PXE High Efficiency Batch Network Installation
Batch deployment of servers
- Scaling: assembling multiple servers at the same time
- Automation: Install systems, configure services
- Remote implementation: no installation media such as CD, U disk, etc.
About PXE Network
PXE
- Pre-boot execution environment, run before operating system
- Can be used for remote installation to build diskless workstations
Server
-
Run the DHCP service to assign addresses, locate bootstrappers
- DHCP Automatically Assign IP Address Location Boot File
-
Run TFTP server, provide bootstrapper Download
- TFTP Simple File Transfer Protocol
- Use UDP protocol
- Port number 69
- Advantages: High efficiency
- Disadvantages: Small capacity
- For storage: bootstrapper pxelinux.0 (syslinux package), compressed kernel vmlinuz, system initialization file initrd.img, Startup menu default
-
Run FTP service to provide mirror file download
-
FTP (vsftpd) File Transfer Protocol
- Advantages: Safe, large capacity
-
Disadvantage: Slow transmission
-
Use TCP protocol
- Port number 20 is for data transfer and port number 21 is for connection
- For storage: system image
-
- Installation package: dhcp, tftp-server, vsftpd, syslinux
Client
- Network Card Supports PXE Protocol
- Motherboard supports network startup
Basic deployment process
- Prepare CentOS 7 installation source (YUM repository)
- Enable TFTP service and provide kernel, bootstrapper
- Enable the DHCP service to assign addresses, indicate bootstrapper locations
- Configure Startup Menu
TFTP Service and Boot File
- Install the tftp-server package to enable the TFTP service
- Prepare the kernel file vmlinuz, initialize the mirror initrd.img
- Prepare bootstrapper file pxelinux.0
PXE settings for DHCP services
- next-server //point to TFTP path
- filename //bootstrapper file location
Default Startup Menu File
- Create/var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
- Directory name pxelinux.cfg is not changeable
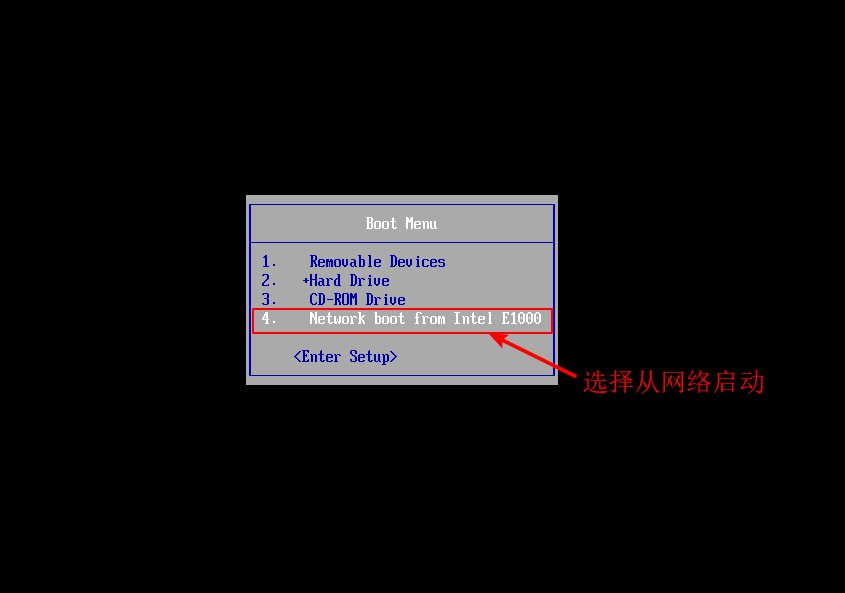
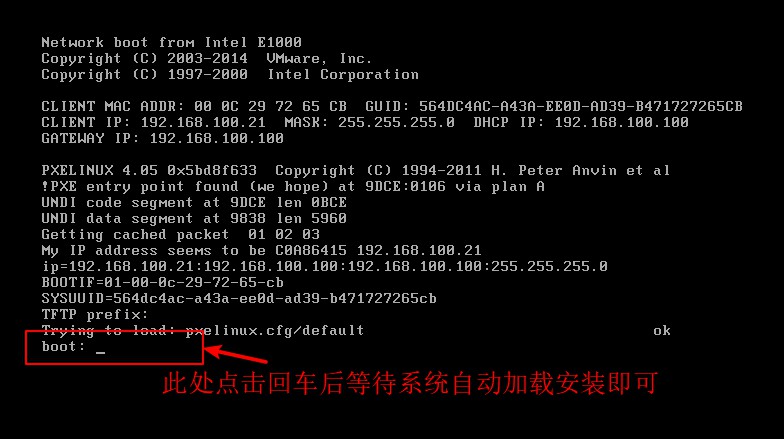
Verify PXE Network Installation
- Adjust BIOS settings to boot from the network
- Obtain IP address automatically and specify CentOS 7 installation source
- The rest is the same as the local installation
Demo
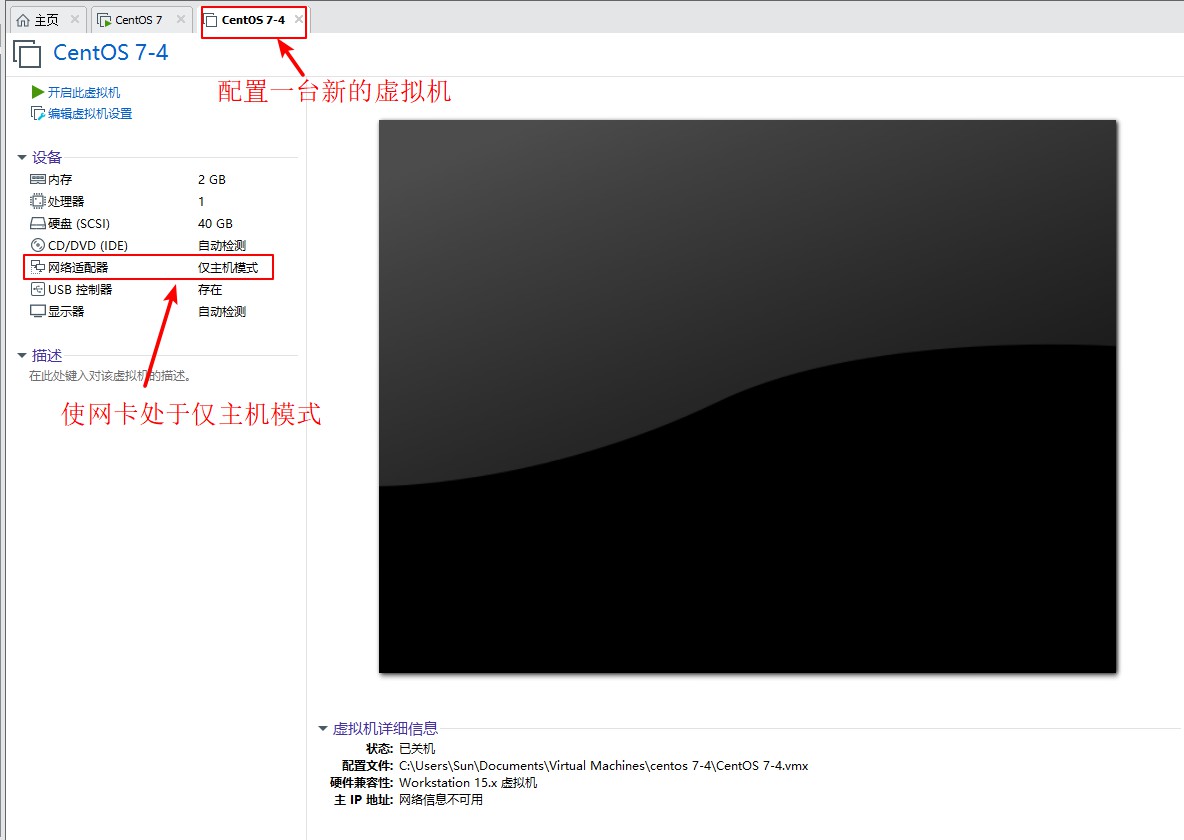
