
Technological process:
Application of single chain table
1. Establishment of single chain table:
Using one-way linked list with head to realize - ranking management of heroes of the marsh
Complete the addition, deletion, modification and query of heroes, note: delete, modify and search
The first method is to add heroes directly to the end of the list
The second way is to insert the hero into the specified position according to the ranking when adding the hero (if there is such ranking, the addition fails and a prompt will be given)
1.1 the first method: when adding heroes, directly add them to the end of the list
Add (create)
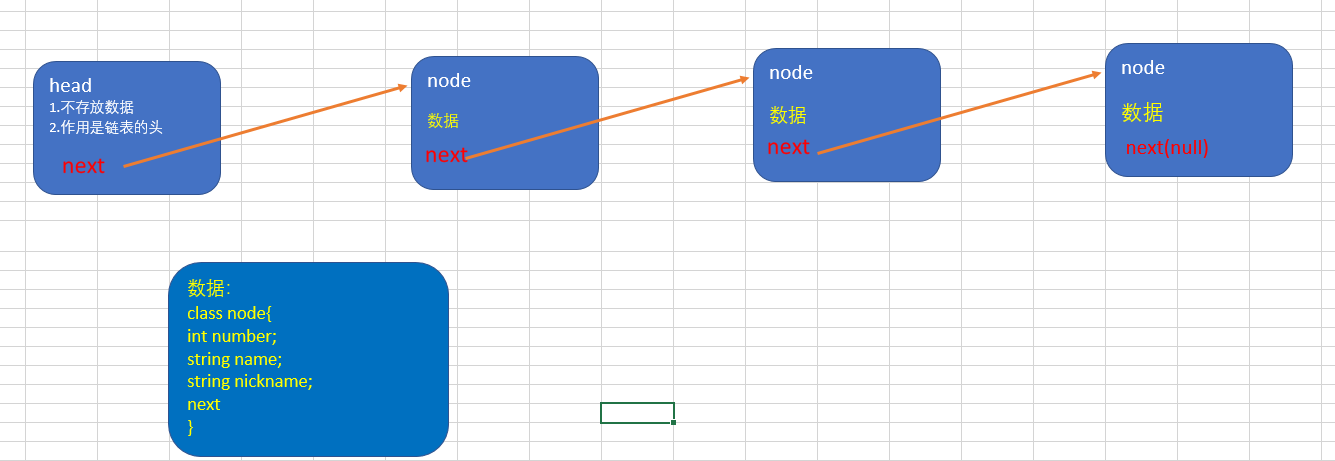
1. Create a head node to represent the head of a single chain table
2. After that, every node we add will be directly added to the end of the list
Traversal:
1. Help traverse the entire linked list by traversing an auxiliary variable
- First define data node information
public class Node { private int num; private String name; private String nickname; private Node next; public Node(int num, String name, String nickname) { this.num = num; this.name = name; this.nickname = nickname; } public Node getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node next) { this.next = next; } @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "num=" + num + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' + '}'; } }
- Define linked list rules
public class SingeLinkedList { //First, create a head node to represent the head of a single chain table private Node firstNode = new Node(0, "", ""); //After that, we add each node directly to the end of the list //Thinking when the sequence of numbers is not considered //1. Find the last node of the current linked list //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node public void add(Node node) { //1. Find the last node, and start from the beginning every time you query the element Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { temp = temp.getNext(); } } //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node temp.setNext(node); } //Through an auxiliary variable traversal, help traverse the entire linked list public void list() { //First, judge whether the linked list is empty if (firstNode.getNext() == null) { System.out.println("Linked list is empty."); } else { //Since the head node cannot move, a secondary variable is required Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { //Judge whether the linked list reaches the end if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { //Output node information System.out.println(temp.getNext()); //Move temp back temp = temp.getNext(); } } } } }
- test
public class DemoNode { public static void main(String[] args) { Node one = new Node(1,"Song Jiang","Timely rain"); Node two = new Node(2,"Lu Jun Yi", "Jade Kirin"); Node three = new Node(3,"Wu Yong","Mastermind"); Node four = new Node(4,"Gong Sun Sheng","Yun Long Yun"); Node five = new Node(5,"Guan Sheng","Broadsword"); SingeLinkedList singeLinkedList = new SingeLinkedList(); singeLinkedList.add(four); singeLinkedList.add(five); singeLinkedList.add(one); singeLinkedList.add(three); singeLinkedList.add(two); singeLinkedList.list(); } }

1.2 the second method: when adding heroes, rank them according to their rank
Own method:
1. Create a list to hold all information of the linked list
2. Use collections.sort to sort, use lambda expression to override Comparator comparator, and sort ascending based on num
3.stream stream forEach traverses array
import java.util.*; public class SingeLinkedList02 { //First, create a head node to represent the head of a single chain table private Node firstNode = new Node(0, "", ""); //After that, we add each node directly to the end of the list //Thinking when the sequence of numbers is not considered //1. Find the last node of the current linked list //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node public void add(Node node) { //1. Find the last node, and start from the beginning every time you query the element Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { temp = temp.getNext(); } } //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node temp.setNext(node); } //Through an auxiliary variable traversal, help traverse the entire linked list public void list() { //Create a list to hold all the information in the list List<Node> array = new ArrayList<>(); Map<Integer,Node> map = new HashMap<>(); //First, judge whether the linked list is empty if (firstNode.getNext() == null) { System.out.println("Linked list is empty."); } else { //Since the head node cannot move, a secondary variable is required Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { //Judge whether the linked list reaches the end if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { array.add(temp.getNext()); temp=temp.getNext(); } } //Sort by collections.sort, override Comparator comparator by lambda expression, sort ascending by num Collections.sort(array,(Node t,Node t1)->{return t.getNum()-t1.getNum();}); //Stream stream forEach traverses array array.stream().forEach(i-> System.out.println(i)); } } }
