pyecharts: Official documents
Here we use the pyecharts module for drawing.
The pyecharts project contains a series of geographic map data. These data are either built-in or need additional installation and loading. We need to download the following six packages.
Choose the installation you need pip install echarts-countries-pypkg pip install echarts-china-provinces-pypkg pip install echarts-china-cities-pypkg pip install echarts-china-counties-pypkg pip install echarts-china-misc-pypkg pip install echarts-united-kingdom-pypkg
In pyecharts, Geo represents data associated with cities, and Map represents data associated with countries and provinces.
World map
from pyecharts import Map, Geo # World map data value = [95.1, 23.2, 43.3, 66.4, 88.5] attr= ["China", "Canada", "Brazil", "Russia", "United States"] map0 = Map("World map example", width=1200, height=600) map0.add("World map", attr, value, maptype="world", is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='#000') map0.render(path="World map.html")
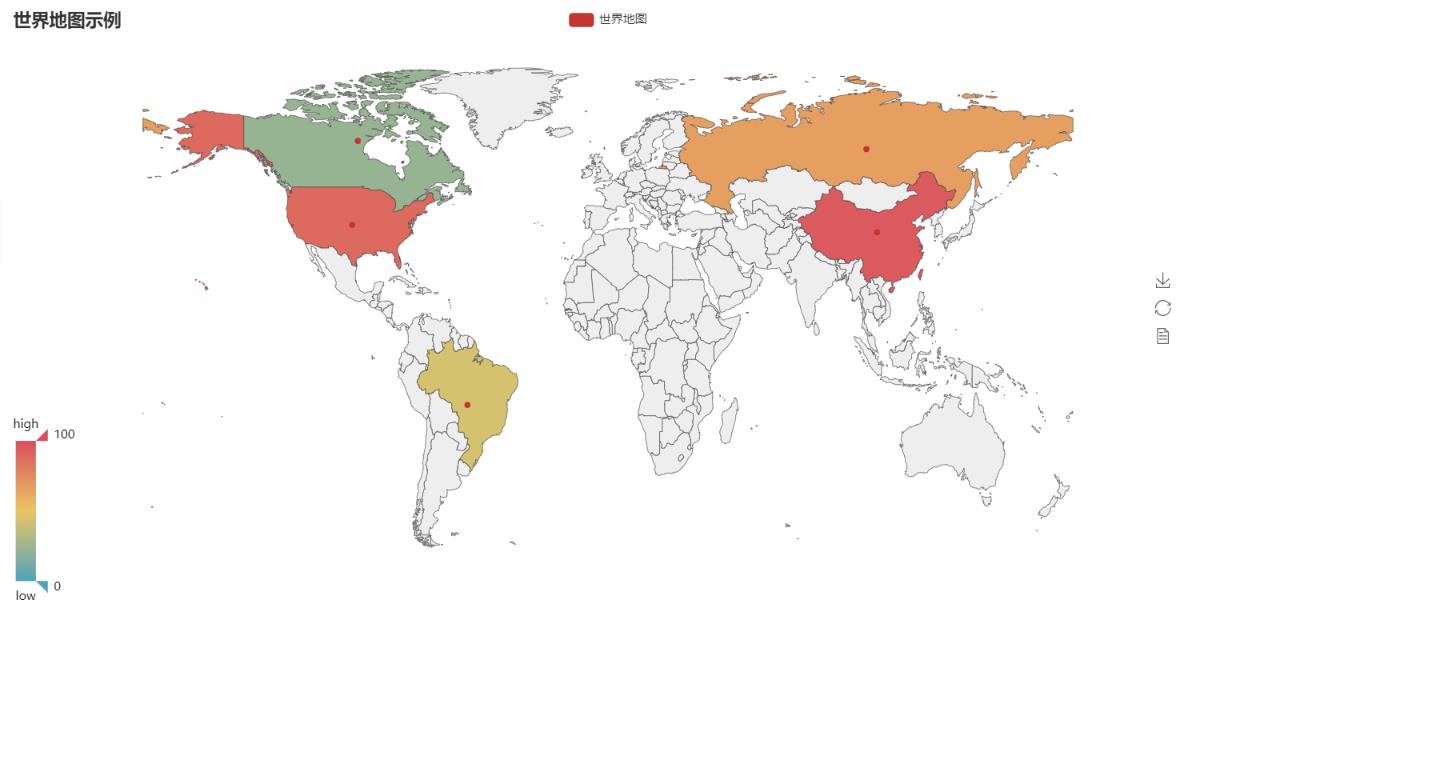
Map of China
from pyecharts import Map, Geo # map of China province_distribution = {'Henan': 45.23, 'Beijing': 37.56, 'Hebei': 21, 'Liaoning': 12, 'Jiangxi': 6, 'Shanghai': 20, 'Anhui': 10, 'Jiangsu': 16, 'Hunan': 9, 'Zhejiang': 13, 'Hainan': 2, 'Guangdong': 22, 'Hubei': 8, 'Heilongjiang': 11, 'Macao': 1, 'Shaanxi': 11, 'Sichuan': 7, 'Inner Mongolia': 3, 'Chongqing': 3, 'Yunnan': 6, 'Guizhou': 2, 'Jilin': 3, 'Shanxi': 12, 'Shandong': 11, 'Fujian': 4, 'Qinghai': 1, 'Helmsman technology, quality assurance': 1, 'Tianjin': 1, 'Other': 1} provice = list(province_distribution.keys()) values = list(province_distribution.values()) map = Map("map of China",'map of China', width=1200, height=600) map.add("", provice, values, visual_range=[0, 50], maptype='china', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='#000') map.show_config() map.render(path="map of China.html")
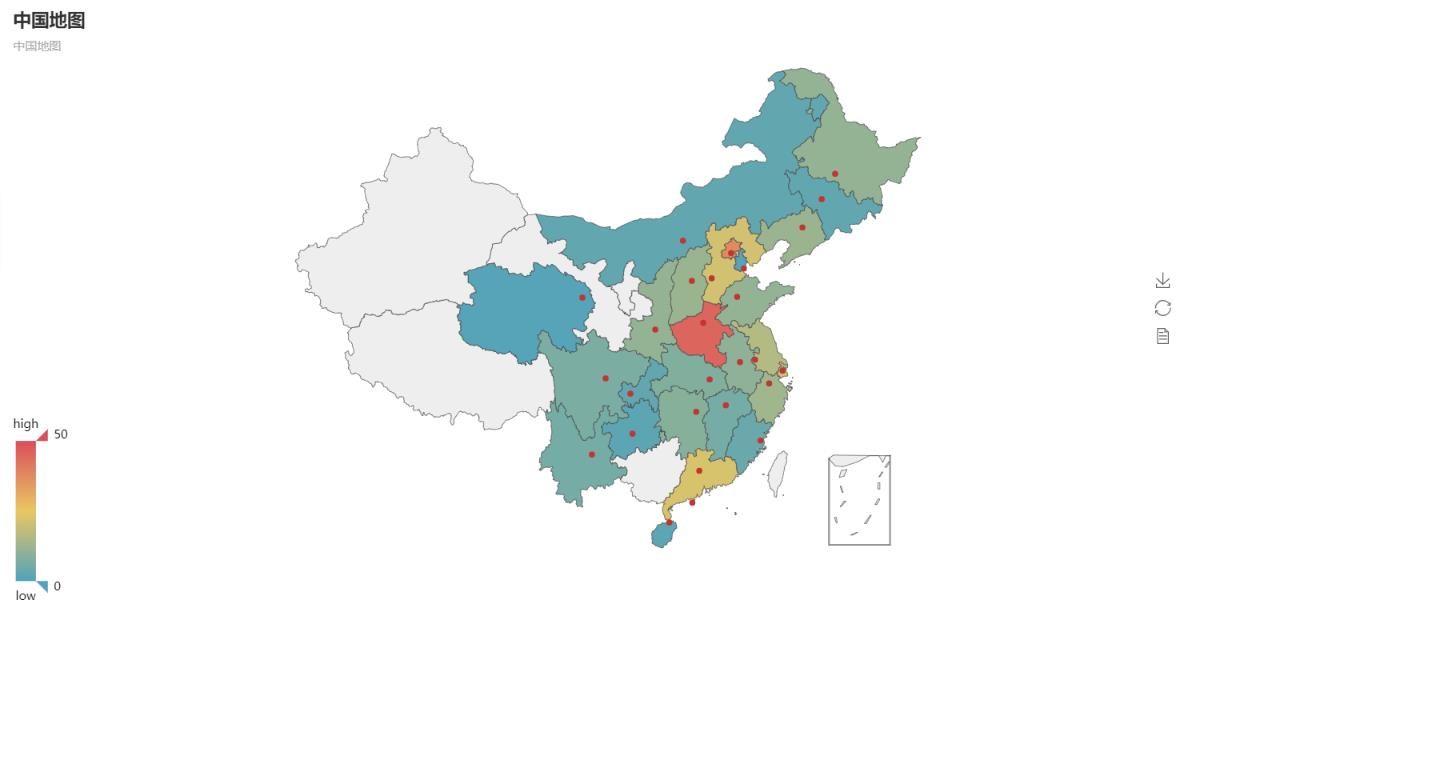
Province Map
from pyecharts import Map, Geo # City -- City of designated Province xx city city = ['Zhengzhou City', 'Anyang City', 'Luoyang City', 'Puyang City', 'Nanyang City', 'Kaifeng City', 'Shangqiu City', 'Xinyang City', 'Xinxiang City'] values2 = [1.07, 3.85, 6.38, 8.21, 2.53, 4.37, 9.38, 4.29, 6.1] map2 = Map("Map of Henan