Stack
Linear tables that are only allowed to insert or delete at one end.
For n different elements in the stack, the number of stack out sequences is (catteland number)
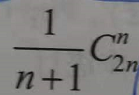
The basic operation code of the sequence stack is as follows:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MaxSize 10
//Sequential storage of stacks
typedef struct {
int data[MaxSize];
int top;
}SqStack;
//Initialization stack
void InitStack(SqStack &s){
s.top=-1;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
s.data[i]=0;
}
printf("Initialization complete\n");
}
//Sentence blank
void StackEmpty(SqStack s){
if(s.top==-1){
printf("The stack is empty.\n");
}else{
printf("Stack is not empty.\n");
}
}
//Push
bool Push(SqStack &s,int e){
if(s.top==MaxSize-1){
printf("The stack is full.\n");
return false;
}
s.data[++s.top]=e;
return true;
}
//Stack out
bool Pop(SqStack &s,int &e){
if(s.top==-1){
printf("The stack is empty.\n");
return false;
}
e=s.data[s.top--];
printf("The element at the top of the stack. The value is%d\n",e);
return true;
}
//Get stack top element
bool GetTop(SqStack &s,int &x){
if(s.top==-1){
printf("The stack is empty.\n");
return false;
}
x=s.data[s.top];
printf("The top element of the stack is:%d\n",x);
return true;
}
//Print stack
void PrintStack(SqStack s){
if(s.top==-1){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
//printf("| |\n");
printf("|_ _ _ _|\n");
}
}
if(s.top!=-1){
for(int i=0;i<MaxSize-s.top;i++){
printf("|_ _ _ _|\n");
}
while(s.top!=-1){
printf("|___%d___|\n",s.data[s.top]);
s.top--;
}
}
}
int main(){
SqStack s;
InitStack(s);
StackEmpty(s);
Push(s,1);
Push(s,2);
Push(s,3);
Push(s,4);
StackEmpty(s);
PrintStack(s);
int e,x;
Pop(s,e);
PrintStack(s);
GetTop(s,x);
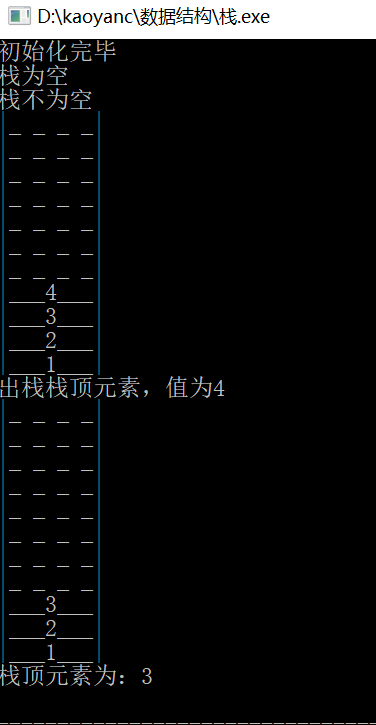
}The screenshot of code operation is as follows:
The basic operation code of chain stack is as follows:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//Chain storage of stack
typedef struct Linknode{
int data;
struct Linknode *next;
}Linknode,*LiStack;
//Initialization stack
void InitStack(LiStack &L){
L =(Linknode*)malloc(sizeof(Linknode));//Create a head node
L->next=NULL;//Initialize to empty
}
//Stack decision space
bool StackEmpty(LiStack L){
if(L->next==NULL){
printf("The stack is empty.\n");
return false;
}
else{
printf("Stack is not empty.\n");
return true;
}
}
//Push
bool Push(LiStack &L,int e){
Linknode *s=(Linknode *)malloc(sizeof(Linknode));
s->data=e;
s->next=L->next;
L->next=s;
return true;
}
//Stack out
bool Pop(LiStack &L,int &e){
if(L->next==NULL){
printf("The stack is empty.\n");
return false;
}
Linknode *p=L->next;
e=p->data;
L->next=p->next;//Chain formation
printf("The stack element value is%d\n",e);
free(p);
return true;
}
bool GetTop(LiStack L,int x){
if(L->next==NULL){
printf("The stack is empty.\n");
return false;
}
Linknode *p=L->next;
x=p->data;
printf("The element value at the top of the stack is%d\n",x);
return true;
}
void PrintStack(LiStack L){
Linknode *n=L->next;
while(n!=NULL){
printf("|___%d___|\n",n->data);
n=n->next;
}
}
int main(){
LiStack s;
InitStack(s);
StackEmpty(s);
Push(s,1);
Push(s,2);
Push(s,3);
Push(s,4);
StackEmpty(s);
PrintStack(s);
int e,x;
Pop(s,e);
PrintStack(s);
GetTop(s,x);
} The screenshot of code operation is as follows:


