Catalog:
1. interpolation
2. instruction
3. filter
4. Computing and listening attributes
Because the knowledge explained in this section is relatively simple, it is mainly embodied in the code (comments)
1. interpolation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.10/vue.js"></script>
<title>interpolation</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li>
<h3>text</h3>
<div v-html="vueHtml"></div>
</li>
<li>
<h3>attribute</h3>
<!--
v-bind: And v-model The difference?
v-model Is the instruction to bind data bidirectionally
v-bind: Just fill in the corresponding values in the specified attributes
//For example, v-bind:value simply means that the value is filled in to value=""
//Then the value of value changes without affecting the value of the variable in the Vue instance.
-->
<input type="text" v-bind:value="msg" />
<!-- Abbreviation: v-bind==: Event use@,Binding: -->
</li>
<li>
<h3>Expression</h3>
{{str.substr(0,6).toUpperCase()}}
{{ number + 1 }}
{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}
</li>
<li :id="'list-' + id">My Id yes js Dynamically generated</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello vue',
vueHtml: '<span style="font-size: 30px;">Vue Yes html Parsing</span>',
str:'http://www.baidu.com',
number:6,
ok:true,
id:5
};
}
});
</script>
</html>
Test:
2. instruction
Refers to the special attribute with the prefix "v-"
Here are some core instructions
(v-if|v-else|v-else-if)/v-show/v-for)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.10/vue.js"></script>
<title>instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li>
<h3>Conditional instruction(if else if else )</h3>
<input type="text" v-model="score" />
<div v-if="score>90">A</div>
<div v-else-if="score>80">B</div>
<div v-else-if="score>70">C</div>
<div v-else-if="score>60">D</div>
<div v-else="">E</div>
</li>
<li>
<h3>v-Show</h3>
<input type="text" v-model="show" />
<div v-show="show">Come on.</div>
</li>
<li>
<h3>v-for</h3>
<div v-for="item,index in arr">
{{item}},{{index}}
</div>
<div v-for="item,index in objArr">
{{item.name}},{{index}}
</div>
</li>
<li>
<h3>dynamic parameter</h3>
<input type="text" v-model="evname" />
<!-- dbclick -->
<button v-on:[evname]="xxx">Point me</button>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello vue',
score: 88,
show: null,
arr: [1, 4, 7, 9],
objArr: [{
id: 's001',
name: 'son of a bitch'
}, {
id: 's002',
name: 'king'
}, {
id: 's003',
name: 'Of'
}],
evname:'click'
};
},
