There is a recorded video at the end of the article. If you are not comfortable with the article, you can slide to the end of the article and watch the video. I hope you like it~
In the work, we often meet the need of merging multiple tables into one table; in the interview, we are sometimes asked by the interviewer about the difference between left connection, right connection and inner connection. This paper introduces common software (including Excel, Power BI, MySQL, Python) to connect data horizontally.
The data used in this paper is simplified medical sales data, including order table, organization information table and price table. Now, three tables need to be spliced into one table. The table data is as follows: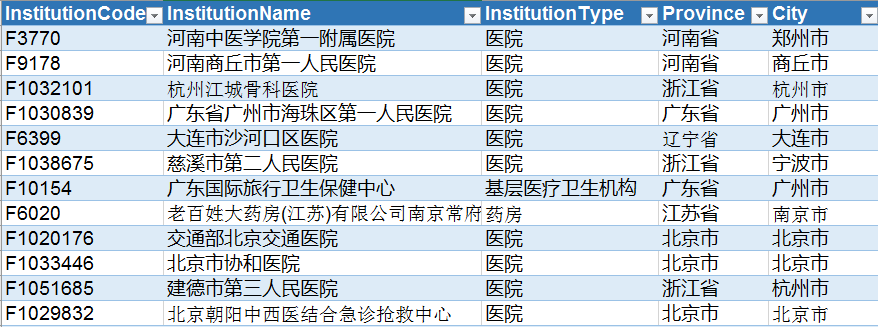
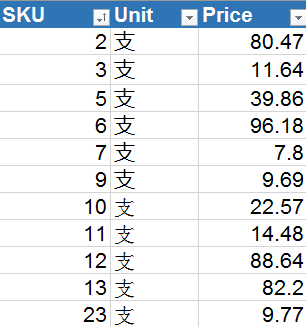
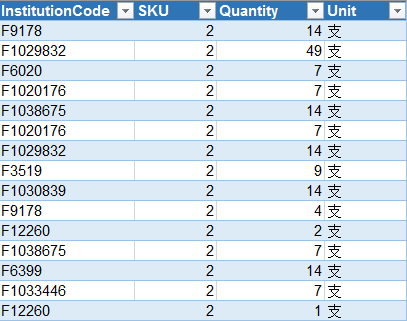
The first method, using the vlookup function
Take the sales table as the main table, and use the vlookup function to reference the data of the price table and the institution table to the sales table. The vlookup function is: = VLOOKUP([@SKU],Price!$A1:1:1:C,3,FALSE). The effect is as follows. If there are many fields in the attached table, you need to use multiple vlookup functions. In addition, if there is a large amount of data, the software is prone to crash. Therefore, this method is not recommended in the case of massive data.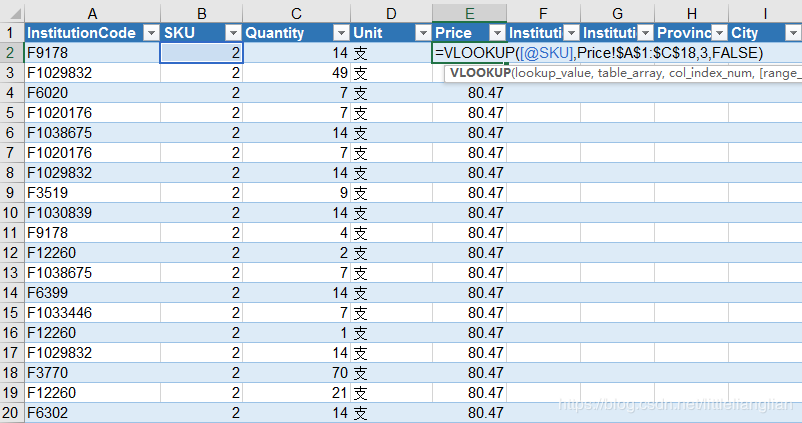
The second method is to use Power Query in Excel BI
From the acquisition and conversion under the Excel Data tab, you can enter the PQ interface. First, import three pieces of data into PQ respectively. Using the PQ merge query function, first merge the sales table and price table, and then merge with the institution table. The advantage is that there is no requirement for the number of fields and records, which can facilitate the consolidation of massive data. The main screenshot is as follows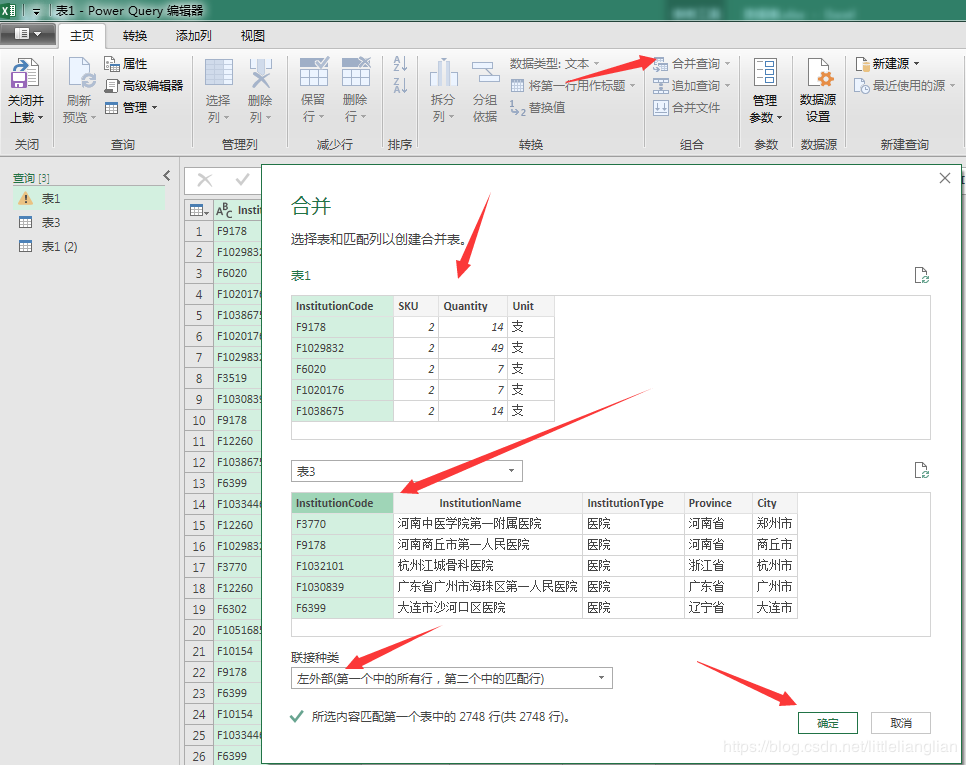
The third method, using MySQL
If the data is no longer in the database, using this method is more cumbersome. First, import the data into the database. The database can only import csv documents or txt documents. First, save the three Excel tables as UTF8 encoded csv documents, and then copy the three documents to the safe path (not in the safe path, the database cannot import external data). Use multi table query statements to export the query results to the external file. The specific code is as follows:
#Create database
create database hos;
#Use database
use hos;
#Create sales table
