Project requirements
Project 10 uses port1,port2,port3,port4,prot5, and set port1, set port2, set port3, set port4, set port5 to manage five ports. The code is bloated and repetitive, which is not easy to maintain.
Solution:
Use an array of structs.
Project realization
Modification:
//Five port variables are defined
//struct port port1;
//struct port port2;
//struct port port3;
//struct port port4;
//struct port port5;
void show_port(struct port port) {
printf("Name[%s]\t state[%s]\tIP[%-15s]\t type[%s]\n",
port.name,
port.status == 0 ? "Prohibit":"activation",
port.ip,
port.type);
}
void show_ports(struct port ports[]) {
system("cls");
printf("---port status---\n");
/*
printf("PORT1:\t");
show_port(port1);
printf("PORT2:\t");
show_port(port2);
printf("PORT3:\t");
show_port(port3);
printf("PORT4:\t");
show_port(port4);
*/
int n;
for (n=0; n<5; n++) {
printf("PORT%d:\t", n+1);
show_port(ports[n]); //Passing the value of the port structure
}
system("pause");
}
void set_port1(void) {
void set_port(struct port ports[], int num) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT1 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", ports[num].name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &ports[num].status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", ports[num].type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", ports[num].ip);
system("pause");
}
void set_port2(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT2 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port2.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port2.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port2.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port2.ip);
}
void set_port3(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT3 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port3.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port3.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port3.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port3.ip);
}
void set_port4(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT4 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port4.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port4.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port4.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port4.ip);
}
void set_port5(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT5 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port5.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port5.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port5.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port5.ip);
}
void set_ports(struct port ports[]) {
char n;
while(1) {
system("cls");
printf("---port settings---\n");
printf("1. PORT1\n");
printf("2. PORT2\n");
printf("3. PORT3\n");
printf("4. PORT4\n");
printf("5. PORT5\n");
printf("6. Return\n");
printf("Please choose: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
switch (n) {
case '1':
set_port1();
break;
case '2':
set_port2();
break;
case '3':
set_port3();
break;
case '4':
set_port4();
break;
case '5':
set_port5();
break;
case '6':
return;
default:
input_error();
break;
}
if (n >= '1' && n <= '5') {
int num = n - '1';
set_port(ports, num);
} else if (n == '6') {
return;
} else {
input_error();
}
}
}
void port_admin(struct port ports[]) {
char n;
while(1) {
system("cls");
printf("1. View port\n");
printf("2. Set port\n");
printf("3. Back to main menu\n");
printf("Please choose: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
if (n == '1') {
show_ports(ports);
} else if (n == '2') {
set_ports(ports);
} else if (n == '3') {
break;
} else {
input_error();
}
}
}
int main(void) {
char n; //User selected menu number
struct port ports[5];
init(); //Initialization
login(); //Sign in
while (1) {
show_memu();
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
switch (n) {
case '1':
create_user();
break;
case '2':
ip_admin();
break;
case '3':
logout();
break;
case '4':
port_admin(ports);
break;
default:
input_error();
break;
}
}
return 0;
}Complete code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
FILE *file;
struct port {
char name[16];
int status; //1: Activate 0: Disable
char ip[16];
char type[4]; //Port type LAN WAN
};
//Five port variables are defined
//struct port port1;
//struct port port2;
//struct port port3;
//struct port port4;
//struct port port5;
void init(void) {
//Open file
file = fopen("users.txt", "r");
if (!file) { //Equivalent to file == NULL
printf("File open failed");
//return 1;
exit(1);
}
}
void login(void) {
char name[32];
char password[16];
char line[128];
char name_tmp[32];
char password_tmp[16];
char *ret;
//Enter user name and password
while (1) {
system("cls");
// Enter user name and password
printf("Please enter the user name:");
scanf("%s", name);
printf("Please input a password:");
scanf("%s", password);
//Read the account from the file and judge!
