This slag wants to analyze Doug Lea's idea of writing high concurrency code, so I found our leading actor, concurrent linked queue, to whip it. To tell you the truth, I've finished all the drafts, but I've almost got a kick in the door
If you look at the problem directly, the result of idea running in Debug mode is different from that in non Debug mode. vscode is repeated, and eclipse is no better
How did you find the problem?
Start with this code
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>(); queue.add("zhazha"); // Break point on the line below Field headField = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("head"); headField.setAccessible(true); Object head = headField.get(queue); Field itemField = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("ITEM"); itemField.setAccessible(true); VarHandle ITEM = (VarHandle) itemField.get(head); Object o = ITEM.get(head); System.out.println(o); }
You'll find a magical phenomenon if we drop the breakpoint in the field headfield= queue.getClass (). Getdeclaredfield ("head"); this line of code can be found when it is executed step by step System.out.println(o) ; zhazha is printed out, but if the breakpoint is not set, run print null directly
In order to prevent the effect of WARNING: An illegal reflective access operation has occurred, I changed the source code and used unsafe to get it
private static Unsafe unsafe; static { Class<Unsafe> unsafeClass = Unsafe.class; Unsafe unsafe = null; try { Field unsafeField = unsafeClass.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); unsafeField.setAccessible(true); ConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo.unsafe = (Unsafe) unsafeField.get(null); } catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>(); queue.add("zhazha"); // Break point on the line below long headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("head")); Object head = unsafe.getObject(queue, headOffset); long itemOffset = unsafe.staticFieldOffset(ConcurrentLinkedQueue.class.getDeclaredField("ITEM")); Object base = unsafe.staticFieldBase(ConcurrentLinkedQueue.class.getDeclaredField("ITEM")); VarHandle ITEM = (VarHandle) unsafe.getObject(base, itemOffset); Object o = ITEM.get(head); System.out.println(o); }
Perfect recurrence
First reaction to my question
Go to the source code to see what happened. But This
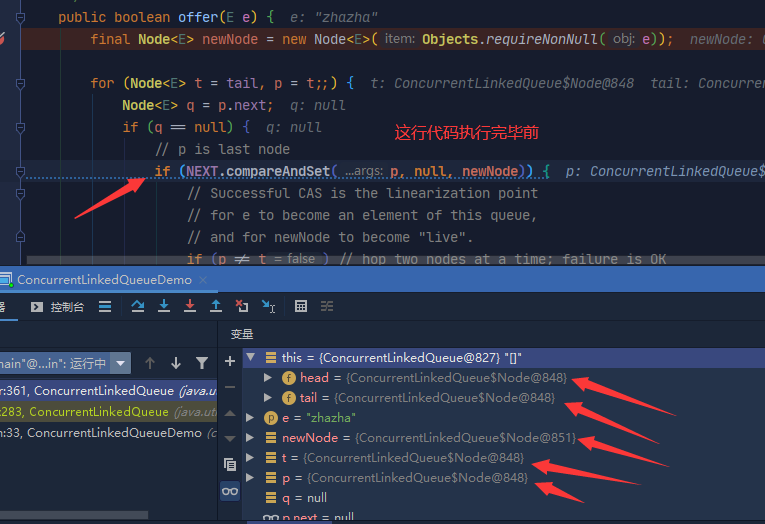
Look carefully at the address of the red arrow. t, p, head and tail are all the same address. Look at the above code and find that they are all assigned by tail to these three variables
And NEXT source
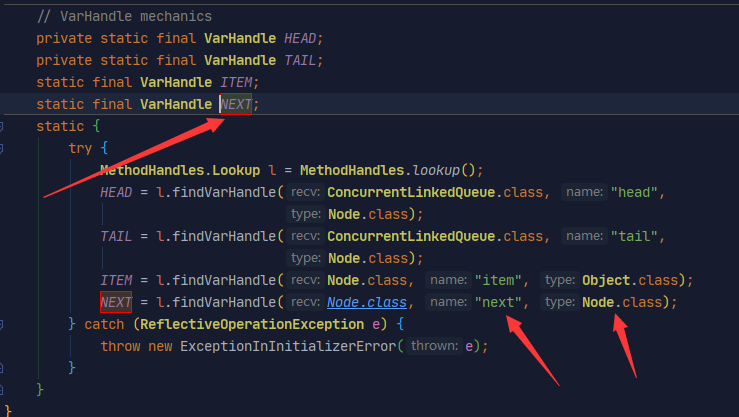
The receiving class is Node, the receiving field is next, and the receiving field type is Node
Look at the momentum of the source code. next modifies the p object. If the next node of the object is null, set the newNode to the node. At this time, the p object points to the tail, and the head also points to the tail node. Therefore, this sentence is executed, head.next and tail.next They are also newNode nodes
But This
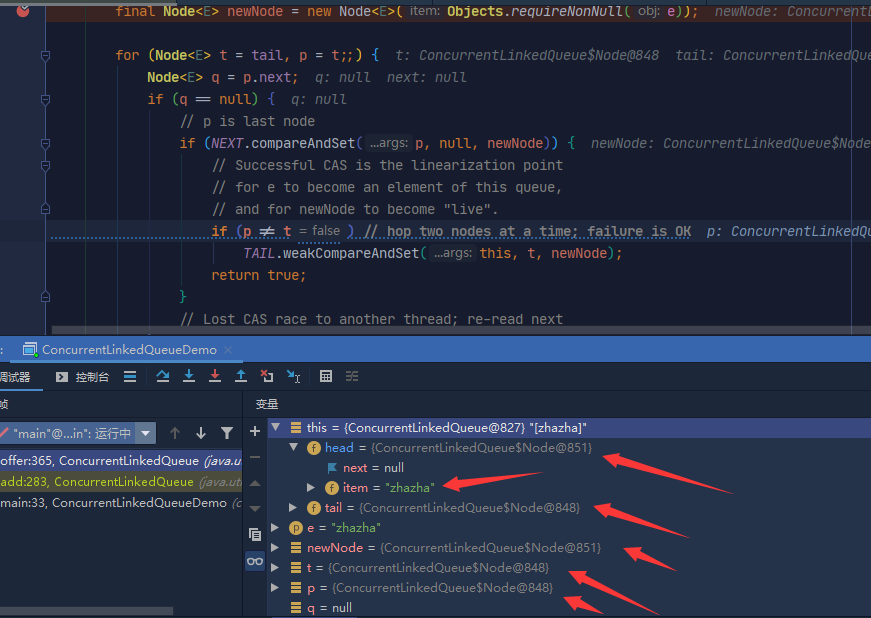
The head node is replaced directly and tail remains unchanged
