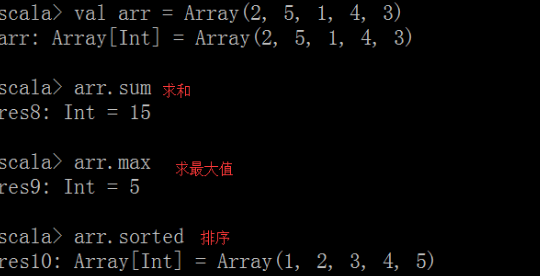
1 fixed length array and variable length array
-
Format of fixed length array definition:
val arr = new Array[T] (array length) -
Variable length array definition format:
val arr = ArrayBuffer[T]()
Note that you need to import the package: import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer -
The code is as follows
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer object ArrayDemo{ def main(args:Array[String]){ //1. Initialize an 8-point fixed length array with all elements of 0 //If it's new, it's the same as calling the apply method of an array to assign values to the array directly val arr1 = new Array[Int](8) //Print fixed length array directly, the content is the hashcode value of the array println(arr1) //By converting an array to an array buffer, you can see the contents of the original array //toBuffer converts an array to a variable length array buffer println(arr1.toBuffer) //2. The second method to define an array, direct assignment val arr2 = Array("hadoop","storm","spark") //Use () to access an element and print an element println(arr2(2)) //The following is a variable length array val ab = ArrayBuffer[Int]() //Appends an element to the end of the array buffer, + = appends an element to the end ab += 1 //Append multiple elements to the tail ab += (2,3,4,5) //Append an array++= ab ++= Array(6,7) //Append an array buffer ab ++= ArrayBuffer(8,9) //Insert the element at some position of the array, insert it from the subscript, //Insert - 1,0 from subscript 0 ab.insert(0,-1,0) //remove the element at a certain position of the array, and delete it according to the subscript ab.remove(0) println(ab) } }
2. Enhance for traversing arrays in Scala
- Enhance for loop traversal
- Use unitl to generate footmark, 0 unitl 10 contains 0 does not contain 10
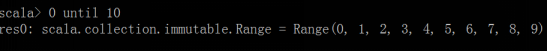
- Code
object ForArrayDemo{ def main(args:Array[String]){ //1. Use enhanced for loop to traverse array val arr = Array(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) for(i <- arr) println(i) //2. Use until to generate a Range //The reverse method reverses the Range from which it was called for(i <- (0 until arr.length).reverse) println(arr(i)) } }
3. Array conversion yield
- yield keyword can transform the original array, and a new array will be generated. The original array will remain unchanged
- Code
object ArrayYieldDemo{ def main(args:Array[String]){ //1. Define an array val arr = Array(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) //2. Multiply the even number by 10 to generate a new array val res = for(e <- arr if e % 2 == 0) yield e * 10 println(res.toBuffer) //3. More advanced writing, more comfortable to use //Filter is a filter that receives a function with a return value of boolean //map is equivalent to taking out every element of the array and applying the function passed in val r = arr.filter(_ % 2 == 0).map(_ * 10) println(t.toBuffer) } }
4. Algorithms commonly used in arrays