
In servlet 3.0, asynchronous request support has been introduced, but in actual business development, there are not many children's shoes that may have used this feature?
As a literacy and usage tutorial for asynchronous requests, this blog post will contain the following knowledge points
- What is asynchronous request? What are its characteristics? Applicable scenarios
- Four use postures:
- AsyncContext mode
- Callable
- WebAsyncTask
- DeferredResult
<!-- more -->
1. Asynchronous request
For us, asynchrony should be a frequently heard word. It will be used more or less in actual development, so what is asynchronous request
1. Asynchronous request description
Let's start with synchronization and asynchrony:
When a normal call is completed, it returns directly. This is called synchronization;
After receiving the call, the main thread will do other things. After the background thread finishes running, the main thread will return the result. This is called asynchronous
Asynchronous request:
The asynchronous request we mentioned here is mainly for the web request, a means for the back-end to respond to the request. Synchronous / asynchronous is insensitive and indistinguishable for the front-end
Synchronous request: after receiving the request, the backend directly executes the business logic in the processing request thread and returns
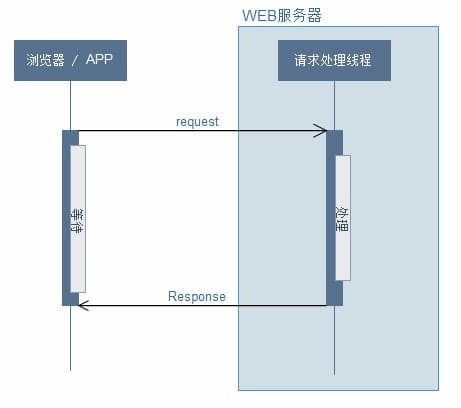
Asynchronous request: after the backend receives the request, a new thread is opened to execute the business logic, release the request thread, and avoid the request thread being full of a large number of time-consuming requests, resulting in the unavailability of the service
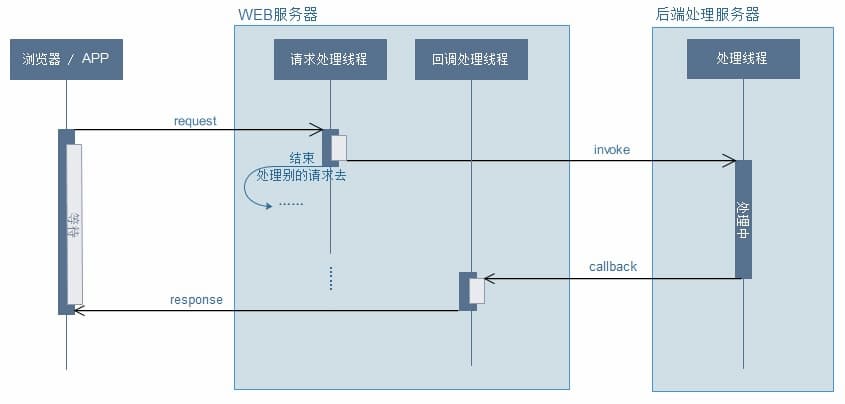
2. characteristics
From the above two figures, you can know the main characteristics of asynchronous request
- Business thread, processing request logic
- Request processing thread releases immediately, and returns results through callback processing thread
3. Scenario analysis
From the characteristics, it is also easy to see asynchronous requests, which are more suitable for time-consuming requests. It can release request processing threads quickly, so as to avoid the web container's request threads being full, resulting in service unavailability
Take a slightly extreme example. For example, a multimedia service I have done before provides editing of pictures, audio and video. These service interfaces have synchronous return results and asynchronous return results. The interface of synchronous return results is fast or slow, most of which can take less than 10ms, while some of them take tens or even hundreds of times
In this scenario, the time-consuming interface can be supported by asynchronous request to avoid taking up too many request processing threads and affecting other services
2. Use posture
Next, we will introduce four usage postures of asynchronous requests, which are consistent in principle, but with slightly different scenarios
1. AsyncContext
After Servlet3.0 +, asynchronous request is supported. The first method is primitive, which is equivalent to directly implementing with servlet specification. Of course, the following case is not directly creating a servlet, but with AsyncContext
@RestController @RequestMapping(path = "servlet") public class ServletRest { @GetMapping(path = "get") public void get(HttpServletRequest request) { AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync(); asyncContext.addListener(new AsyncListener() { @Override public void onComplete(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException { System.out.println("Operation completed:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } @Override public void onTimeout(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException { System.out.println("Timeout returns!!!"); asyncContext.getResponse().setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); asyncContext.getResponse().setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter().println("Time out!!!!"); } @Override public void onError(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException { System.out.println("Appeared m Some anomalies"); asyncEvent.getThrowable().printStackTrace(); asyncContext.getResponse().setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); asyncContext.getResponse().setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter().println("There are some exceptions!!!!"); } @Override public void onStartAsync(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException { System.out.println("Start execution"); } }); asyncContext.setTimeout(3000L); asyncContext.start(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(Long.parseLong(request.getParameter("sleep"))); System.out.println("Internal thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); asyncContext.getResponse().setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); asyncContext.getResponse().setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter().println("Asynchronous return!"); asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter().flush(); // Asynchronous completion, release asyncContext.complete(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); System.out.println("Main thread over!!! " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }
For the complete implementation, see the general steps
- Javax. Servlet. ServletRequest? Startasync() get AsyncContext
- Add listener asyncContext.addListener(AsyncListener) (this is optional)
- User request start, timeout, exception, callback on completion
- Set timeout asyncContext.setTimeout(3000L) (optional)
- Asynchronous task asyncContext.start(Runnable)
2. Callable
Compared with the above complex example, spring MVC can be very easy to implement, just return a Callable directly
@RestController @RequestMapping(path = "call") public class CallableRest { @GetMapping(path = "get") public Callable<String> get() { Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { System.out.println("do some thing"); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("Execution complete, return to!!!"); return "over!"; } }; return callable; } @GetMapping(path = "exception") public Callable<String> exception() { Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { System.out.println("do some thing"); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("Exception, return!!!"); throw new RuntimeException("some error!"); } }; return callable; } }
Please pay attention to the above two case s, one is normal return and the other is exception thrown during business execution
The output is as follows
# http://localhost:8080/call/get do some thing Execution finished, return!!!
Exception request: http://localhost:8080/call/exception

do some thing //Exception, return!!! 2020-03-29 16:12:06.014 ERROR 24084 --- [nio-8080-exec-5] o.a.c.c.C.[.[.[/].[dispatcherServlet] : Servlet.service() for servlet [dispatcherServlet] threw exception java.lang.RuntimeException: some error! at com.git.hui.boot.async.rest.CallableRest$2.call(CallableRest.java:40) ~[classes/:na] at com.git.hui.boot.async.rest.CallableRest$2.call(CallableRest.java:34) ~[classes/:na] at org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManager.lambda$startCallableProcessing$4(WebAsyncManager.java:328) ~[spring-web-5.2.1.RELEASE.jar:5.2.1.RELEASE] at java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:511) ~[na:1.8.0_171] at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run$$$capture(FutureTask.java:266) ~[na:1.8.0_171] at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java) ~[na:1.8.0_171] at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149) ~[na:1.8.0_171] at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624) ~[na:1.8.0_171] at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) [na:1.8.0_171]
3. WebAsyncTask
The callable method is very intuitive and simple, but the timeout + exception processing that we often pay attention to is not very good. At this time, we can use WebAsyncTask to implement the simple gesture. Just wrap the callable and set various callback events
@RestController @RequestMapping(path = "task") public class WebAysncTaskRest { @GetMapping(path = "get") public WebAsyncTask<String> get(long sleep, boolean error) { Callable<String> callable = () -> { System.out.println("do some thing"); Thread.sleep(sleep); if (error) { System.out.println("Exception, return!!!"); throw new RuntimeException("Abnormal.!!!"); } return "hello world"; }; // Specify a timeout of 3s WebAsyncTask<String> webTask = new WebAsyncTask<>(3000, callable); webTask.onCompletion(() -> System.out.println("over!!!")); webTask.onTimeout(() -> { System.out.println("Overtime"); return "Timeout returns!!!"; }); webTask.onError(() -> { System.out.println("Something's wrong!!!"); return "Abnormal return"; }); return webTask; } }
4. DeferredResult
The biggest difference between DeferredResult and WebAsyncTask is that the former is not sure when the result will be returned,