My face should be like this

Suspected feline
private static Unsafe unsafe; static { Class<Unsafe> unsafeClass = Unsafe.class; Unsafe unsafe = null; try { Field unsafeField = unsafeClass.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); unsafeField.setAccessible(true); ConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo.unsafe = (Unsafe) unsafeField.get(null); } catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>(); queue.add("zhazha"); // Break point here Class<? extends ConcurrentLinkedQueue> queueClass = queue.getClass(); Object head = unsafe.getObject(queue, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(queueClass.getDeclaredField("head"))); Field itemField = queueClass.getDeclaredField("ITEM"); itemField.setAccessible(true); VarHandle ITEM = (VarHandle) itemField.get(queue); Object item = ITEM.get(head); System.out.println(item); // zhazha long itemOffset = unsafe.staticFieldOffset(queueClass.getDeclaredField("ITEM")); Object base = unsafe.staticFieldBase(queueClass.getDeclaredField("ITEM")); VarHandle ITEM2 = (VarHandle) unsafe.getObject(base, itemOffset); Object item2 = ITEM2.get(head); System.out.println(item2); // zhazha }
It's zhazha after single step debugging. In order to prevent reflection problems, I use both Unsafe and reflection methods

copy source code, add your own debugging function to test again
Come on, let's try the ultimate move. copy ConcurrentLinkedQueue source code is changed to MyConcurrentLinkedQueue
Add several outputs to the offer method
public boolean offer(E e) { final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(Objects.requireNonNull(e)); for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t; ; ) { Node<E> q = p.next; if (q == null) { if (NEXT.compareAndSet(p, null, newNode)) { System.out.println("this.head.item = " + this.head.item); System.out.println("this.tail.item = " + this.tail.item); System.out.println("this.head.next.item = " + this.head.next.item); System.out.println("this.tail.next.item = " + this.tail.next.item); if (p != t) { TAIL.weakCompareAndSet(this, t, newNode); } return true; } } else if (p == q) { p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head; } else { p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q; } } }
The main function is simpler and more direct
public static void main(String[] args) { MyConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new MyConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>(); queue.add("zhazha"); }
Run it directly in non Debug mode and find that the print is
this.head.item = null this.tail.item = null this.head.next.item = zhazha this.tail.next.item = zhazha Process finished with exit code 0
Step through discovery in Debug mode
this.head.item = zhazha this.tail.item = null Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException at com.zhazha.juc.MyConcurrentLinkedQueue.offer(MyConcurrentLinkedQueue.java:117) at com.zhazha.juc.MyConcurrentLinkedQueue.add(MyConcurrentLinkedQueue.java:67) at com.zhazha.juc.MyConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo.main(MyConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo.java:13) Process finished with exit code 1
what?