Province",'Henan', width=1200, height=600) map2.add('Henan', city, values2, visual_range=[1, 10], maptype='Henan', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='#000') map2.show_config() map2.render(path="Map of Henan Province.html")
Urban map
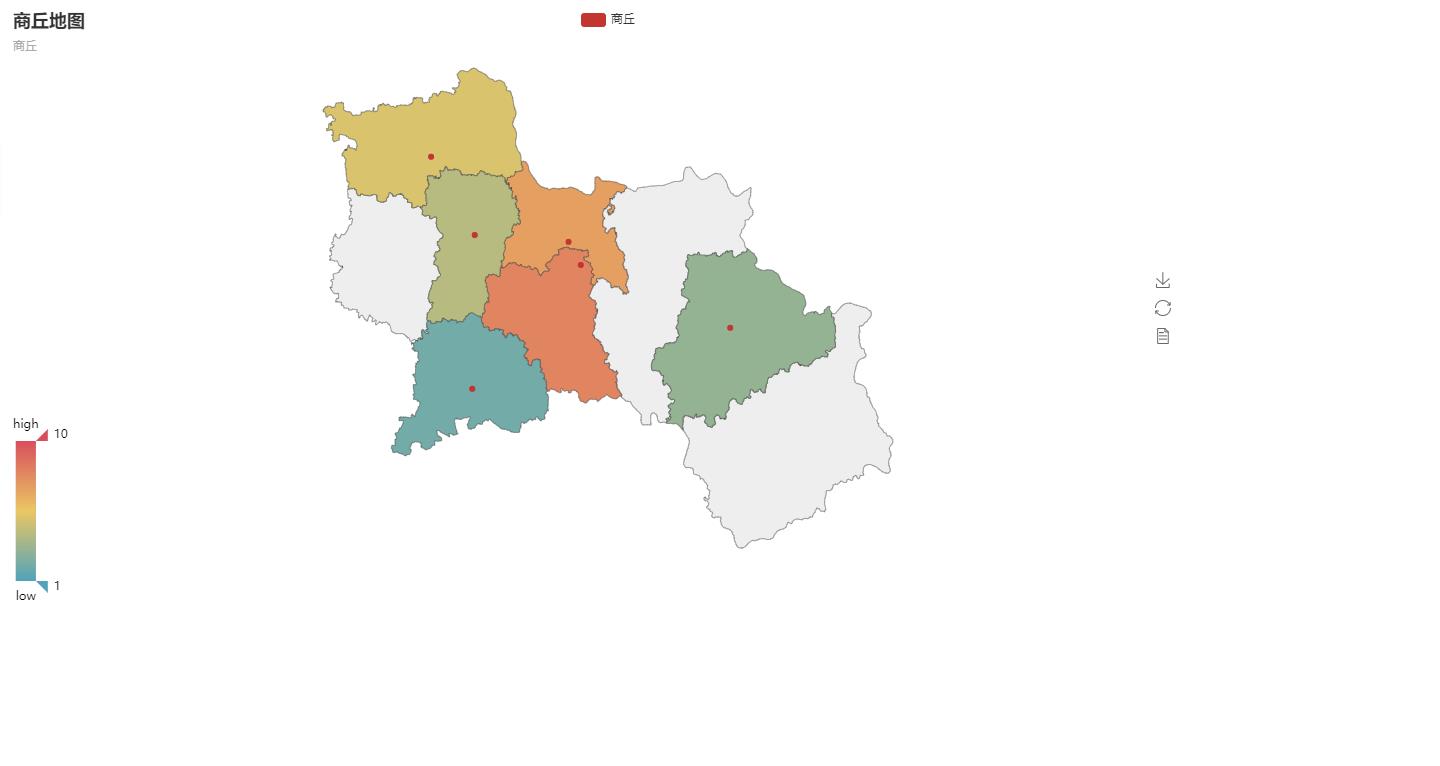
from pyecharts import Map, Geo # District and county -- Districts and counties in specific cities xx county quxian = ['Xiayi County', 'Civil rights county', 'Liang Park', 'Suiyang District', 'Zhecheng County', 'Ningling County'] values3 = [3, 5, 7, 8, 2, 4] map3 = Map("Shangqiu map",'Shangqiu', width=1200, height=600) map3.add("Shangqiu", quxian, values3, visual_range=[1, 10], maptype='Shangqiu', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='#000') map3.render(path="Shangqiu map.html")
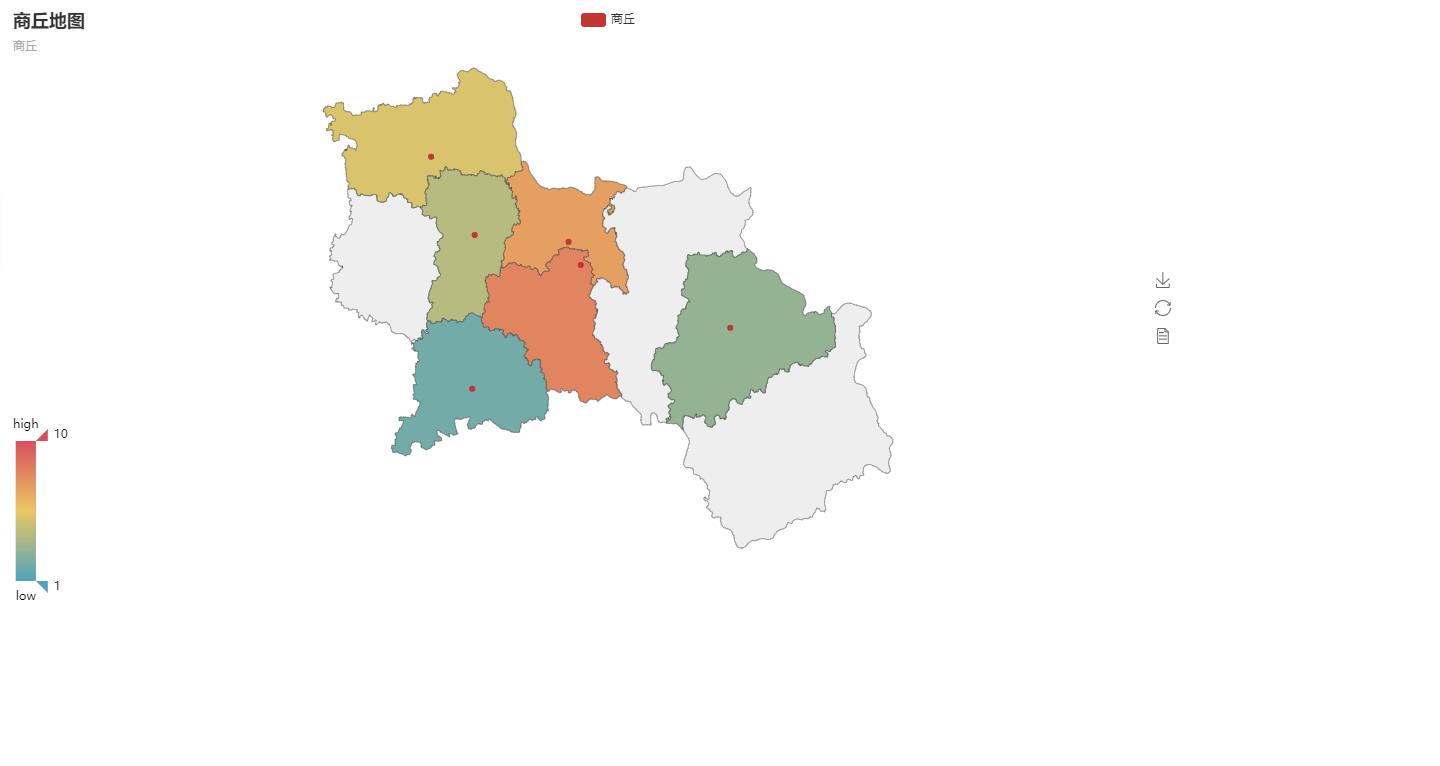
Thermograph
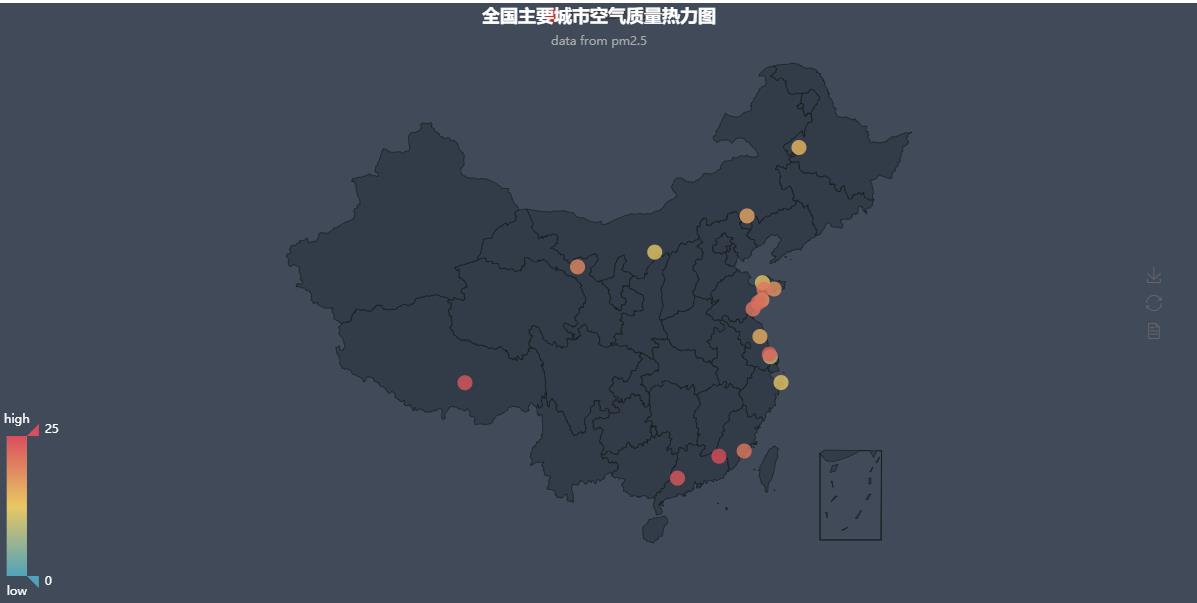
from pyecharts import Map, Geo data = [ ("Haimen", 9), ("erdos", 12), ("Zhaoyuan", 12), ("Zhoushan", 12), ("Qiqihar", 14), ("ynz", 15), ("Chifeng", 16), ("Qingdao", 18), ("Rushan", 18), ("Jinchang", 19), ("Quanzhou", 21), ("Laixi", 21), ("sunshine", 21), ("Jiaonan", 22), ("Nantong", 23), ("Lhasa", 24), ("Yunfu", 24), ("Meizhou", 