1, Role addition, deletion, modification and query
① Create a new schema about role table, model > role.js Next new role.js , type the following code:
module.exports = app => { const mongoose = app.mongoose; const Schema = mongoose.Schema; var d = new Date(); const RoleSchema = new Schema({ title: { type: String }, description: { type: String }, status: { type: Number, default: 1 }, add_time: { type: Number, default: d.getTime() } }); return mongoose.model("Role", RoleSchema, "role"); };
② Create a new routing rule. The new role submission form will be called.
router.post("/admin/role/doAdd", controller.admin.role.doAdd);
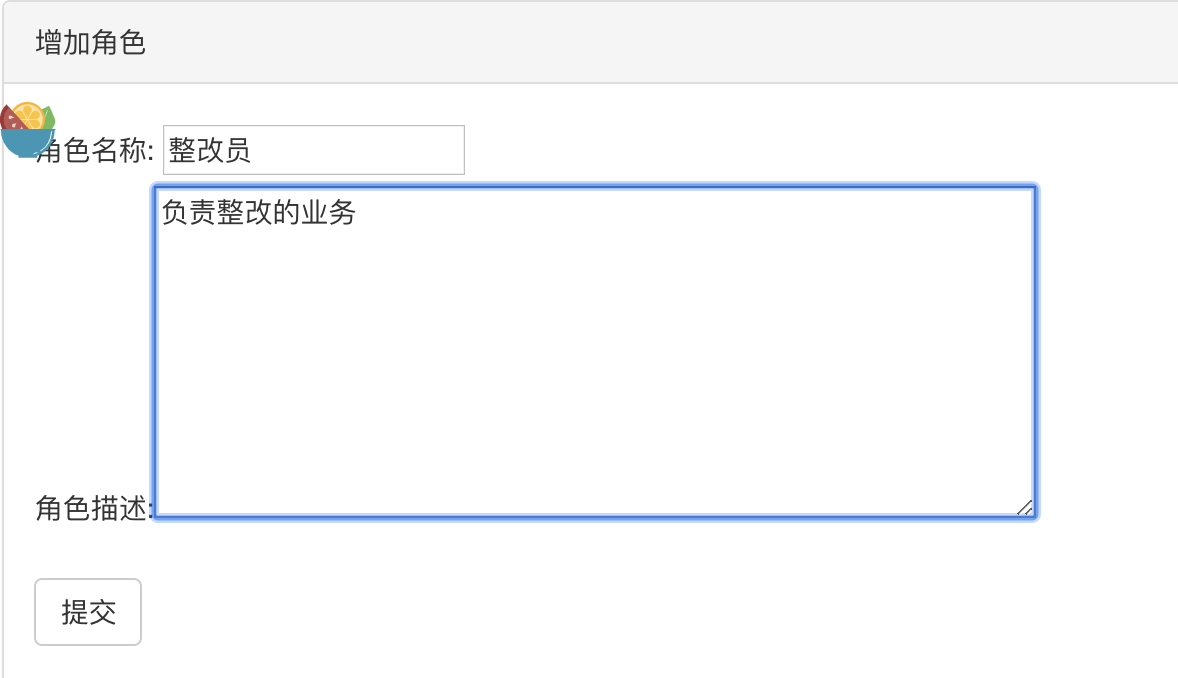
③ Add role form (add hidden field csrf validation)
<form action="/admin/role/doAdd" method="post"> <ul> <input type='hidden' name="_csrf" value="<%=csrf%>"></input> <li> Role name: <input type="text" name="title"/></li> Role description:<textarea name="description" id="" cols="60" rows="8"></textarea> <li> <br/> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">Submit</button> </li> </ul> </form>
④ role controller print post data:
async doAdd() { console.log(this.ctx.request.body); }
⑤ Add role form and click Submit
⑥ Execute the method of doAdd controller under role to print the data submitted by post
async doAdd() { console.log(this.ctx.request.body); }

⑥ Change to the following logic: insert data into the database
async doAdd() { // console.log(this.ctx.request.body); let role = this.ctx.model.Role({ title: this.ctx.request.body.title, description: this.ctx.request.body.description }); let result = await role.save(); console.log(result); await this.success("/admin/role", "Role added successfully"); }
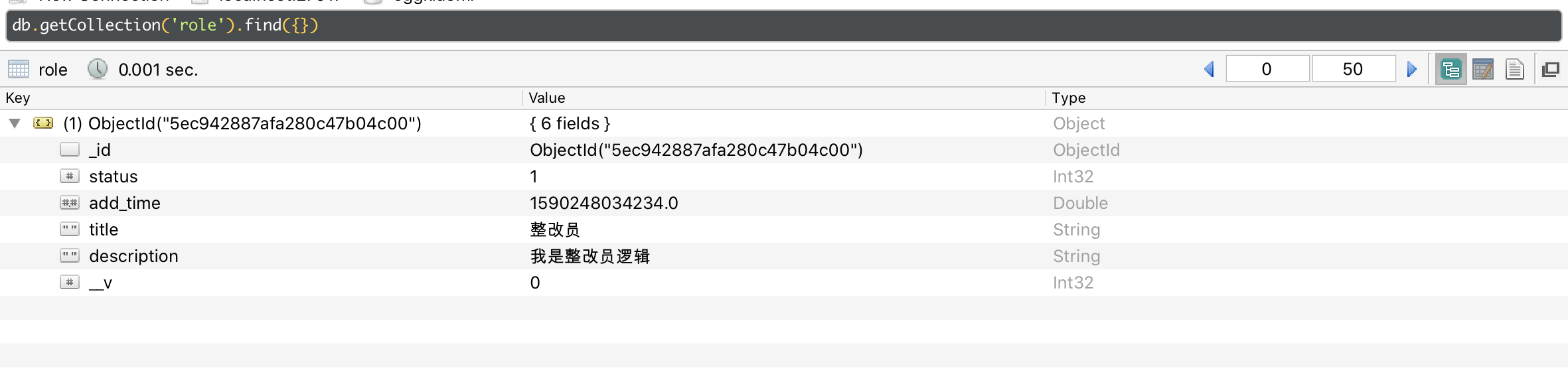
⑦ As can be seen from the visualization tool, a piece of data is inserted into the database:
⑧ Modifying the controller executed by the role list page
async index() { let list = await this.ctx.model.Role.find({}); // console.log(list); await this.ctx.render("admin/role/index", { list }); }
⑨ The controller of the role template page is modified as follows:
<table class="table table-bordered"> <thead> <tr class="th"> <th>Role name</th> <th>describe</th> <th>Increase time</th> <th>operation</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <%for(var i = 0;i<list.length;i++){%> <tr> <td><%=list[i].title%></td> <td><%=list[i].description%></td> <td><%=list[i].addTime%></td> <td class="text-center">Modify delete</td> </tr> <%}%> </tbody> </table>
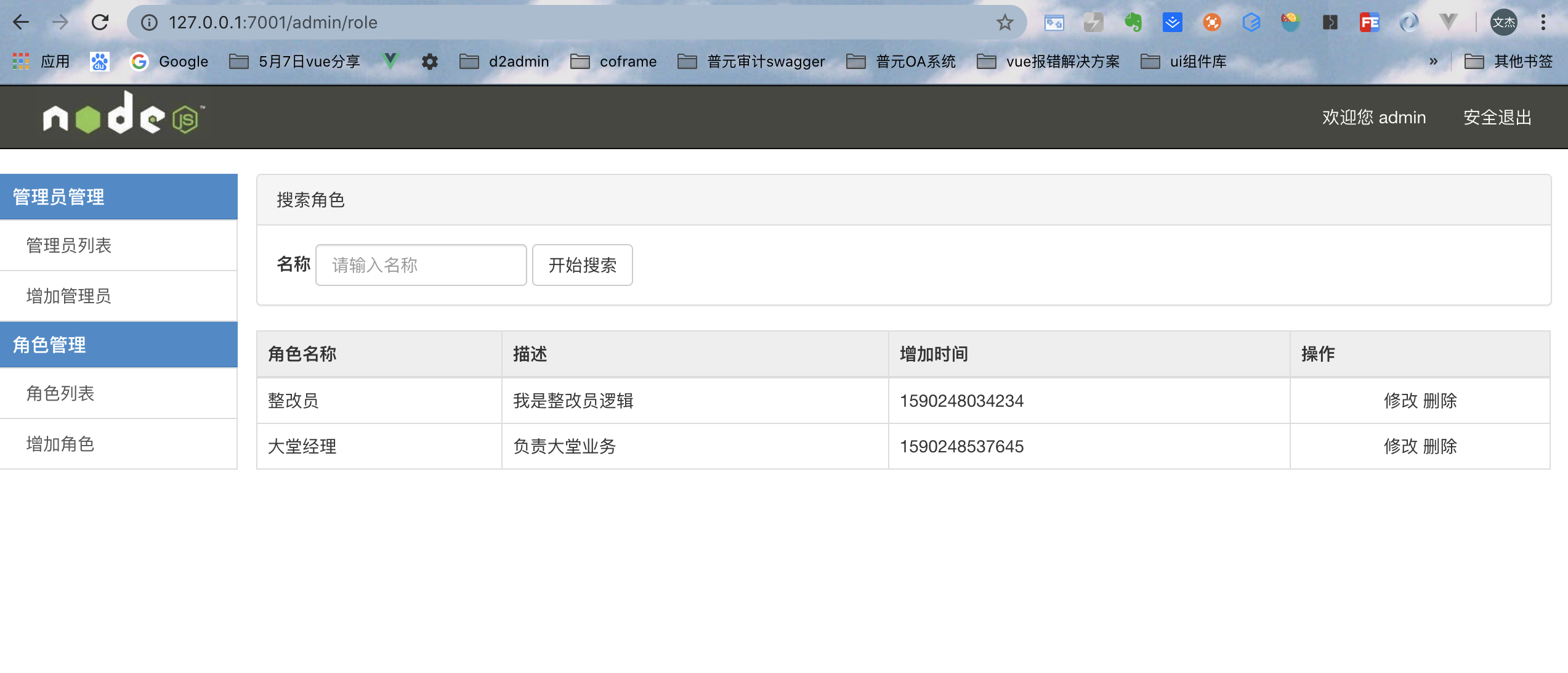
⑩ After the character is added successfully, the data can be read out for page rendering:
11. Edit function modification button: access edit route, execute the edit method of controller, and pass an id to the next page.