I added the sleep method before and after the NEXT cas operation to run in non Debug mode
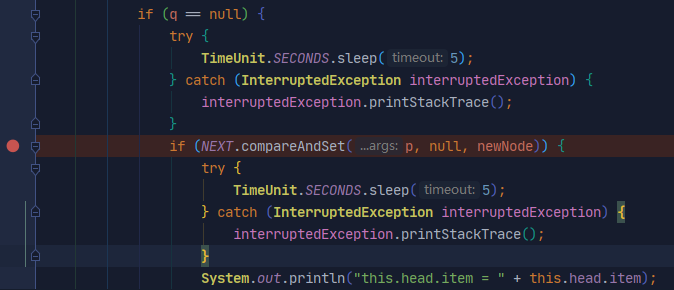
this.head.item = null this.tail.item = null this.head.next.item = zhazha this.tail.next.item = zhazha
It's still different
Multi environment IDE test
Put the ultimate ultimate ultimate SVIP tips = = > try it on eclipse or vscode???
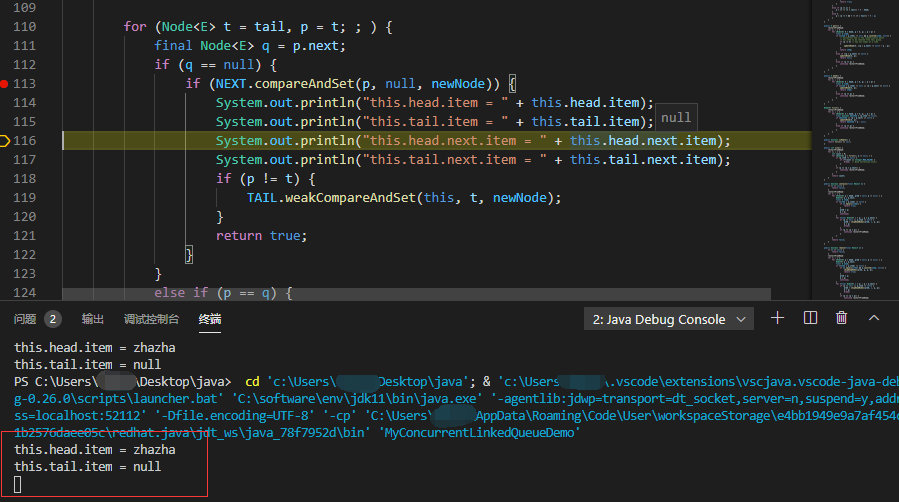
Step through the output in Debug mode on vscode
this.head.item = zhazha this.tail.item = null Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException at MyConcurrentLinkedQueue.offer(MyConcurrentLinkedQueue.java:116) at MyConcurrentLinkedQueue.add(MyConcurrentLinkedQueue.java:66) at MyConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo.main(MyConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo.java:11)
Direct output in non Debug mode
this.head.item = null this.tail.item = null this.head.next.item = zhazha this.tail.next.item = zhazha
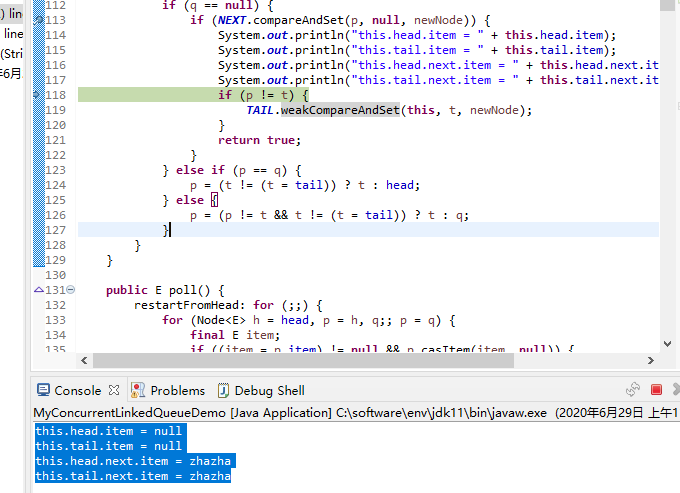
Running the output step by step in Debug mode on eclipse
this.head.item = null this.tail.item = null this.head.next.item = zhazha this.tail.next.item = zhazha
Non Debug run output
this.head.item = null this.tail.item = null this.head.next.item = zhazha this.tail.next.item = zhazha
Did you find out? Or did I stick with eclipse