public class DemoNode { public static void main(String[] args) { Node one = new Node(1, "Song Jiang", "Timely rain"); Node two = new Node(2, "Lu Jun Yi", "Jade Kirin"); Node three = new Node(3, "Wu Yong", "Mastermind"); Node four = new Node(4, "Gong Sun Sheng", "Yun Long Yun"); Node five = new Node(5, "Guan Sheng", "Broadsword"); /* SingeLinkedList singeLinkedList = new SingeLinkedList(); singeLinkedList.add(four); singeLinkedList.add(five); singeLinkedList.add(one); singeLinkedList.add(three); singeLinkedList.add(two); singeLinkedList.list();*/ SingeLinkedList02 singeLinkedList02 = new SingeLinkedList02(); singeLinkedList02.add(five); singeLinkedList02.add(one); singeLinkedList02.add(three); singeLinkedList02.add(two); singeLinkedList02.add(four); singeLinkedList02.list(); } }
Tutorial method:
1. First, find the location of the newly added node through the auxiliary variable temp (pointer), through traversal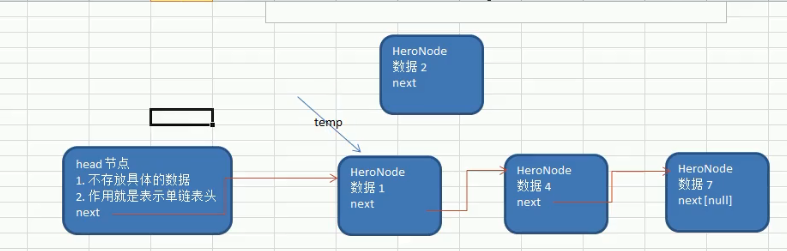
2. New node. next = temp.next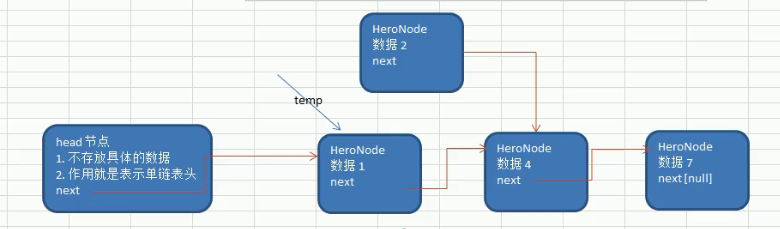
3. Set temp.next = new node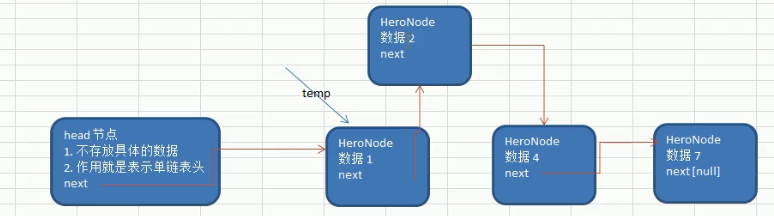

public class SingeLinkedList { //First, create a head node to represent the head of a single chain table private Node firstNode = new Node(0, "", ""); //After that, we add each node directly to the end of the list //Thinking when the sequence of numbers is not considered //1. Find the last node of the current linked list //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node public void add(Node node) { //1. Find the last node, and start from the beginning every time you query the element Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { temp = temp.getNext(); } } //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node temp.setNext(node); } //Add order of consideration numbers //If the same order exists, the addition fails and shows that it already exists public void addByOrder(Node node) { Node temp = firstNode; boolean flag = false;//Identifies whether the serial number of the inserted node already exists //Use the loop to find the previous node of the node while (true) { if (temp.getNext()==null){ break;//If the next node of the first node is empty, the first node is the previous node of the node. Find the previous node of the node }else if (temp.getNext().getNum()>node.getNum()){//If the next node number of temp is greater than the node number, the node should be inserted between the next node of temp and temp break;//Find the previous node of the node }else if (temp.getNext().getNum()==node.getNum()){//If the number of the next node of temp is equal to the number of node, the node is duplicate flag=true; break; } temp=temp.getNext();//loop } //node should be inserted into the linked list //If the same order exists, the addition fails and shows that it already exists if (flag==true){ System.out.println("Number is"+node.getNum()+"The node for already exists"); }else { node.setNext(temp.getNext());//Insert the node node before the next node after temp temp.setNext(node);//After inserting the node into the temp node } } //Through an auxiliary variable traversal, help traverse the entire linked list public void list() { //First, judge whether the linked list is empty if (firstNode.getNext() == null) { System.out.println("Linked list is empty."); } else { //Since the head node cannot move, a secondary variable is required Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { //Judge whether the linked list reaches the end if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { //Output node information System.out.println(temp.getNext()); //Move temp back temp = temp.getNext(); } } } } }