<td class="text-center"> <a href="/admin/role/edit?id=<%=list[i]._id%>">modify</a> </td>
12. The next page will query the form according to this id and make editing echo.
async edit() { let id = this.ctx.query.id; console.log(id); let list = await this.ctx.model.Role.find({ _id: id }); console.log(list); await this.ctx.render("admin/role/edit", { list }); }
13. Click submit to modify the form, then configure the modify route:
router.post("/admin/role/doEdit", controller.admin.role.doEdit);
14. doEdit performs the following logic: find the corresponding id to modify the data.
async doEdit() { let { _id, title, description } = this.ctx.request.body; let result = await this.ctx.model.Role.updateOne( { _id }, { title, description } ); console.log(result); if (result) { await this.success("/admin/role", "Edit role succeeded"); } else { await this.error("/admin/role", "Failed to edit role"); } }
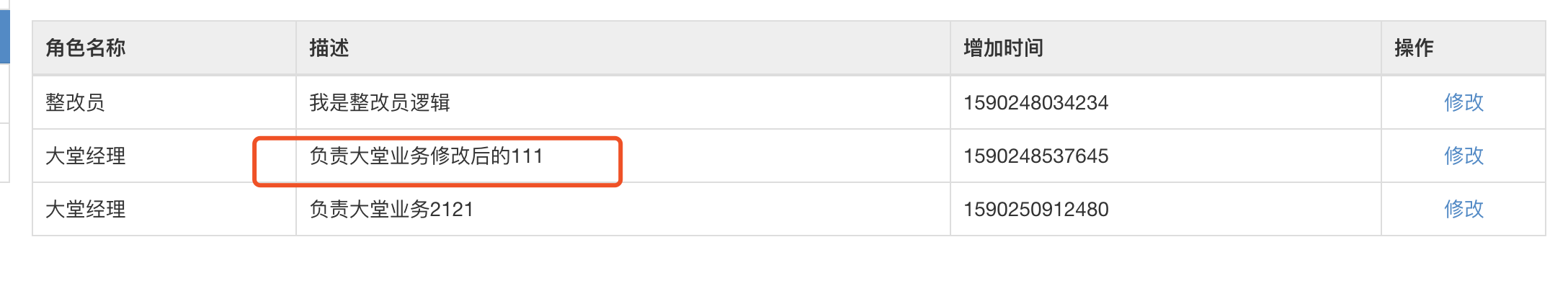
15.
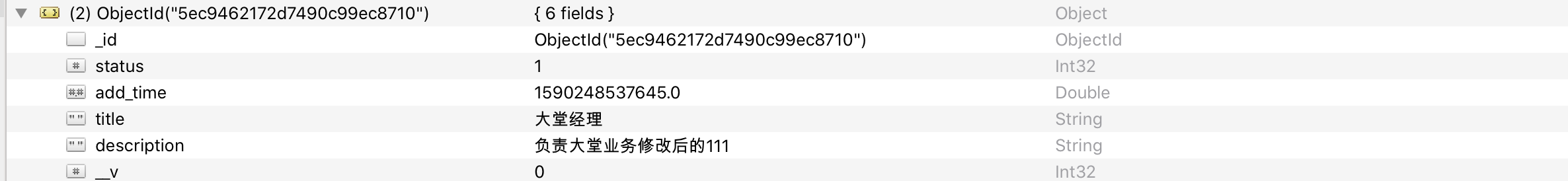
16. If you want to delete, you need to take an id to perform the deletion. Tomorrow, you need to encapsulate the public deletion method. Broken sleep.