while (1) {
//Read a row
ret = fgets(line, sizeof(line), file); //line: "admin 123456\n"
if (!ret) {
break;
}
sscanf(line, "%s %s", name_tmp, password_tmp);
if (!strcmp(name, name_tmp) && !strcmp(password, password_tmp)) {
break;
}
}
if (ret) { //User name and password match successfully
break;
} else {
printf("Wrong user name or password!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_SET); //Set the location pointer inside the file to the file header
}
}
}
void create_user(void) {
system("cls");
printf("\n\n---Create account---\n\n");
printf("To be realized...\n\n");
printf("\n\n Press any key to return to the main menu");
fflush(stdin);
getchar();
}
void ip_admin(void) {
system("cls");
printf("\n\n---IP Administration---\n\n");
printf("To be realized...\n\n");
printf("\n\n Press any key to return to the main menu");
fflush(stdin);
getchar();
}
void logout(void) {
system("cls");
fclose(file);
exit(0);
}
void input_error(void) {
system("cls");
printf("\n\n Input error!\n\n");
printf("\n\n After pressing any key, please re-enter\n\n");
fflush(stdin);
getchar();
}
void show_memu(void) {
system("cls");
// Print function menu
printf("---Switch background management---\n");
printf("1. Create account\n");
printf("2. IP Administration\n");
printf("3. Sign out\n");
printf("4. Port management\n");
printf("Please choose: ");
}
void show_port(struct port port) {
printf("Name[%s]\t state[%s]\tIP[%-15s]\t type[%s]\n",
port.name,
port.status == 0 ? "Prohibit":"activation",
port.ip,
port.type);
}
void show_ports(struct port ports[]) {
system("cls");
printf("---port status---\n");
/*
printf("PORT1:\t");
show_port(port1);
printf("PORT2:\t");
show_port(port2);
printf("PORT3:\t");
show_port(port3);
printf("PORT4:\t");
show_port(port4);
*/
int n;
for (n=0; n<5; n++) {
printf("PORT%d:\t", n+1);
show_port(ports[n]); //Passing the value of the port structure
}
system("pause");
}
//void set_port1(void) {
void set_port(struct port ports[], int num) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT1 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", ports[num].name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &ports[num].status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", ports[num].type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", ports[num].ip);
system("pause");
}
void set_ports(struct port ports[]) {
char n;
while(1) {
system("cls");
printf("---port settings---\n");
printf("1. PORT1\n");
printf("2. PORT2\n");
printf("3. PORT3\n");
printf("4. PORT4\n");
printf("5. PORT5\n");
printf("6. Return\n");
printf("Please choose: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
/*
switch (n) {
case '1':
set_port1();
break;
case '2':
set_port2();
break;
case '3':
set_port3();
break;
case '4':
set_port4();
break;
case '5':
set_port5();
break;
case '6':
return;
default:
input_error();
break;
}
*/
if (n >= '1' && n <= '5') {
int num = n - '1';
set_port(ports, num);
} else if (n == '6') {
return;
} else {
input_error();
}
}
}
void port_admin(struct port ports[]) {
char n;
while(1) {
system("cls");
printf("1. View port\n");
printf("2. Set port\n");
printf("3. Back to main menu\n");
printf("Please choose: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
if (n == '1') {
show_ports(ports);
} else if (n == '2') {
set_ports(ports);
} else if (n == '3') {
break;
} else {
input_error();
}
}
}
int main(void) {
char n; //User selected menu number
struct port ports[5];
init(); //Initialization
login(); //Sign in
while (1) {
show_memu();
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
switch (n) {
case '1':
create_user();
break;
case '2':
ip_admin();
break;
case '3':
logout();
break;
case '4':
port_admin(ports);
break;
default:
input_error();
break;
}
}
return 0;
}Project presentation
1. Why to use array
Occasion of use:
A lot of data of the same type needs to be saved, and the data has a strict order.
Storage method of array:
Store in the direction of increasing address.
2. Definition of array
Definition of array
Please review item 4
Initialization of arrays
Please review item 4
Definition and initialization of structure array
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct position {
int x;
int y;
};
int main (void){
struct position ps[10] = {
{10,20}, {20,30}, {.x=50, .y=80},
};
for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
printf("x=%d, y=%d\n", ps[i].x, ps[i].y);
}
return 0;
}3. Variable length array (VLA)
demo1
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
int x;
int buff[x];
//When the program is running, it is likely to crash! Because the value of x is uncertain at this time, it is likely to be a large number.
printf("x=");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("%d\n", sizeof(buff));
return 0;
}demo2
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
int x;
int buff[x];
//When the program is running, it is likely to crash! Because the value of x is uncertain at this time, it is likely to be a large number.
printf("x=");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("%d\n", sizeof(buff));
return 0;
}Variable length arrays cannot be used in global variables.
4. Two dimensional array
Use of two-dimensional array
There are 50 students in each class
There are 20 classes in the school
Each student can be represented by a structure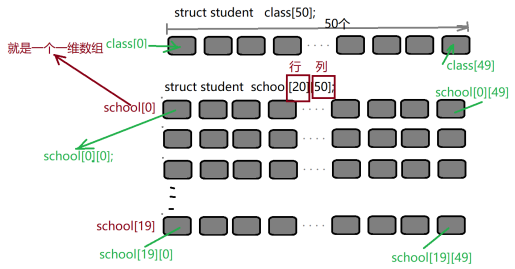
In addition, two-dimensional array is often used in mathematical calculation.