public class DemoNode { public static void main(String[] args) { Node one = new Node(1, "Song Jiang", "Timely rain"); Node two = new Node(2, "Lu Jun Yi", "Jade Kirin"); Node three = new Node(3, "Wu Yong", "Mastermind"); Node four = new Node(4, "Gong Sun Sheng", "Yun Long Yun"); Node five = new Node(5, "Guan Sheng", "Broadsword"); SingeLinkedList singeLinkedList = new SingeLinkedList(); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(four); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(five); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(one); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(three); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(two); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(two); singeLinkedList.list(); /* SingeLinkedList02 singeLinkedList02 = new SingeLinkedList02(); singeLinkedList02.add(five); singeLinkedList02.add(one); singeLinkedList02.add(three); singeLinkedList02.add(two); singeLinkedList02.add(four); singeLinkedList02.list();*/ } }
2. Modification of node information
Modify the information in the node according to the node number
public class SingeLinkedList { //First, create a head node to represent the head of a single chain table private Node firstNode = new Node(0, "", ""); /*Add node method 1: add a node directly to the end of the list*/ //After that, we add each node directly to the end of the list //Thinking when the sequence of numbers is not considered //1. Find the last node of the current linked list //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node public void add(Node node) { //1. Find the last node, and start from the beginning every time you query the element Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { temp = temp.getNext(); } } //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node temp.setNext(node); } /*Method 2 of adding nodes in linked list: for each node added, the order of number shall be considered*/ //Add order of consideration numbers //If the same order exists, the addition fails and shows that it already exists public void addByOrder(Node node) { Node temp = firstNode; boolean flag = false;//Identifies whether the serial number of the inserted node already exists //Use the loop to find the previous node of the node while (true) { if (temp.getNext()==null){ break;//If the next node of the first node is empty, the first node is the previous node of the node. Find the previous node of the node }else if (temp.getNext().getNum()>node.getNum()){//If the next node number of temp is greater than the node number, the node should be inserted between the next node of temp and temp break;//Find the previous node of the node }else if (temp.getNext().getNum()==node.getNum()){//If the number of the next node of temp is equal to the number of node, the node is duplicate flag=true; break; } temp=temp.getNext();//loop } //node should be inserted into the linked list //If the same order exists, the addition fails and shows that it already exists if (flag==true){ System.out.println("Number is"+node.getNum()+"The node for already exists"); }else { node.setNext(temp.getNext());//Insert the node node before the next node after temp temp.setNext(node);//After inserting the node into the temp node } } /*Traverse the entire list*/ //Through an auxiliary variable traversal, help traverse the entire linked list public void list() { //First, judge whether the linked list is empty if (firstNode.getNext() == null) { System.out.println("Linked list is empty."); } else { //Since the head node cannot move, a secondary variable is required Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { //Judge whether the linked list reaches the end if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { //Output node information System.out.println(temp.getNext()); //Move temp back temp = temp.getNext(); } } } } /*Modify node information*/ public void updata(Node node){ if (firstNode.getNext()==null){//If the next node of the header node is null, the list is empty System.out.println("Linked list is empty."); }else{ Node temp = firstNode;//If it is not empty, start to traverse the list and find num while (true){ if (temp.getNum()==node.getNum()){//Find number, modify data temp.setName(node.getName()); temp.setNickname(node.getNickname()); break; }else if (temp.getNext()==null){//No number found, print information System.out.println("No number exists"+node.getNum()+"Node"); break; }else {//temp pointer loop temp=temp.getNext(); } } } } }
