1. License plate recognition project installation
https://blog.csdn.net/lilai619/article/details/79695109
1.git clone's latest documents
cd /opt/deploy git clone https://github.com/sergiomsilva/alpr-unconstrained.git
2. Download the pre training model
cd alpr-unconstrained/ bash get-networks.sh
3. Delete the project's own darknet and replace it with the official own darknet
rm -rf darknet git clone https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet
4. Change the official darknet support gpu and make because my cudn driver is installed in the default location, I only need to change three places
cd darknet/ vim Makefile //Will be the first1,2Supported for lines GPU GPU=0 CUDNN=0 //Revised to: GPU=1 CUDNN=1 //take24Line support cudnn NVCC=nvcc //Revised to: NVCC=/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc :wq
5. compilation
Make all-j6 adjust according to its own core number
6. Re enter the home directory
cd /opt/alpr-unconstrained cp -R data/* darknet/data/
7. Change the names file
vim data/ocr/ocr-net.names 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Beijing Shanghai Tianjin Chongqing Hebei Jin Dynasty Meng Liao Luck black Soviet Zhejiang Wan Fujian short name for Jiangxi province Lu Yu Hubei Xiang Guangdong GUI Joan Chuan Expensive cloud hide Shaanxi Province Gan young Ning new
8. Modify the location of corresponding training files
vim data/ocr/ocr-net.data classes=66 names=data/ocr/ocr-net.names train=data/ocr/train.txt backup=data/ocr/output
9. Create output directory
mkdir -p data/ocr/output
10. Modify the layers and training parameters of the CFG network layer
cp /opt/deploy/darknet/cfg/yolov3.cfg data/ocr/ocr-net.cfg vim data/ocr/ocr-net.cfg //Specify the cfg part according to its GPU and memory //During the training3,4Supported for lines GPU batch=64 subdivisions=4 [net] # Testing # batch=1 # subdivisions=1 # Training batch=64 subdivisions=8 ...... [convolutional] size=1 stride=1 pad=1 filters=33###75 activation=linear [yolo] mask = 6,7,8 anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326 classes=6###20 num=9 jitter=.3 ignore_thresh = .5 truth_thresh = 1 random=0###1 ...... [convolutional] size=1 stride=1 pad=1 filters=33###75 activation=linear [yolo] mask = 3,4,5 anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326 classes=6###20 num=9 jitter=.3 ignore_thresh = .5 truth_thresh = 1 random=0###1 ...... [convolutional] size=1 stride=1 pad=1 filters=33###75 activation=linear [yolo] mask = 0,1,2 anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326 classes=6###20 num=9 jitter=.3 ignore_thresh = .5 truth_thresh = 1 random=0###1 ------ filters How is the number calculated: 3 x(classes Number+5),It is related to the number distribution of clusters, which is explained in the paper; //For example, I have66Class then 3* (66+5)=213
2. Method of license plate correction
Reference: https://github.com/zeuses/hyperlpr
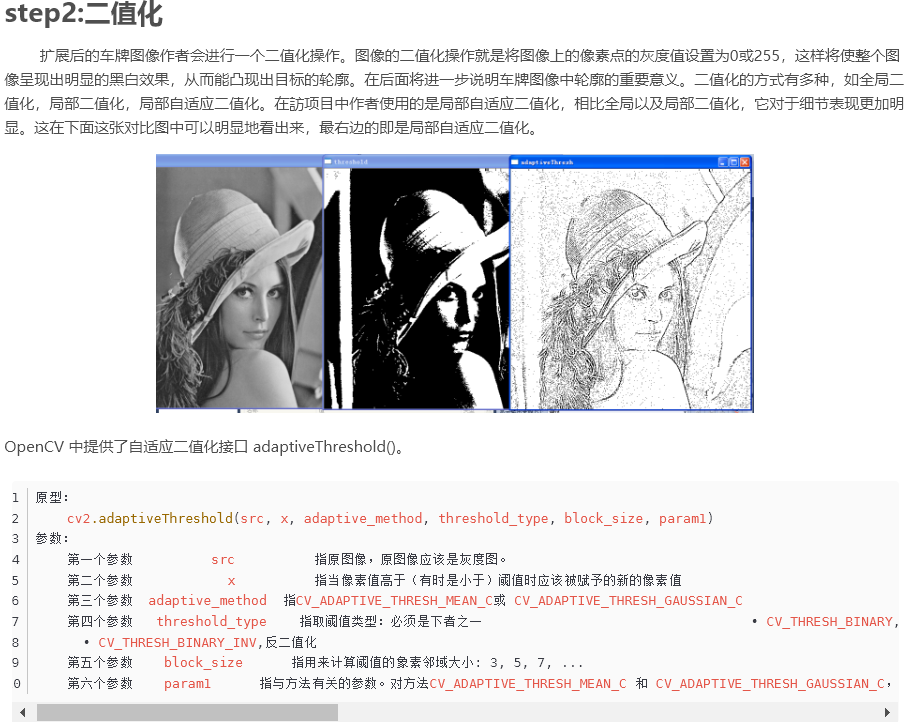


Part of the source code (I added some comments)
def findContoursAndDrawBoundingBox(image_rgb): line_upper = []; line_lower = []; line_experiment = [] grouped_rects = [] gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image_rgb,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # for k in np.linspace(-1.5, -0.2,10): for k in np.linspace(-50, 0, 15): # thresh_niblack = threshold_niblack(gray_image, window_size=21, k=k) # binary_niblack = gray_image > thresh_niblack # binary_niblack = binary_niblack.astype(np.uint8) * 255 # When different parts of an image have different brightness, we need to adopt adaptive threshold, which is calculated according to each small area of the image # Therefore, different thresholds are used in different areas of the same image, so that we can get better results under different brightness """ Args: - src, Original image,It should be grayscale - x, When the pixel value is higher than(Sometimes below)Threshold should be given a new pixel value, 255 It's white. - adaptive_method, CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C or CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C - threshold_type: Index threshold type . CV_THRESH_BINARY, Binary thresholding . CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV, Anti binary thresholding - block_size: Pixel neighborhood size used to calculate threshold(Block size):3,5,7,... - param1: Parameter related to method.Method for CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C and CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,It is a constant extracted from mean or weighted mean,Although it can be negative. . Method for CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,Find the average value in the block first, and then subtract it param1. . Method for CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C ,First find the weighted sum in the block(gaussian), Lose again param1. """ binary_niblack = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray_image,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY,17,k) #Is neighborhood size 17 too big?? #cv2.imshow("image1",binary_niblack) #cv2.waitKey(0) #imagex, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary_niblack.copy(),cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary_niblack.copy(),cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # modified by bigz for contour in contours: #Using the smallest rectangle, wrap the shapes you find bdbox = cv2.boundingRect(contour) if (bdbox[3]/float(bdbox[2])>0.7 and bdbox[3]*bdbox[2]>100 and bdbox[3]*bdbox[2]<1200) or (bdbox[3]/float(bdbox[2])>3 and bdbox[3]*bdbox[2]<100): # cv2.rectangle(rgb,(bdbox[0],bdbox[1]),(bdbox[0]+bdbox[2],bdbox[1]+bdbox[3]),(255,0,0),1) line_upper.append([bdbox[0],bdbox[1]]) line_lower.append([bdbox[0]+bdbox[2],bdbox[1]+bdbox[3]]) line_experiment.append([bdbox[0],bdbox[1]]) line_experiment.append([bdbox[0]+bdbox[2],bdbox[1]+bdbox[3]]) # grouped_rects.append(bdbox) """ //If you want to create an edge around an image, you can use an access function, which is often used in convolution or zero filling Args: - src: input image - top,bottom,left,right Number of pixels corresponding to the boundary - borderType: What type of boundary do you want to add - BORDER_CONSTANT #Fixed pixel value is used for edge filling, for example, 0 is used for black edge filling, and 255 is used for white edge filling - BORDER_REPLICATE #Fill with the pixels of the corresponding edge of the original image, which seems to have the effect of "pasting" the edge of the image """ rgb = cv2.copyMakeBorder(image_rgb,30,30,0,0,cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE) leftyA, rightyA = fitLine_ransac(np.array(line_lower),3) rows,cols = rgb.shape[:2] # rgb = cv2.line(rgb, (cols - 1, rightyA), (0, leftyA), (0, 0, 255), 1,cv2.LINE_AA) leftyB, rightyB = fitLine_ransac(np.array(line_upper),-3) rows,cols = rgb.shape[:2] # rgb = cv2.line(rgb, (cols - 1, rightyB), (0, leftyB), (0,255, 0), 1,cv2.LINE_AA) pts_map1 = np.float32([[cols - 1, rightyA], [0, leftyA],[cols - 1, rightyB], [0, leftyB]]) pts_map2 = np.float32([[136,36],[0,36],[136,0],[0,0]]) mat = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts_map1,pts_map2) image = cv2.warpPerspective(rgb,mat,(136,36),flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC) #Correction angle #cv2.imshow("before correction", image) #cv2.waitKey(0) image,M = deskew.fastDeskew(image) #cv2.imshow("after correction", image) #cv2.waitKey(0) return image