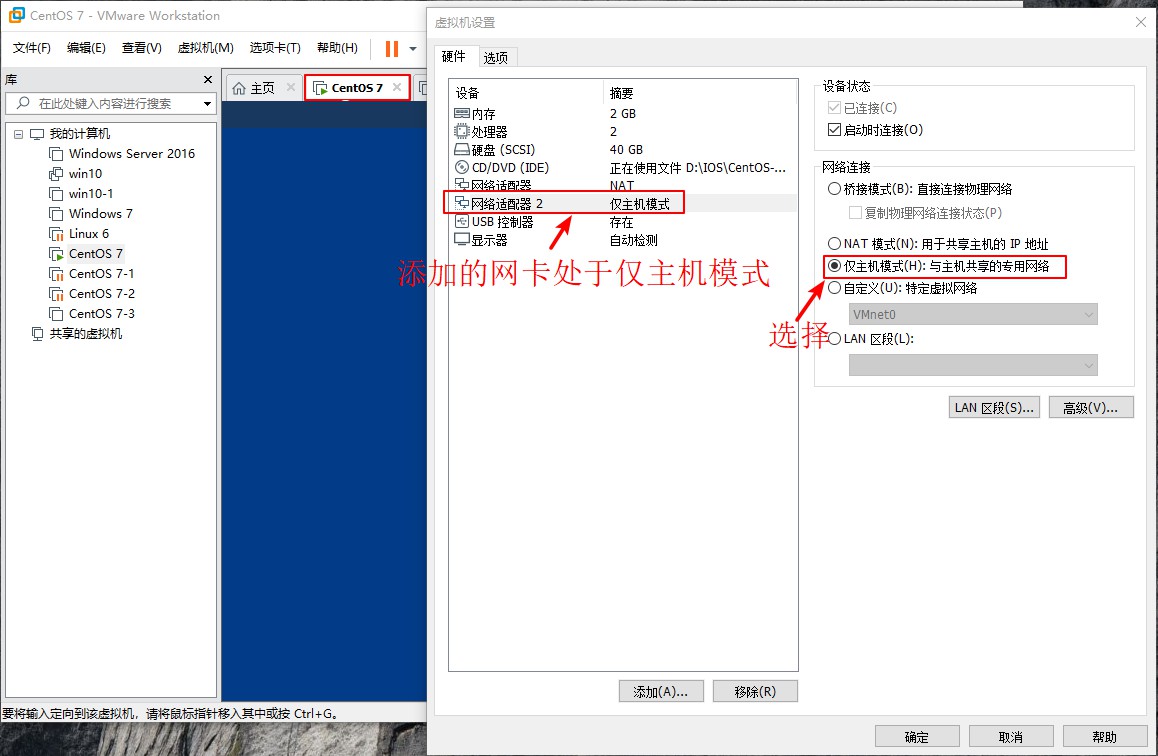
1. First configure a virtual machine in the VMware 15 virtual machine, without installing the system, the network card is set in the host-only mode, which is used to verify the PXE network installation, turn on the CentOS 7 virtual machine, configure the dual network card mode, the original network card is used for network connection, which makes it easy for us to install service software, and the added network card is set to the host-only mode.To bind it to the same device as the configured virtual machine and configure the static IP address in the added network card to provide the IP address to the configured virtual machine.
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig //View network card information in CentOS 7 system
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 //Original Network Card Information
inet 192.168.144.133 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.144.255
inet6 fe80::a85a:c203:e2e:3f3c prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:5b:d3:a0 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 26199 bytes 36984367 (35.2 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 8391 bytes 524793 (512.4 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
ens36: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 //Added Network Card Information
inet6 fe80::deb1:3cec:3e26:5ec2 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:5b:d3:aa txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 10 bytes 1308 (1.2 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@localhost ~]# Cd/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ //Enter network card profile directory
[root@localhost network-scripts]# ls //View Information
ifcfg-ens33 ifdown-ippp ifdown-sit ifup-bnep ifup-plip ifup-Team network-functions-ipv6
ifcfg-lo ifdown-ipv6 ifdown-Team ifup-eth ifup-plusb ifup-TeamPort
ifdown ifdown-isdn ifdown-TeamPort ifup-ib ifup-post ifup-tunnel
ifdown-bnep ifdown-post ifdown-tunnel ifup-ippp ifup-ppp ifup-wireless
ifdown-eth ifdown-ppp ifup ifup-ipv6 ifup-routes init.ipv6-global
ifdown-ib ifdown-routes ifup-aliases ifup-isdn ifup-sit network-functions
[root@localhost network-scripts]# Cp-p ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens36 //Copy ens33 configuration file as ens36
