Recently, the epidemic broke out. I didn't have a look at the idle fish IOSApp at home. I found that the function of auto hiding the navigation bar of the commodity list was very good, so I decided to write one myself.
Leisure fish:
Train of thought:
The navigation will follow the upward movement of the table view below to hide. It will reappear according to the pull-up. That is to get the offset contentOffset through the delegate of tableView, and judge the pull-up and pull-down actions at the same time.
Own effect: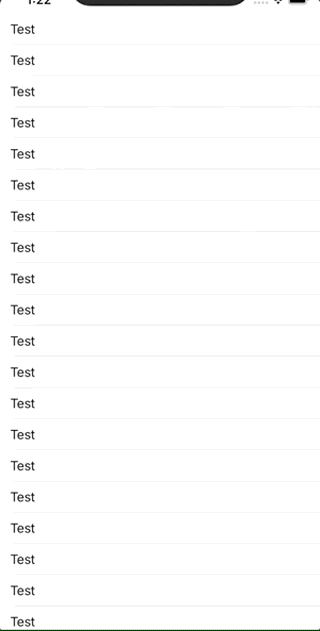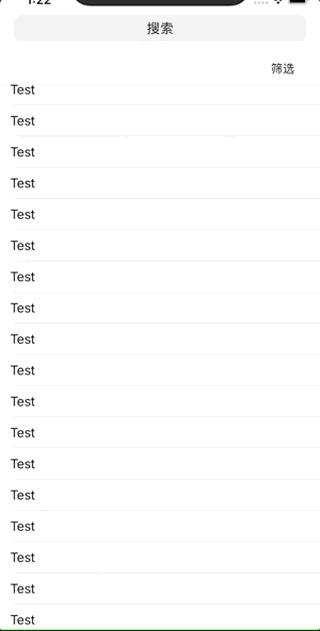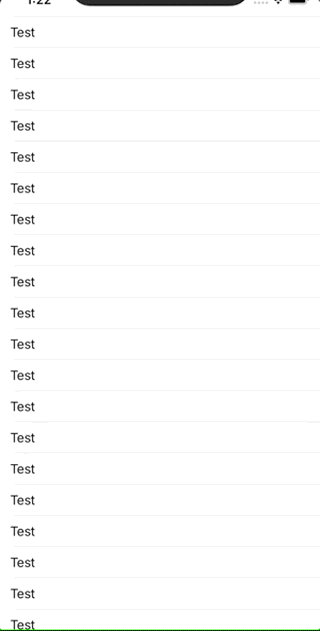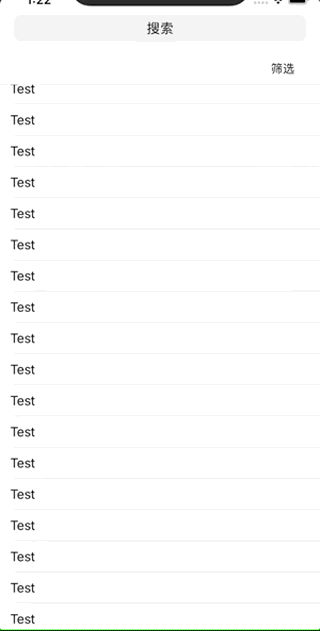
step
Initialize project:
Create a new project. I'm pure code. So don't use the storyBoard. SnapKit is used.
If the iPad is not suitable, please uncheck the iPad in project generic, and then comment out all the related scenes. There are two parts, one is in AppDelegate, the other is in SceneDelegate. SceneDelegate can be deleted or commented out in full code.
Initialization configuration of IOS 13 and above:
- Uncheck iPad in project Genral
- The code with Mark as the part of SceneSession is commented out in AppDelegate
- Comment out all the codes in SceneDelegate, or delete them
- Delete Application Scene Manifest in info.plist
- Add some initialization codes to AppDelegate, as follows:
var window: UIWindow? func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool { // Override point for customization after application launch. window = UIWindow(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds) window?.backgroundColor = UIColor.white let navVc = UINavigationController() navVc.viewControllers = [ViewController()] window?.rootViewController = navVc window?.makeKeyAndVisible() return true }
Run the simulator, the normal white background plus a navigation bar is initialized.
To customize a navBar:
It's relatively simple. I put the code directly and replace the original navBar.