create table sales(
InstitutionCode varchar(100),
SKU varchar(100),
Quantity int,
Unit varchar(100));
#Create price list
create table price(
SKU varchar(50),
Price float,
Unit varchar(20));
#Create organization information table
create table institution(
InstitutionCode varchar(100),
InstitutionName varchar(100),
InstitutionType varchar(100),
Province varchar(100),
City varchar(100));
#Import sales data
load data infile "C:\\ProgramData\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 8.0\\Uploads\\sales.csv"
into table sales
fields terminated by ","
ignore 1 lines;
#Import price data
load data infile "C:\\ProgramData\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 8.0\\Uploads\\price.csv"
into table price
fields terminated by ","
ignore 1 lines;
#Import institution data
load data infile "C:\\ProgramData\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 8.0\\Uploads\\institution.csv"
into table institution
fields terminated by ","
ignore 1 lines;
#Multi table query results
select sales.*,price,institutionname,institutiontype,province,city
from sales left join price on sales.sku=price.sku
left join institution on sales.institutioncode=institution.institutioncode;
The fourth method, using python
First, import the data into Python, and then connect multiple tables. The code is as follows:
#Import pandas package import pandas as pd #Import three copies of data sales=pd.read_excel(r"E:\360MoveData\Users\Administrator\Desktop\data set.xlsx", sheet_name="Sales") price=pd.read_excel(r"E:\360MoveData\Users\Administrator\Desktop\data set.xlsx", sheet_name="Price") institution=pd.read_excel(r"E:\360MoveData\Users\Administrator\Desktop\data set.xlsx", sheet_name="Institution") #Combine three pieces of data df=pd.merge(sales,price,left_on="SKU",right_on="SKU") df=df.merge(institution,left_on="InstitutionCode",right_on="InstitutionCode") #Delete unnecessary fields df=df[['InstitutionCode', 'SKU', 'Quantity', 'Unit_x', 'Price', 'InstitutionName', 'InstitutionType', 'Province', 'City']] #Rename column name df.rename(columns={"Unit_x":"Unit"},inplace=True) #Consolidated data export df.to_excel(r"E:\360MoveData\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Data merging 2.xlsx",index=False)
The above four methods are recorded in the video. For more details, please watch:
30 minutes to learn a variety of commonly used data analysis software - to achieve horizontal data connection method!
-
Welcome to our team's account:
WeChat official account: Data lovers
Station B: Data lovers
CSDN: Data enthusiast
Zhihu: Cao Liang cda.cn * *