25)] attr, value = Geo.cast(data) geo = Geo("Thermal map of air quality of major cities in China", "data from pm2.5", title_color="#fff", title_pos="center", width=1200, height=600, background_color='#404a59') geo.add("Thermodynamic diagram of air quality", attr, value, visual_range=[0, 25], type='heatmap', visual_text_color="#fff", symbol_size=15, is_visualmap=True, is_roam=False) geo.show_config() geo.render(path="Thermodynamic diagram of air quality.html")
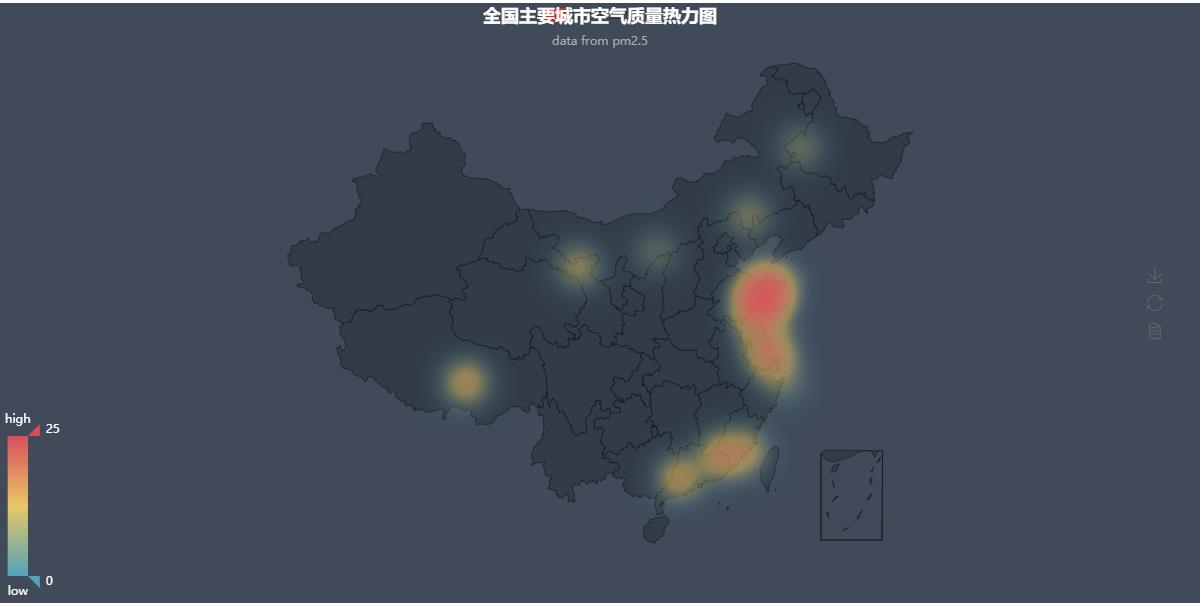
from pyecharts import Map, Geo indexs = ['Shanghai', 'Beijing', 'Hefei', 'Harbin', 'Guangzhou', 'Chengdu', 'Wuxi', 'Hangzhou', 'Wuhan', 'Shenzhen', 'Xi'an', 'Zhengzhou', 'Chongqing', 'Changsha'] values = [4.07, 1.85, 4.38, 2.21, 3.53, 4.37, 1.38, 4.29, 4.1, 1.31, 3.92, 4.47, 2.40, 3.60] geo = Geo("Air quality rating of major cities in China", "data from pm2.5", title_color="#fff", title_pos="center", width=1200, height=600, background_color='#404a59') # type="effectScatter", is_random=True, effect_scale=5 Make points divergent geo.add("Air quality score", indexs, values, type="effectScatter", is_random=True, effect_scale=5, visual_range=[0, 5], visual_text_color="#fff", symbol_size=15, is_visualmap=True, is_roam=False) geo.show_config() geo.render(path="Air quality score.html")