[root@localhost network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-ens36 //Edit network card information
TYPE=Ethernet
PROXY_METHOD=none
BROWSER_ONLY=no
BOOTPROTO=static //Change dhcp to static
DEFROUTE=yes
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6INIT=yes
IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes
IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy
NAME=ens36 //Change 33 to 36
DEVICE=ens36 //Change 33 to 36
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=192.168.100.100 //Configure IP Address
NETMASK=255.255.255.0 //Configure Subnet Mask
GATEWAY=192.168.100.1 //configure gateway
~ //Note: Delete UUID entries
~
~
~
~
~
~
:wq
[root@localhost network-scripts]# service network restart //restart network card service
Restarting network (via systemctl): [ Determine ]
[root@localhost network-scripts]# ifconfig //View network card information
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.144.133 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.144.255
inet6 fe80::a85a:c203:e2e:3f3c prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:5b:d3:a0 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 124487 bytes 178695031 (170.4 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 35758 bytes 2193524 (2.0 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
ens36: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 //Get static IP address
inet 192.168.100.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.100.255
inet6 fe80::f6eb:23e3:3afb:fef4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:5b:d3:aa txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 2 bytes 486 (486.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 186 bytes 32776 (32.0 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 02. Install the DHCP service and edit the DHCP service configuration file
[root@localhost network-scripts]# yum install dhcp -y
//Plugins loaded: fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.163.com
* extras: mirrors.huaweicloud.com
* updates: mirrors.huaweicloud.com
//Resolving dependencies
--> Checking transactions
---> software package dhcp.x86_64.12.4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1 Will be installed
...//Omit some content...
