I. overview
scala is similar to higher-order function, which is a function that can receive another function as a parameter.
2, Import base package
import random from functools import reduce
3, Custom higher order function
#Define common functions and generate lists automatically def getList(): hList = list(range(5)) return [key * random.randint(0,3) for key in hList] #Generate random number #Define common functions to find the largest union in different lists def getMaxSet(listA,listB): setA = set(listA) #Turn to set setB = set(listB) setAll = setA | setB #Seeking Union return list(setAll)#Turn to list #Defining higher order functions def highFunction(listA,listB,getMaxSet): return getMaxSet(listA,listB)
4, Application of custom higher order function
# Get two sets listA = getList() print("aggregate A:{}".format(listA)) listB = getList() print("aggregate B:{}".format(listB)) # Get union of two sets listC = getMaxSet(listA, listB) print("aggregate A And set B Union:{}".format(listC)) #Call higher-order function values = highFunction(listA,listB,getMaxSet) print("Call higher-order function to get set A And set B Union:{}".format(values))
5, Custom high order function execution results

6, map practice and execution results
#map(f,Iterable):f;What to do, Iterable: Recyclable def mapF(arg): return len(arg) # Call built-in higher-order function map,Get the length of each string test = ['python', 'tensorflow', 'keris', 'tensorboard', 'tensorflow', 'tensorflow', 'keris'] maps = list(map(mapF, test)) print("The length of each string is:{}".format(maps))
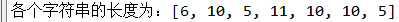
7, reduce practice and implementation results
#reduce(f,Iterable):f;What to do, Iterable: Recyclable def reduceF(arg1,arg2): return arg1 + arg2 # Call built-in higher-order function reduce,Sum the length of all strings reduces = reduce(reduceF, maps) print("The total length of the string is:{}".format(reduces))
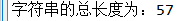
8, And operator and strip() test
# test and Operator sum strip()Remove string space operator a = " a" and " a".strip() b = "b " and "b ".strip() c = " c " and " c ".strip() print("test and Operator sum strip()Remove string space operator:a:{},b:{},c:{}".format(a,b,c))
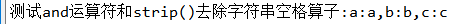
9, filter() filter
# filter(f,Iterable):filter() Function is used to filter the sequence, filter out unqualified elements, and return a new list of qualified elements. #It receives two parameters, the first is a function, the second is a sequence, each element of the sequence is passed to the function as a parameter for judgment, and then returns True or False, #Will return True The elements of are placed in the new list. # Filter the empty string and do not modify the data that meets the conditions def del_empty(s): return s and s.strip() #strip()Used to remove characters specified at the beginning and end of a string (space or newline by default) filterList = list(filter(del_empty, [" a", "", "b ", None, "v", " "])) print(filterList)
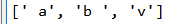
10, sorted sort
#Basics sort() print(sorted([36, 5, -12, 9, -21])) #Digital by size print(sorted(["36", "5", "-12", "9", "-21"])) #String pressing ASCII code #Advanced print(sorted([36, 5, -12, 9, -21], key=abs))#Take absolute value first, and then sort (without affecting the original data) print(sorted(['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'], key=str.lower, reverse=True)) #Convert to lowercase first, sort by transpose (do not affect the original data)

11, Operators
1. Bit operator
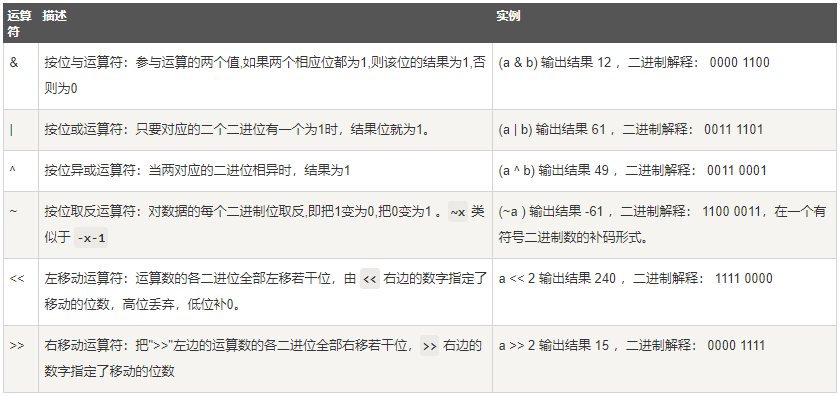
2. Logical operators
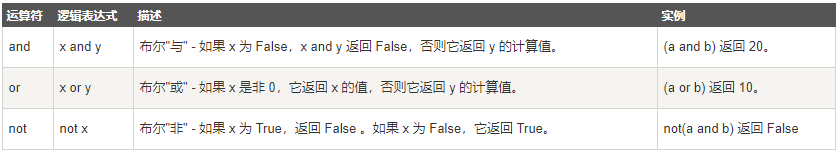
3. Member operator
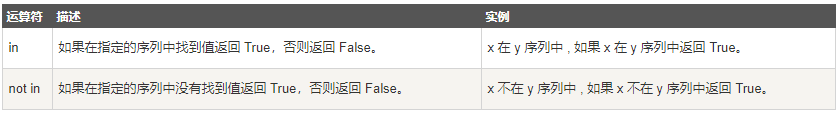
4. Identity operator

These operators are similar to the usage in other programming languages, so we will not give an example here!