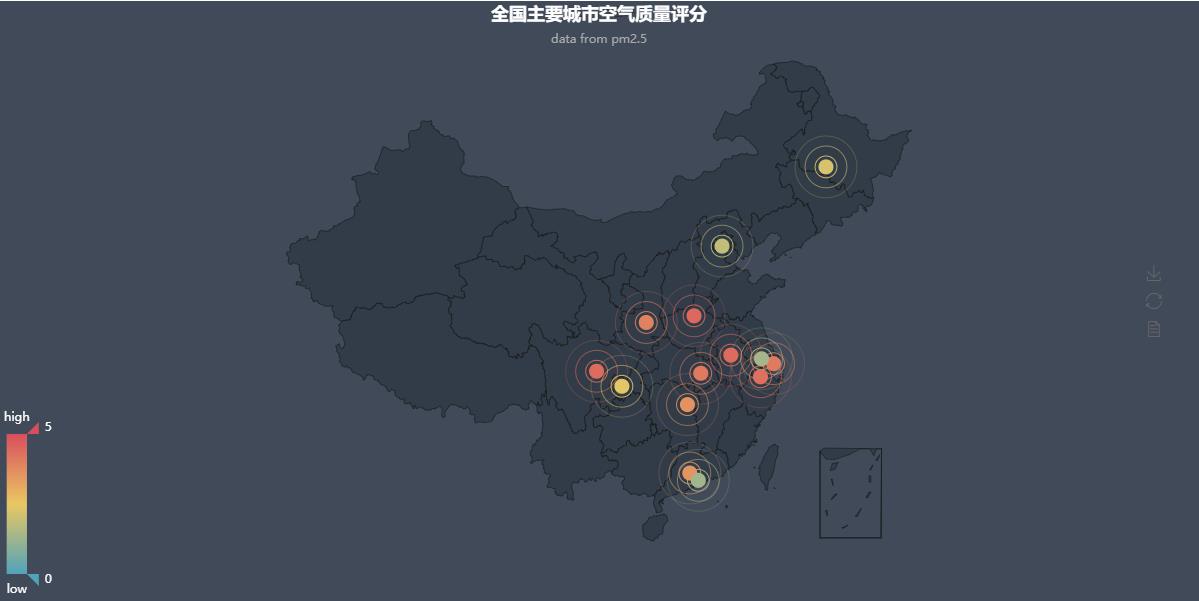
from pyecharts import Map, Geo data = [ ("Haimen", 9), ("erdos", 12), ("Zhaoyuan", 12), ("Zhoushan", 12), ("Qiqihar", 14), ("ynz", 15), ("Chifeng", 16), ("Qingdao", 18), ("Rushan", 18), ("Jinchang", 19), ("Quanzhou", 21), ("Laixi", 21), ("sunshine", 21), ("Jiaonan", 22), ("Nantong", 23), ("Lhasa", 24), ("Yunfu", 24), ("Meizhou", 25)] attr, value = Geo.cast(data) geo = Geo("Thermal map of air quality of major cities in China", "data from pm2.5", title_color="#fff", title_pos="center", width=1200, height=600, background_color='#404a59') geo.add("Thermodynamic diagram of air quality", attr, value, visual_range=[0, 25], type='scatter', visual_text_color="#fff", symbol_size=15, is_visualmap=True, is_roam=False) geo.show_config() geo.render(path="Mass thermograph.html")
Example: capture and visualize coronavirus infection data
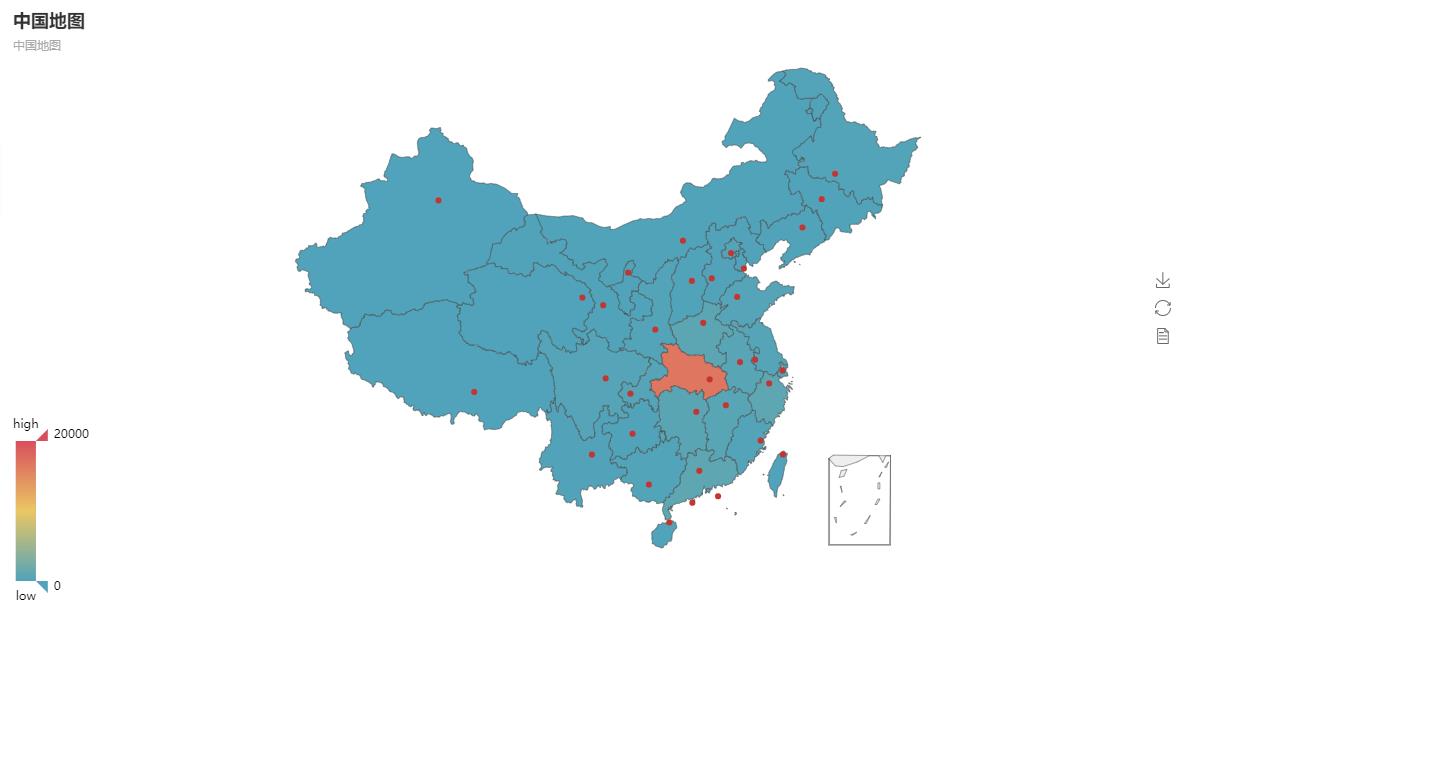
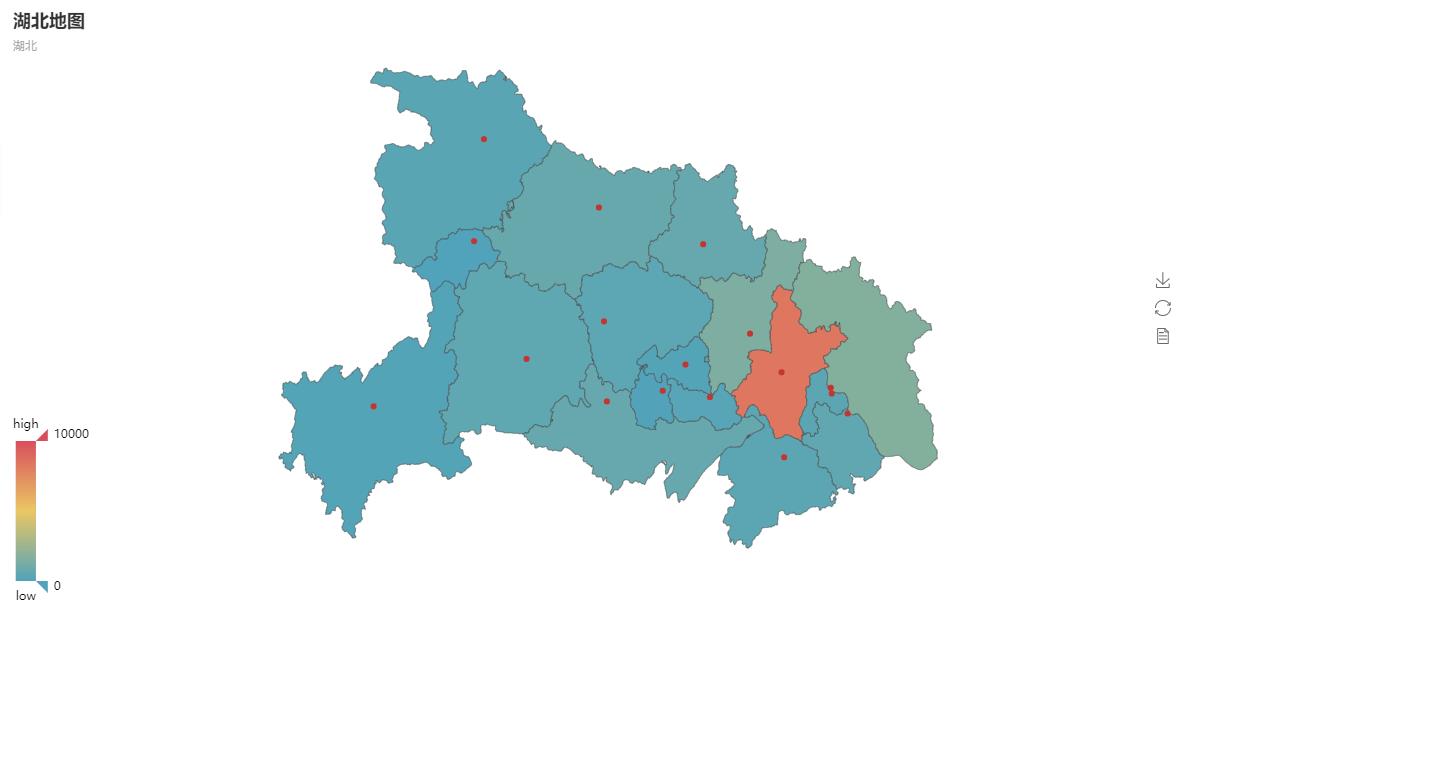
