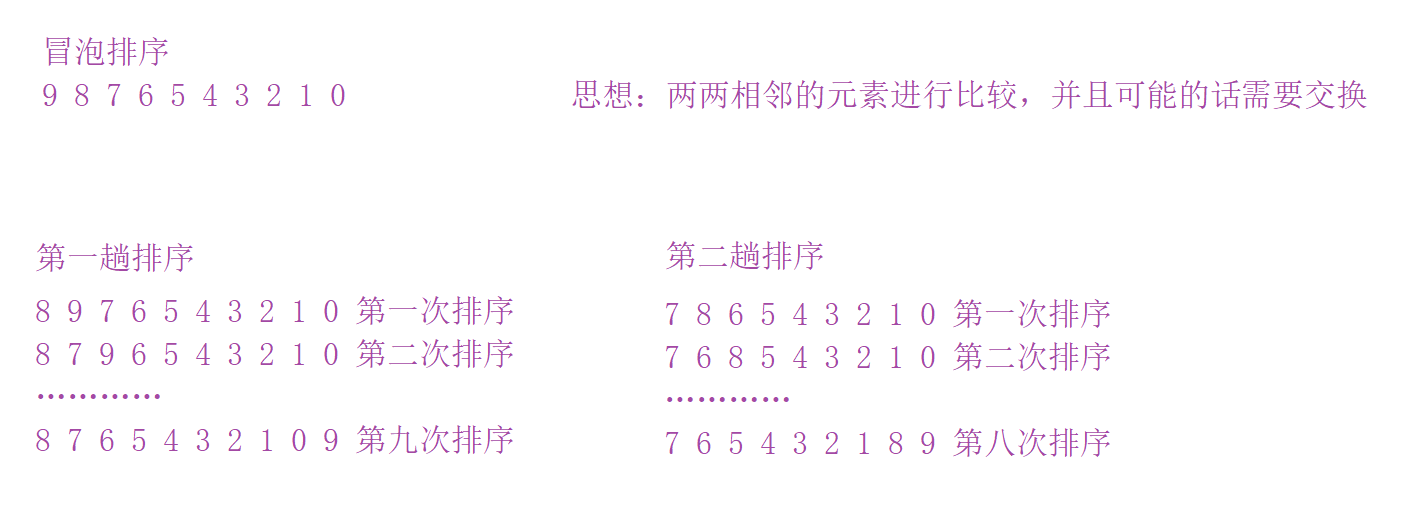
- qsort function:

💛 BC40. Running for president
Description:
Suppose your club wants to run for president, there are two candidates, respectively A and B,Each student of the club must and can only cast one vote, and the one who gets more votes in the end is the president
Enter Description:
One line, character sequence, containing A or B,Input ends with character 0
Output Description:
One line, one character, A or B or E,output A express A More votes, less output B express B More votes, less output E It means that two people have an equal number of votes
Example:
Input: ABBABBAAB0 Output: B
code:
//Create 2 variable counts
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
char buf[100] = { 0 };
gets(buf);//Get one line of string
//Statistics
int count_a = 0;
int count_b = 0;
int i = 0;
while ((buf[i] != 0)&&(buf[i] != EOF))
{
if (buf[i] == 'A')
{
count_a++;
}
if (buf[i] == 'B')
{
count_b++;
}
i++;
}
//output
if (count_a > count_b)
{
printf("A\n");
}
else if (count_a < count_b)
{
printf("B\n");
}
else
{
printf("E\n");
}
return 0;
}
//Create a variable to count
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
char buf[100] = { 0 };
gets(buf);//Get one line of string
//Statistics
int flag = 0;
int i = 0;
while ((buf[i] != 0)&&(buf[i] != EOF))
{
if (buf[i] == 'A')
{
flag++;
}
if (buf[i] == 'B')
{
flag--;
}
i++;
}
//output
if (flag>0)
{
printf("A\n");
}
else if (flag<0)
{
printf("B\n");
}
else
{
printf("E\n");
}
return 0;
}
//Read one character at a time
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//input
char ch = 0;
int flag = 0;
//Statistics
while (((ch = getchar()) != 0) && (ch != EOF))
{
if (ch == 'A')
{
flag++;
}
if (ch == 'B')
{
flag--;
}
}
//output
if (flag>0)
{
printf("A\n");
}
else if (flag<0)
{
printf("B\n");
}
else
{
printf("E\n");
}
return 0;
}
result:

Don't forget before you leave 👍 follow 💡 Collection 💖
I hope this article can help you ~!