Summary
In distributed systems, there are scenarios where a globally unique ID is required. In order to prevent ID conflicts, a 36-bit UUID can be used, but it has some drawbacks. First, it is relatively long, and UUIDs are generally out of order.
Sometimes we want to be able to use a simpler ID, and we want IDs to be generated in time order.
TWitter's snowflake addressed this need by initially migrating the storage system from MySQL to Cassandra, which had no sequential ID generation mechanism and developed such a set of globally unique ID generation services.
structure
The structure of the snowflake is as follows (each part is -separated):
0 - 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0 - 00000 - 00000 - 000000000000
The first is unused, the next 41 bits are in milliseconds (41 bits can last 69 years), then 5 bits of datacenterId and 5 bits of workerId(10 bits can support deployment of up to 1024 nodes), and the last 12 bits are counts in milliseconds (12 bits of counting sequence numbers support 4096 ID numbers per millisecond per node), which together add up to exactly 64 bits, to one Long type.(Maximum length 19 after conversion to string).
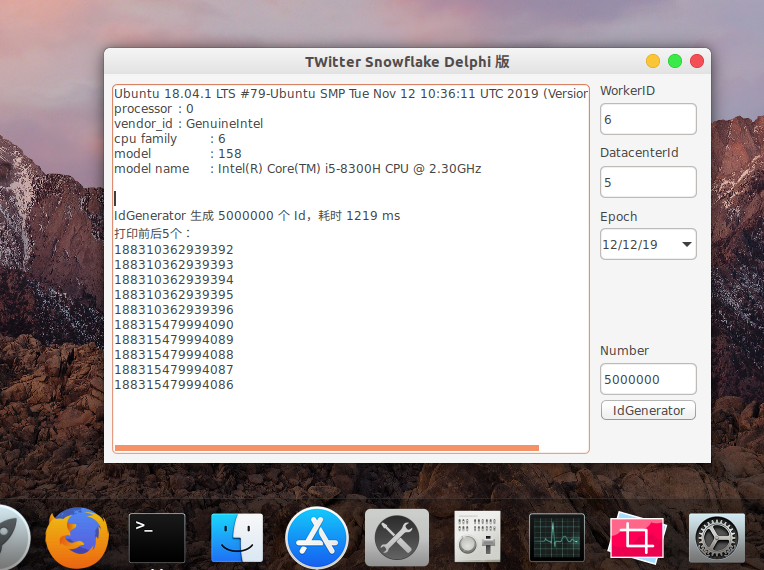
Snowflake generates IDs that are sorted by time as a whole, do not produce ID collisions (distinguished by datacenter and workerId) across the distributed system, and are efficient.Tested snowflake produces 5 million IDs per second.
Screenshot running under Ubuntu 18.04:
Source code
{ * * Twitter_Snowflake https://github.com/twitter-archive/snowflake * SnowFlake The structure is as follows(Use for each part-Separate): * 0 - 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0 - 00000 - 00000 - 000000000000 * 1 Bit ID, because long The basic types are Java The middle is signed, the highest bit is the symbol bit, the positive number is 0, the negative number is 1, so id Normally positive, the highest bit is 0 * 41 Bit time truncation(millisecond),Note that the 41-bit time truncation is not the time truncation storing the current time, but the difference storing the time truncation (the current time truncation) - Start time truncation) * The resulting value), where the start time is cut off, is usually ours id The time at which the generator starts to be used is specified by our program (as follows IdWorker Class startTime Attribute).41-bit time cutoff, available for 69 years, year T = (1L << 41) / (1000L * 60 * 60 * 24 * 365) = 69 * 10 Bit data machine bit, which can be deployed at 1024 nodes, including 5 bits datacenterId And 5 digits workerId * 12 Bit Sequence, Count in Milliseconds, 12-bit Count Sequence Number supports each node per millisecond(Same machine, same time cut)4096 generated ID Sequence Number * Add up to just 64 bits, one Long Type. * SnowFlake The advantage is that, as a whole, the order increases by time and does not occur within the entire distributed system ID collision(By Data Center ID And machines ID Make a distinction),And efficient, tested, SnowFlake 409 generated per second.6 ten thousand ID About. * * This algorithm refers to the official Twitter Snowflake Modified, but also learned from the Internet Java Language version. * Author: omnipotent middleware 64445322 https://www.centmap.cn/server * Usage method: var OrderId := IdGenerator.NextId(),IdGenerator There is no need to create or release, and the method is thread-safe. * } // Reference Meituan Point Score Layout ID generating system // https://tech.meituan.com/2017/04/21/mt-leaf.html // https://github.com/Meituan-Dianping/Leaf/blob/master/leaf-core/src/main/java/com/sankuai/inf/leaf/snowflake/SnowflakeIDGenImpl.java unit rtcMW.System.Snowflake; interface uses System.SysUtils, System.SyncObjs; type TSnowflakeIdWorker = class(TObject) private const // Maximum available 69 years MaxYears = 69; // machine id Number of digits occupied WorkerIdBits = 5; // Data Identification id Number of digits occupied DatacenterIdBits = 5; // Sequence in id Number of digits occupied in SequenceBits = 12; // machine ID 12 bits left WorkerIdShift = SequenceBits; // Data Identification id 17 bits left(12+5) DatacenterIdShift = SequenceBits + WorkerIdBits; // Time Truncation Left 22 Bits(5+5+12) TimestampLeftShift = SequenceBits + WorkerIdBits + DatacenterIdBits; {$WARNINGS OFF} // Generate sequence mask, 4095 here (0b111111111111=0xfff=4095) SequenceMask = -1 xor (-1 shl SequenceBits); // Maximum machine supported id MaxWorkerId = -1 xor (-1 shl WorkerIdBits); // Maximum supported data identity id,The result is 31 MaxDatacenterId = -1 xor (-1 shl DatacenterIdBits); {$WARNINGS ON} private type TWorkerID = 0 .. MaxWorkerId; TDatacenterId = 0 .. MaxDatacenterId; strict private FWorkerID: TWorkerID; FDatacenterId: TDatacenterId; FEpoch: Int64; FSequence: Int64; FLastTimeStamp: Int64; FStartTimeStamp: Int64; FUnixTimestamp: Int64; FIsHighResolution: Boolean; /// <summary> /// Block until next millisecond until new timestamp is obtained /// </summary> /// <param name="ATimestamp ">Last Generation ID Time Cut</param> /// <returns>Current timestamp </returns> function WaitUntilNextTime(ATimestamp: Int64): Int64; /// <summary> /// Returns the current time in milliseconds /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// Time is expressed in milliseconds as the difference between the current computer time and 10:0 minutes and 0 seconds on January 1, 1970 /// </remarks> function CurrentMilliseconds: Int64; inline; function CurrentTimeStamp: Int64; inline; function ElapsedMilliseconds: Int64; inline; private class var FLock: TSpinLock; class var FInstance: TSnowflakeIdWorker; class function GetInstance: TSnowflakeIdWorker; static; class constructor Create; class destructor Destroy; protected function GetEpoch: TDateTime; procedure SetEpoch(const Value: TDateTime); public constructor Create; overload; /// <summary> /// Get Next ID (This method is thread safe) /// </summary> function NextId: Int64;inline; /// <summary> /// Work Machine ID(0~31) /// </summary> property WorkerID: TWorkerID read FWorkerID write FWorkerID; /// <summary> /// Data Center ID(0~31) /// </summary> property DatacenterId: TDatacenterId read FDatacenterId write FDatacenterId; /// <summary> /// start time /// </summary> property Epoch: TDateTime read GetEpoch write SetEpoch; class property Instance: TSnowflakeIdWorker read GetInstance; end; function IdGenerator: TSnowflakeIdWorker; const ERROR_CLOCK_MOVED_BACKWARDS = 'Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds'; ERROR_EPOCH_INVALID = 'Epoch can not be greater than current'; implementation uses System.Math, System.TimeSpan {$IF defined(MSWINDOWS)} , Winapi.Windows {$ELSEIF defined(MACOS)} , Macapi.Mach {$ELSEIF defined(POSIX)} , Posix.Time {$ENDIF} , System.DateUtils; function IdGenerator: TSnowflakeIdWorker; begin Result := TSnowflakeIdWorker.GetInstance; end; { TSnowflakeIdWorker } constructor TSnowflakeIdWorker.Create; {$IF defined(MSWINDOWS)} var Frequency: Int64; {$ENDIF} begin inherited; {$IF defined(MSWINDOWS)} FIsHighResolution := QueryPerformanceFrequency(Frequency); {$ELSEIF defined(POSIX)} FIsHighResolution := True; {$ENDIF} FSequence := 0; FWorkerID := 1; FDatacenterId := 1; FLastTimeStamp := -1; FEpoch := DateTimeToUnix(EncodeDate(2019, 12, 12), True) * MSecsPerSec; FUnixTimestamp := DateTimeToUnix(Now, True) * MSecsPerSec; FStartTimeStamp := CurrentTimeStamp; end; class destructor TSnowflakeIdWorker.Destroy; begin FreeAndNil(FInstance); end; class constructor TSnowflakeIdWorker.Create; begin FInstance := nil; FLock := TSpinLock.Create(False); end; class function TSnowflakeIdWorker.GetInstance: TSnowflakeIdWorker; begin FLock.Enter; try if FInstance = nil then FInstance := TSnowflakeIdWorker.Create; Result := FInstance; finally FLock.Exit; end; end; function TSnowflakeIdWorker.CurrentTimeStamp: Int64; {$IF defined(POSIX) and not defined(MACOS)} var res: timespec; {$ENDIF} begin {$IF defined(MSWINDOWS)} if FIsHighResolution then QueryPerformanceCounter(Result) else Result := GetTickCount * Int64(TTimeSpan.TicksPerMillisecond); {$ELSEIF defined(MACOS)} Result := Int64(AbsoluteToNanoseconds(mach_absolute_time) div 100); {$ELSEIF defined(POSIX)} clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, @res); Result := (Int64(1000000000) * res.tv_sec + res.tv_nsec) div 100; {$ENDIF} end; function TSnowflakeIdWorker.ElapsedMilliseconds: Int64; begin Result := (CurrentTimeStamp - FStartTimeStamp) div TTimeSpan.TicksPerMillisecond; end; function TSnowflakeIdWorker.GetEpoch: TDateTime; begin Result := UnixToDateTime(FEpoch div MSecsPerSec, True); end; function TSnowflakeIdWorker.NextId: Int64; var Offset: Integer; Timestamp: Int64; begin FLock.Enter; try Timestamp := CurrentMilliseconds(); // If the current time is less than the last time ID Generated timestamp indicating that an exception should be thrown when the system clock falls back if (Timestamp < FLastTimeStamp) then begin Offset := FLastTimeStamp - Timestamp; if Offset <= 5 then begin // Time deviation less than 5 ms,Wait twice as long System.SysUtils.Sleep(Offset shr 1); Timestamp := CurrentMilliseconds(); // Or less than, throw an exception and report if Timestamp < FLastTimeStamp then raise Exception.CreateFmt(ERROR_CLOCK_MOVED_BACKWARDS, [FLastTimeStamp - Timestamp]); end; end; // If generated at the same time, the sequence is in milliseconds if (FLastTimeStamp = Timestamp) then begin FSequence := (FSequence + 1) and SequenceMask; // Sequence overflow in milliseconds if (FSequence = 0) then // Block to next millisecond,Get a new timestamp Timestamp := WaitUntilNextTime(FLastTimeStamp); end // Timestamp change, sequence reset in milliseconds else FSequence := 0; // Last Generation ID Time Cut FLastTimeStamp := Timestamp; // Shifted and combined by or operations to form a 64-bit ID Result := ((Timestamp - FEpoch) shl TimestampLeftShift) or (DatacenterId shl DatacenterIdShift) or (WorkerID shl WorkerIdShift) or FSequence; finally FLock.Exit; end; end; function TSnowflakeIdWorker.WaitUntilNextTime(ATimestamp: Int64): Int64; var Timestamp: Int64; begin Timestamp := CurrentMilliseconds(); while Timestamp <= ATimestamp do Timestamp := CurrentMilliseconds(); Result := Timestamp; end; procedure TSnowflakeIdWorker.SetEpoch(const Value: TDateTime); begin if Value > Now then raise Exception.Create(ERROR_EPOCH_INVALID); if YearsBetween(Now, Value) <= MaxYears then FEpoch := DateTimeToUnix(Value, True) * MSecsPerSec; end; function TSnowflakeIdWorker.CurrentMilliseconds: Int64; begin Result := FUnixTimestamp + ElapsedMilliseconds; end; end.