import urllib import urllib.request import json import os import prettytable as pt from pyecharts import Map, Geo class Searchdata(object): def __init__(self,url): self.url = url self.china_list = {} self.china_data = {} self.province_list = {} self.province_data = {} def get_data(self): try: data = urllib.request.urlopen(self.url) data = json.loads(data.read()) self.save(data) return data except: print("Request data error!") def is_exist(self): for i in os.listdir(os.getcwd()): if i == "data.txt": return 1 return 0 def save(self,data): if self.is_exist() == 0: with open("data.txt",'w') as fp: fp.write(str(data)) def get_china(self,data): data = data['data'] self.china_data['total'] = data['gntotal'] self.china_data['deathNum'] = data['deathtotal'] self.china_data['susNum'] = data['sustotal'] self.china_data['cureNum'] = data['curetotal'] for i in data['list']: dic ={} dic['total'] = i['value'] dic['deathNum'] = i['deathNum'] dic['susNum'] = i['susNum'] dic['cureNum'] = i['cureNum'] self.china_list[i['name']] = dic def get_province(self,data): data = data['data'] for i in data['list']: if i['name'] == 'Hubei': self.province_data['total'] = i['value'] self.province_data['deathNum'] = i['deathNum'] self.province_data['susNum'] = i['susNum'] self.province_data['cureNum'] = i['cureNum'] for temp in i['city']: dic = {} dic['total'] = temp['conNum'] dic['deathNum'] = temp['deathNum'] dic['susNum'] = temp['susNum'] dic['cureNum'] = temp['cureNum'] self.province_list[temp['name']] = dic return def get_sheet1(self): self.tb = pt.PrettyTable() self.tb.field_names = ["Province", "Total", "death", "Suspected", "Cure"] for k, v in self.china_list.items(): self.tb.add_row([k, v['total'], v['deathNum'], v['susNum'],v['cureNum']]) self.tb.add_row(['Total', self.china_data['total'],self.china_data['deathNum'], self.china_data['susNum'], self.china_data['cureNum']]) print(self.tb) def get_sheet2(self): self.tb = pt.PrettyTable() self.tb.field_names = ["Prefecture level city", "Total", "death", "Suspected", "Cure"] for k, v in self.province_list.items(): self.tb.add_row([k, v['total'], v['deathNum'], v['susNum'], v['cureNum']]) self.tb.add_row(['Total', self.province_data['total'], self.province_data['deathNum'], self.province_data['susNum'], self.province_data['cureNum']]) print(self.tb) def get_graph1(self): provice = list(self.china_list.keys()) values = [] for k, v in self.china_list.items(): values.append(v['total']) # map of China map = Map("map of China", 'map of China', width=1200, height=600) map.add("", provice, values, visual_range=[0, 20000], maptype='china', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='#000') map.show_config() map.render(path="Map.html") def get_graph2(self): city = list(self.province_list.keys()) new_city = [] for str in city: if len(str) == 2: str = str+"city" new_city.append(str) elif len(str) == 3: str = "Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture " new_city.append(str) else: new_city.append(str) values = [] for k, v in self.province_list.items(): values.append(v['total']) map2 = Map("Map of Hubei Province", 'Hubei', width=1200, height=600) map2.add('', new_city, values, visual_range=[0,10000], maptype='Hubei', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='#000') map2.show_config() map2.render(path="Map of Hubei Province.html") Searchtool =Searchdata('http://43.250.238.179:9090/showData') data = Searchtool.get_data() Searchtool.get_province(data) Searchtool.get_sheet2() Searchtool.get_graph2()
refer:
http://pyecharts.herokuapp.com/
https://05x-docs.pyecharts.org/#/
The most complete pyecharts data visualization, 30 minutes to learn