class CustomNavBar:UINavigationBar{ //Save reference of BarContentView private var rootBackView:UIView? //Specific content private var contentView:UIView? private var isInit = false private let contentViewHeight:CGFloat = 90 override func layoutSubviews() { super.layoutSubviews() for subview in self.subviews { let stringFromClass = NSStringFromClass(subview.classForCoder) if stringFromClass.contains("BarBackground") { subview.frame = self.bounds } else if stringFromClass.contains("UINavigationBarContentView") { subview.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: self.frame.width, height: contentViewHeight + statusBarHeight) subview.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in make.edges.equalToSuperview() } subview.backgroundColor = UIColor.white if rootBackView == nil{ rootBackView = subview } } } if !isInit{ initSelf() } } //Hide your way public func toggleVisible(_ value:Bool){ if value{ UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.2, animations: { self.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: self.frame.width, height:self.contentViewHeight + statusBarHeight) self.layoutIfNeeded() }) } else{ UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.2, animations: { self.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: self.frame.width, height: statusBarHeight) self.layoutIfNeeded() }) } } private func initSelf(){ isInit = true contentView = UIView() self.rootBackView?.addSubview(contentView!) contentView?.snp.makeConstraints({ (make) in make.height.equalTo(contentViewHeight) make.left.right.equalToSuperview() make.bottom.equalToSuperview() }) let titleLabel:UILabel = UILabel() self.contentView?.addSubview(titleLabel) titleLabel.text = "search" titleLabel.textColor = UIColor.black titleLabel.backgroundColor = UIColor(red: 240/255, green: 240/255, blue: 240/255, alpha: 1) titleLabel.layer.cornerRadius = 10 titleLabel.clipsToBounds = true titleLabel.textAlignment = .center titleLabel.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in make.top.equalToSuperview() make.left.equalTo(20) make.right.equalTo(-20) make.height.equalTo(35) } let flit_btn = UIButton() self.contentView?.addSubview(flit_btn) flit_btn.setTitle("screen", for: .normal) flit_btn.setTitleColor(UIColor.black, for: .normal) flit_btn.titleLabel?.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 15) //flit_btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.lightGray flit_btn.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in make.bottom.equalToSuperview().offset(-1) make.right.equalToSuperview() make.width.equalTo(100) make.height.equalTo(40) } //The dividing line of navBar let darkLine = UIView() self.contentView?.addSubview(darkLine) darkLine.backgroundColor = UIColor(red: 235/255, green: 235/255, blue: 235/255, alpha: 1) darkLine.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in make.bottom.equalToSuperview() make.left.right.equalToSuperview() make.height.equalTo(1) } //Used to block the content entering the statusBar let maskView = UIView() self.rootBackView?.addSubview(maskView) maskView.backgroundColor = rootBackView?.backgroundColor maskView.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in make.left.top.right.equalToSuperview() make.height.equalTo(statusBarHeight) } } }
Add the navBar and a UITableView to the ViewController:
The custom cell code is not given here. It's too simple. It's a nib
class ViewController: UIViewController ,UITableViewDelegate,UITableViewDataSource{ private lazy var navBar:CustomNavBar = { let navBar = CustomNavBar() navBar.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: kScreenW, height: statusBarHeight+90) navBar.clipsToBounds = true return navBar }() private lazy var tableView:UITableView = { let view = UITableView() view.delegate = self view.dataSource = self view.showsVerticalScrollIndicator = false view.register(UINib(nibName: "CustomTableViewCell", bundle: nil), forCellReuseIdentifier: "itemCell") return view }() private var navBarItem:UINavigationItem = UINavigationItem() override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() setupUI() navigationController?.setNavigationBarHidden(true, animated: false) self.view.addSubview(navBar) navBar.items = [navBarItem] self.view.backgroundColor = UIColor(red: 235/255, green: 235/255, blue: 235/255, alpha: 1) } private func setupUI(){ self.view.addSubview(tableView) tableView.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in make.edges.equalToSuperview() } } } extension ViewController { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int { return 100 } func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGFloat { return 40 } func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell { let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "itemCell", for: indexPath) as! CustomTableViewCell cell.setText("Test") return cell } }
Now that the UI is over, go to the core:
Define several private variables
//offset when TableView was last touched private var lastContentOffset:CGFloat = 0 //Touch drag distance private var tempValue:CGFloat = 0 //Last drag direction (1) - up (- 1) - down private var lastDirection:Int = 0
Add three methods to extension:
//When scollView is sliding func scrollViewDidScroll(_ scrollView: UIScrollView) { //If you don't judge when scrollView is swiped by fingers, this method will be called several times when tableView is loaded, causing you to hide. if scrollView.isTracking{ //Down positive up negative let currentOffset = scrollView.contentOffset.y let offset = currentOffset - lastContentOffset //Amplitude of single action tempValue += offset if offset <= 0{ //Upward //Variable direction zero clearing if lastDirection != 0{ tempValue = 0 lastDirection = 0 } scroll_handler(direct: -1, range: tempValue) }else{ //down //Variable direction zero clearing if lastDirection != 1{ tempValue = 0 lastDirection = 1 } scroll_handler(direct: 1, range: tempValue) } lastContentOffset = currentOffset } } //When the finger ends dragging away from the screen func scrollViewWillEndDragging(_ scrollView: UIScrollView, withVelocity velocity: CGPoint, targetContentOffset: UnsafeMutablePointer<CGPoint>) { //If not completely hidden if self.navBar.frame.height > statusBarHeight { //If there is downward inertia if velocity.y > 0{ //Automatic hiding self.navBar.toggleVisible(false) tempValue = 0 } } } //Handle public func scroll_handler(direct:Int,range:CGFloat){ if direct < 0{ //Move up to display navBar directly self.navBar.toggleVisible(true) } else{ //Move down to adjust the height of navBar according to the range if self.navBar.frame.height > statusBarHeight { let _f = navBar.frame var height = statusBarHeight + 90 + range * -1 height = height >= statusBarHeight ? height :statusBarHeight navBar.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: _f.width, height: height) } } }
Run to see the effect.
This is my first blog post. Please indicate the source. If you think it's useful, please like it.