methods:{
xxx(){
console.log('xxx Method execution');
}
}
});
</script>
</html>
Test:
Our conditional instruction:
When entering 88:00:
When entering 99:
v-Show:
When we didn't lose:
When it's worth it:
v-for:
Our index and attributes are here:
Dynamic parameters:
When we enter click:
Click the singular number method to call: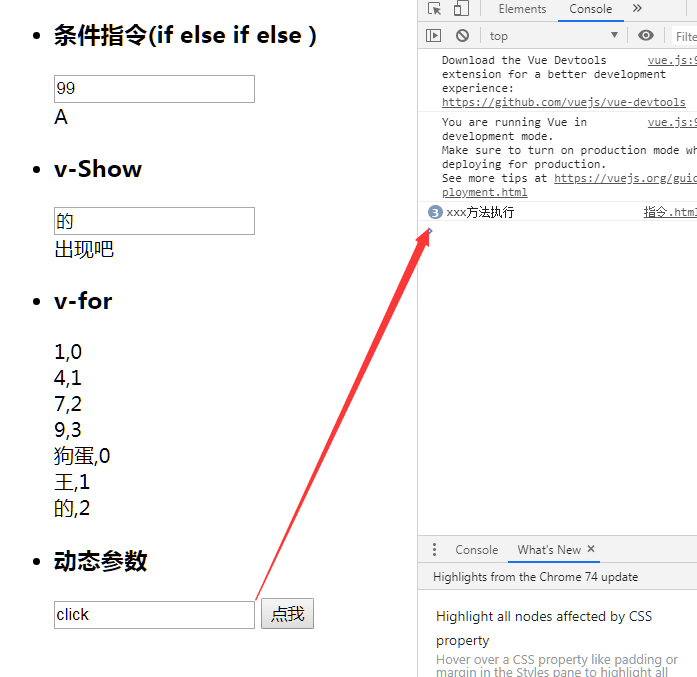
But when entering dblclick, it is useless to click singular times, and you must click double times.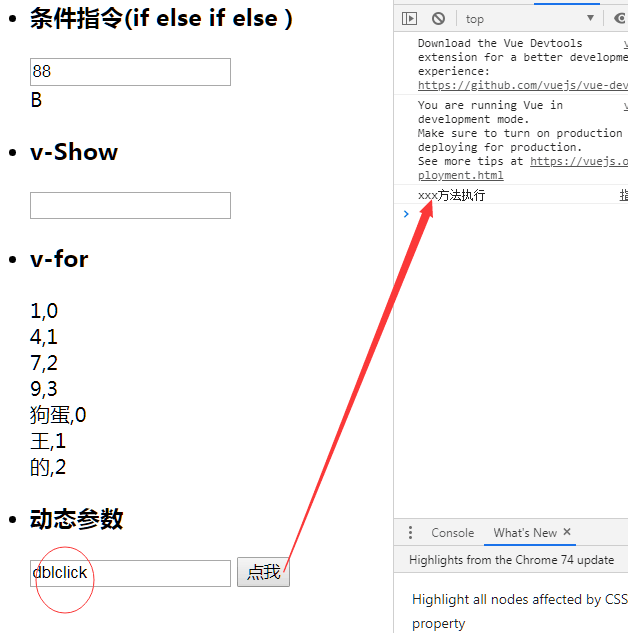
3. filter
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.10/vue.js"></script>
<title>Filter</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li>
<h3>Local filter</h3>
{{msg}}<br />
{{msg | a}}
</li>
<li>
<h3>Local filters can be connected in series</h3>
{{msg}}<br />
{{msg | a | b}}
</li>
<li>
<h3>Global filter</h3>
{{msg | c}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.filter('c',function(v){
return v.substring(7);
})
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
msg: 'http://www.baidu.com'
};
},
filters:{
a(v){
return v.substring(4);
},
b(v){
return v.substring(3,12);
}
}
});
</script>
</html>
Test:
Local filter
Will intercept a paragraph of text
Local filters can be connected in series
Intercept after interception
Global filter
Cross-page filtering can occur
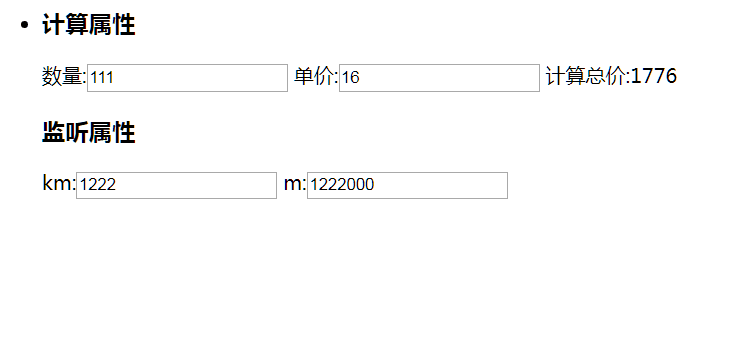
Computing and listening attributes
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.10/vue.js"></script>
<title>Computing attributes listening attributes</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li>
<h3>Calculated attribute</h3>
//Quantity: <input type="text" v-model="num"/>
//Unit price: <input type="text" v-model="price"/>
//Calculate total Price: {Tot}
<h3>Listener attribute</h3>
km:<input type="text" v-model="km" />
m:<input type="text" v-model="m" />
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
num:1,
price:16 ,
km:1,
m:1000
};
},
computed:{
total(){
//When calculating attribute definitions, any variable can be defined in the Vue instance.
return parseInt(this.num) * parseInt(this.price);
}
},
watch:{
km(v){
this.m = v*1000;
},
m(v){
this.km = v/1000;
}
}
});
</script>
</html>
Calculated attribute
Computational attributes can be used to quickly compute the attributes displayed in the View. These calculations will be cached and updated only when needed.
computed:{}
Listener attribute
watch attributes, we can respond to changes in data through watch
watch:{}
Comparison map: