Introduction to Spring MVC:
1. Create a maven project and import dependencies
maven project pom configuration:
<dependencies> <dependency> <!-- Junit test --> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!-- jstl --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <!-- Add to Spring package --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- To facilitate unit testing, add spring-test package --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.8.5</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
2. Configure the core controller:
Configure Dispatcher Servlet Core Controller (Servlet) in web.xml
<! - Configure Spring MVC Core Controller: -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<! - Configure the initial cu lt ural parameters of Dispatcher Servlet: Set the path and file name of the file - >.
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<! -- The point at which the object to configure the servlet is created: when the application is loaded. Values can only be non-zero positive integers, indicating the order of start-up - >.
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<! - Servlet access paths, which requests need to be managed by Springmvc - >
<! - / Indicates that all requests are managed - >
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
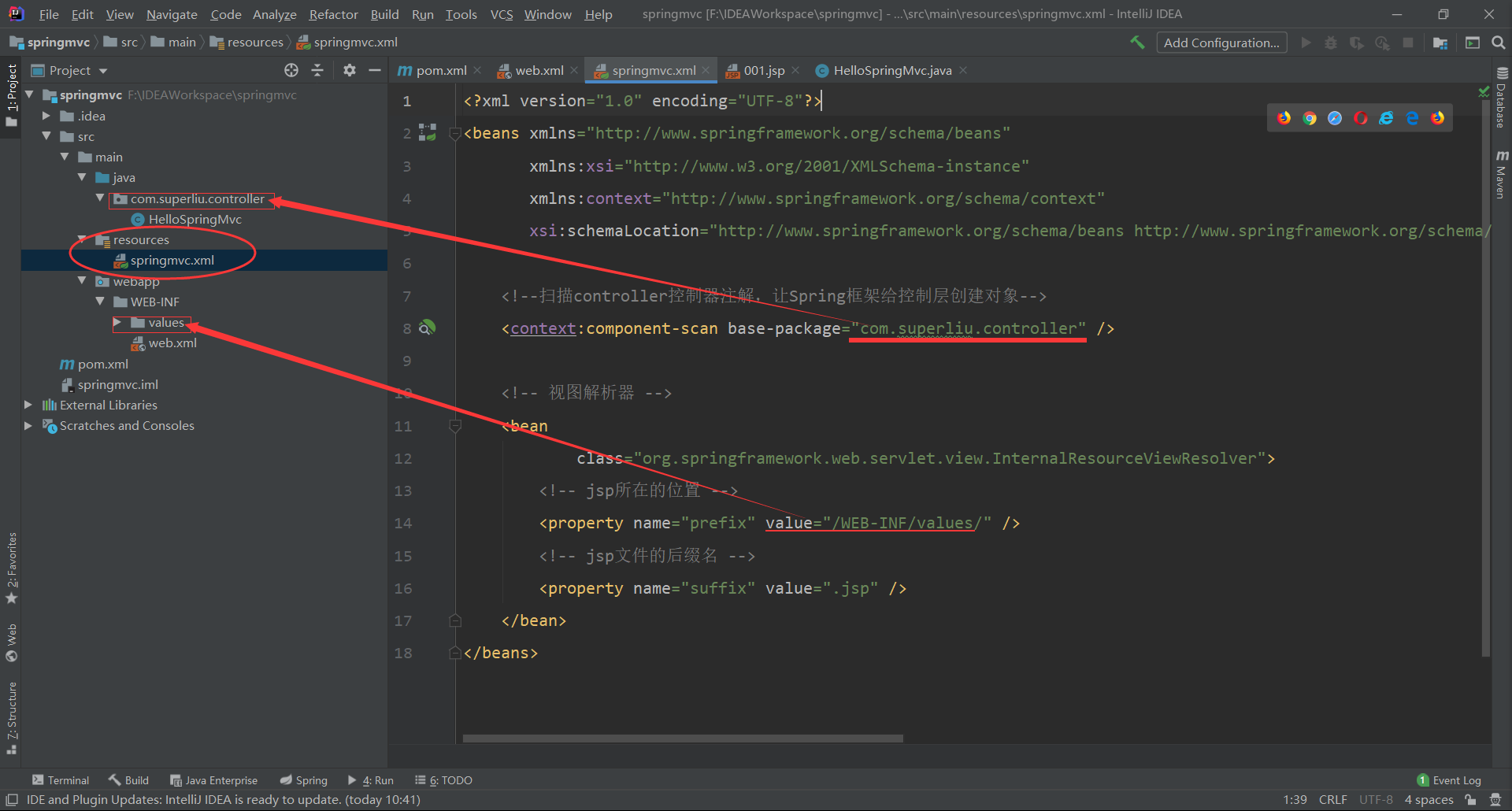
3. Create configuration files for spring MVC (as shown below):
<!--scanning controller Controller Annotation Spring Framework creates objects for the control layer--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.springmvc.controller" /> <!-- view resolver --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!-- jsp Location --> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/values/" /> <!-- jsp File suffix name --> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean>
4. Write controllers and use annotations to configure:
/** * Controller */ @Controller//Note that this class is a controller class //Action method public class HelloSpringMvc { @RequestMapping(value = "/HelloSpringMvc")// Request mapping annotations public String hello(Model model){ System.out.println("HelloSpringMvc~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~"); model.addAttribute("message","My first SpringMvc program"); return "001"; } }
5. Test Spring MVC:
Publish the project, through the browser, access the corresponding address of the current project +/HelloSpring Mvc can be