Definition of 2D array
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
//3 years, 2 classes, 5 students
//Each student has 3 courses
//Now you need to define an array to represent these scores.
//Equivalent to: 5 rows, 3 columns (3 for each row)
// [number of rows] [number of columns]
int score[5][3];
}Storage mode of two-dimensional array (mainly in line order)
After storing the first line, store the second line
Store line by line!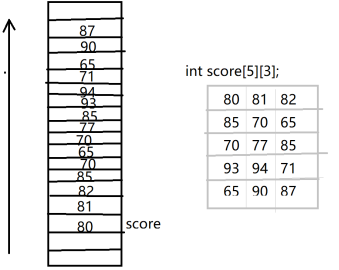
Initialization of 2D array
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
//Mode 1
/*
int score[5][3] = {
60,61,62, //socre[0] In order: score[0][0], score[0][1], score[0][2]
63,64,65,
66,67,68,
69,70,71,
72,73,74 };
*/
//Mode 2
/*
int score[5][3] = {
{60,61,62},
{63,64,65},
{66,67,68}
};
*/
//Mode 3
int score[5][3] = {
[1] = {63, 64, 65},
[0] = {60, 61, 62}
};
//Print entire array
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<3; j++) {
printf("%d\t", score[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}The use of 2D array
1. The value cannot be set directly for the array name of 2D array
int a[3][2] = {1,2,3};
int b[3][2];
b = a; ///error
b[0] = {1,2}; //error
b[0][1] = 9; / / correct!
2. Two dimensional array of char type, which can store multiple strings
char data[3][16];
printf("Please input your name: ");
scanf("%s", data[0]);
printf("name=%s\n", data[0]);
printf("Please input your telephone: ");
scanf("%s", data[1]);
printf("Tel=%s\n", data[1]);5. Multidimensional array
Supplement: initialization of 2D array
char data[][4] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
printf("%d", sizeof(data)); //8
char data2[4][] = {1,2,3,4,5,6}; //error!Use of multidimensional array
1) 3D processing
2) Image processing
char pic[800][600][3];
Definition, initialization and use of multidimensional array
demo
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
//data[0][0][0], data[0][0][1], data[0][1][0]
int data[2][3][2] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};
int data2[2][3][2] = {
{ //data2[0]
{1,2},
{3,4},
{5,6}
},
{ //data2[1]
{7,8},
{9,10},
{11,12}
},
};
for (int i=0; i<2; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < 3; j++) {
for (int k=0; k<2; k++) {
printf("data2[%d][%d][%d] = %d\n", i, j, k, data2[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}6. Array as parameter of function
demo.
#include <stdio.h>
/*
There are 10 students in a class
Each student has a test score
1. Define a function to calculate the average score
2. Define a function, and if a score is less than 60, add 5 points.
*/
float average(int data[]) {
float s = 0;
for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
s += data[i];
}
s = s / 10;
printf("size=%d\n", sizeof(data));
return s;
}
float add_score(int n, int data[n]) {
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
if (data[i] < 60) {
data[i] += 5;
}
}
}
int main(void) {
int scores[10] = {80, 70, 55, 40, 30, 38, 95, 85, 77, 61};
printf("The average score is:%.2f\n", average(scores));
add_score(10, scores);
for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
printf("%d\t", scores[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}Project practice
Exercise 1
Independent implementation project 11
Exercise 2
There are 4 participants, each with 3 courses.
All the scores of these 4 students are required to be entered, and the average scores of each course and all courses are calculated respectively.
Tip: it is required to save the scores with a two-dimensional array.
Exercise 3
Define a function to reverse the square matrix.
Principle analysis: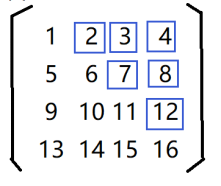
Reference resources:
#include <stdio.h>
void reverse(int n, int data[n][n]) {
int tmp;
for (int i=0; i<n-1; i++) {
for (int j=i+1; j<n; j++) {
//data[i][j] and data[j][i] are interchangeable
tmp = data[i][j];
data[i][j] = data[j][i];
data[j][i] = tmp;
}
}
}
void show(int n, int data[n][n]) {
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<n; j++) {
printf("%d\t", data[i][j]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
}
int main(void) {
int buff[5][5];
int val = 100;
//Set the value of array buff
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<5; j++) {
buff[i][j] = val++;
}
}
printf("Before reversal:\n");
show(5, buff);
reverse(5, buff);
printf("\n After reversal:\n");
show(5, buff);
return 0;
}