This feature of DeferredResult can be used to implement many interesting things. For example, SseEmitter will use it later
Here is an example
@RestController @RequestMapping(path = "defer") public class DeferredResultRest { private Map<String, DeferredResult> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); @GetMapping(path = "get") public DeferredResult<String> get(String id) { DeferredResult<String> res = new DeferredResult<>(); cache.put(id, res); res.onCompletion(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("over!"); } }); return res; } @GetMapping(path = "pub") public String publish(String id, String content) { DeferredResult<String> res = cache.get(id); if (res == null) { return "no consumer!"; } res.setResult(content); return "over!"; } }
In the above example, if the user accesses http://localhost:8080/defer/get?id=yihuihui first, there will be no result immediately. Until the user accesses http: / / localhost: 8080 / defer / pub? Id = yihuihui & content = ha ha, the previous request will have a result returned
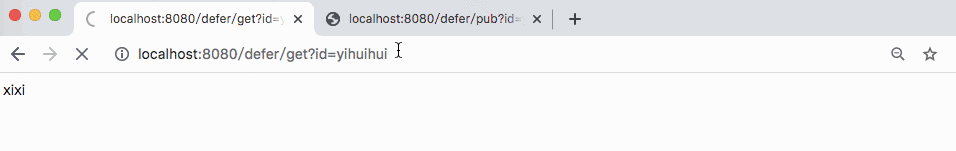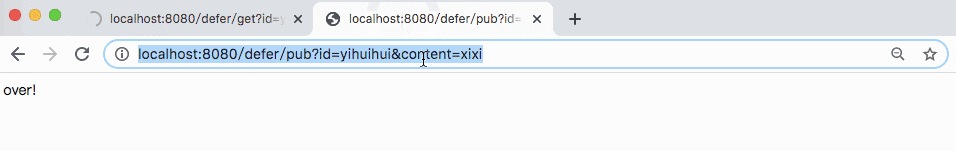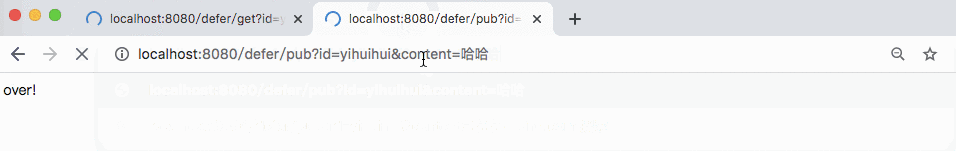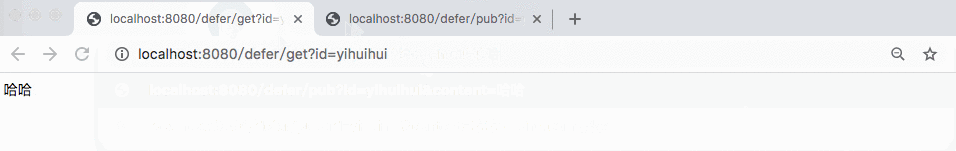
Can I set timeout for this? If I hang the front end all the time, it seems that it's not suitable
- Specify timeout in constructor: new deferredresult < > (3000l)
- Set the global default timeout
@Configuration @EnableWebMvc public class WebConf implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void configureAsyncSupport(AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer) { // Timeout set to 60s configurer.setDefaultTimeout(TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(10)); } }
II. other
0. project
Related blog
- 007 - optimize web request three - asynchronous call [WebAsyncTask]
- Key technology of high performance experience the basic use of Spring MVC asynchronous mode (Callable, WebAsyncTask, DeferredResult)
Series of blog posts
- 200105 spring boot series of web articles custom return HTTP code n postures
- 191222 spring boot series of tutorials: custom request matching conditionrequestcondition
- Four kinds of registration postures of Listener in web part of 191206 spring boot series
- Four postures of Servlet registration in 191122 spring boot series
- Open GZIP data compression in Web part of 191120 spring boot series
- 191018 spring boot series of tutorials web chapter Filter user guide extension
- 191016 spring boot series tutorials Filter guide in web
- HandlerExceptionResolver for custom exception handling in the web part of the 191012 spring boot series
- Global exception handling in the web part of the 191010 spring boot series
- The 404 and 500 abnormal page configuration of the 190930 spring boot series
- Redirection of web part of 190929 spring boot series
- 190913 spring boot series of tutorials: return text, web page, picture operation posture
- 190905 spring boot series of tutorials: how to solve the problem of Chinese scrambling
- How to customize parameter resolver in the web part of 190831 spring boot series
- Post request parameter parsing posture summary of 190828 spring boot series web
- Get request parameter parsing posture summary of 190824 spring boot series web
- 190822 spring boot series of tutorials: building the Beetl environment in the web chapter
- Building the Thymeleaf environment in the web part of the 190820 spring boot series
- 190816 spring boot series of tutorials: Freemaker environment construction in web chapter
- Instructions for using websocket in 190421 spring boot advanced WEB
- 190327 spring resttemplate's urlencode parameter parsing exception full process analysis
- 190317 spring MVC web application construction based on java config without xml configuration
- 190316 spring MVC web application construction based on xml configuration
- The temporary upload location xxx is not valid
Source code
- Works: https://github.com/liuyueyi/spring-boot-demo
- Project source code: https://github.com/liuyueyi/spring-boot-demo/blob/master/spring-boot/219-web-asyn
1. A grey Blog
The best letter is not as good as the above. It's just a one-of-a-kind remark. Due to my limited ability, there are inevitably omissions and mistakes. If you find a bug or have better suggestions, you are welcome to criticize and correct. Thank you very much
Here is a grey personal blog, recording all the blogs in study and work. Welcome to visit
- A grey Blog personal Blog https://blog.hhui.top
- A grey blog spring special blog http://spring.hhui.top