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Node one = new Node(1, "Song Jiang", "Timely rain"); Node two = new Node(2, "Lu Jun Yi", "Jade Kirin"); Node three = new Node(3, "Wu Yong", "Mastermind"); Node four = new Node(4, "Gong Sun Sheng", "Yun Long Yun"); Node five = new Node(5, "Guan Sheng", "Broadsword"); SingeLinkedList singeLinkedList = new SingeLinkedList(); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(four); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(five); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(one); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(three); singeLinkedList.addByOrder(two); singeLinkedList.list(); Node newNode = new Node(2,"change name","change nickname"); singeLinkedList.updata(newNode); System.out.println("Update as follows:"); singeLinkedList.list(); Node newNode2 = new Node(12,"change name","change nickname"); singeLinkedList.updata(newNode2); System.out.println("Update as follows:"); singeLinkedList.list(); } }

3. Delete node

public class SingeLinkedList { //First, create a head node to represent the head of a single chain table private Node firstNode = new Node(0, "", ""); /*Add node method 1: add a node directly to the end of the list*/ //After that, we add each node directly to the end of the list //Thinking when the sequence of numbers is not considered //1. Find the last node of the current linked list //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node public void add(Node node) { //1. Find the last node, and start from the beginning every time you query the element Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { temp = temp.getNext(); } } //2. Point the next of the last node to the new node temp.setNext(node); } /*Method 2 of adding nodes in linked list: for each node added, the order of number shall be considered*/ //Add order of consideration numbers //If the same order exists, the addition fails and shows that it already exists public void addByOrder(Node node) { Node temp = firstNode; boolean flag = false;//Identifies whether the serial number of the inserted node already exists //Use the loop to find the previous node of the node while (true) { if (temp.getNext() == null) { break;//If the next node of the first node is empty, the first node is the previous node of the node. Find the previous node of the node } else if (temp.getNext().getNum() > node.getNum()) {//If the next node number of temp is greater than the node number, the node should be inserted between the next node of temp and temp break;//Find the previous node of the node } else if (temp.getNext().getNum() == node.getNum()) {//If the number of the next node of temp is equal to the number of node, the node is duplicate flag = true; break; } temp = temp.getNext();//loop } //node should be inserted into the linked list //If the same order exists, the addition fails and shows that it already exists if (flag == true) { System.out.println("Number is" + node.getNum() + "The node for already exists"); } else { node.setNext(temp.getNext());//Insert the node node before the next node after temp temp.setNext(node);//After inserting the node into the temp node } } /*Traverse the entire list*/ //Through an auxiliary variable traversal, help traverse the entire linked list public void list() { //First, judge whether the linked list is empty if (firstNode.getNext() == null) { System.out.println("Linked list is empty."); } else { //Since the head node cannot move, a secondary variable is required Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { //Judge whether the linked list reaches the end if (temp.getNext() == null) { break; } else { //Output node information System.out.println(temp.getNext()); //Move temp back temp = temp.getNext(); } } } } /*Modify node information*/ public void updata(Node node) { if (firstNode.getNext() == null) {//If the next node of the header node is null, the list is empty System.out.println("Linked list is empty."); } else { Node temp = firstNode;//If it is not empty, start to traverse the list and find num while (true) { if (temp.getNum() == node.getNum()) {//Find number, modify data temp.setName(node.getName()); temp.setNickname(node.getNickname()); break; } else if (temp.getNext() == null) {//No number found, print information System.out.println("No number exists" + node.getNum() + "Node"); break; } else {//temp pointer loop temp = temp.getNext(); } } } } /*Delete node according to node number*/ public void deletNode(int n) { if (firstNode.getNext() == null) { System.out.println("Linked list is empty."); } else { Node temp = firstNode; while (true) { if (temp.getNext().getNum() == n) {//If the next node num of temp is n, find the node to delete temp.setNext(temp.getNext().getNext());//Link the next node of temp to the next node break; } else if (temp.getNext() == null) { System.out.println("Not in the list" + n + "node"); break; } else { temp = temp.getNext(); } } } } }