//Installed:
dhcp.x86_64 12:4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1
//Upgraded as a dependency:
dhclient.x86_64 12:4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1 dhcp-common.x86_64 12:4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1
dhcp-libs.x86_64 12:4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1
//Complete!
[root@localhost network-scripts]# cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.2.5/dhcpd.conf.example /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
cp: Whether to Overwrite"/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf"? yes //Copy the DHCP profile template to the profile and enter yes confirmation
[root@localhost network-scripts]# Vim/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf //Edit Configuration DHCP Profile
...//Omit some content...
ubnet 192.168.100.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { //Set Segment Address
range 192.168.100.20 192.168.100.30; //Set IP Address Assignment Range
option routers 192.168.100.100; //Set up a gateway that points to you to make it easier for the server to assign addresses
option domain-name-servers 8.8.8.8; //Set Assignment DNS Address
next-server 192.168.100.100; //Set the address to the TFTP server, which is local
filename "pxelinux.0"; //Set to point to the boot file location, note: File name cannot be mistyped
}
...//Omit some content...
:wq //Save Exit3. Install bootstrapper files
[root@localhost network-scripts]# Yum install syslinux-y //install bootstrapper Plugins loaded: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.163.com * extras: mirrors.huaweicloud.com * updates: mirrors.huaweicloud.com Resolving dependencies -->Checking transactions --->Package syslinux.x86_64.0.4.05-15.el7 will be installed ...//Omit some content... Installed: syslinux.x86_64 0:4.05-15.el7 Complete! [root@localhost network-scripts]# rpm-ql syslinux | grep pxelinux.0 //Check to see if the boot file was successfully installed in the installed software /usr/share/syslinux/gpxelinux.0 /usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0//program boot file
4. Install TFTP service software
[root@localhost network-scripts]# Yum install tftp-server-y //install TFTP service //Plugins loaded: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.163.com * extras: mirrors.huaweicloud.com * updates: mirrors.huaweicloud.com //Resolving dependencies --> Checking transactions ---> software package tftp-server.x86_64.0.5.2-22.el7 Will be installed ...//Omit some content... //Installed: tftp-server.x86_64 0:5.2-22.el7 //Complete! [root@localhost network-scripts]# Rpm-ql tftp-server //View TFTP service list /etc/xinetd.d/tftp //tftp profile directory /usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.socket /usr/sbin/in.tftpd /usr/share/doc/tftp-server-5.2 /usr/share/doc/tftp-server-5.2/CHANGES /usr/share/doc/tftp-server-5.2/README /usr/share/doc/tftp-server-5.2/README.security /usr/share/man/man8/in.tftpd.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/tftpd.8.gz /var/lib/tftpboot //tftp Site Directory
5. Put the bootstrapper file in the tftp service site and turn on the tftp service function
[root@localhost network-scripts]# Cp/usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0/var/lib/tftpboot/ //Copy the file into the tftp site
[root@localhost network-scripts]# Cd/var/lib/tftpboot/ //Enter the tftp site
[root@localhost tftpboot]# ls //View directory information
pxelinux.0 //Bootstrapper file added to site
[root@localhost tftpboot]# Vim/etc/xinetd.d/tftp //Enter editing TFTP master profile
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer \
# protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless \
# workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers, \
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
service tftp
{
socket_type = dgram
protocol = udp
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -s /var/lib/tftpboot
disable = no //Change yes to turn on service capabilities for no
per_source = 11
cps = 100 2
flags = IPv4
}
~
:wq //Save Exit
6. Install the ftp service function and mount the mirror file CentOS 7 on the ftp site. Find the system initial file and the compressed kernel file and add them to the tftp site.
[root@localhost tftpboot]# yum install vsftpd -y //Plugins loaded: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.163.com * extras: mirrors.huaweicloud.com * updates: mirrors.huaweicloud.com //Resolving dependencies --> Checking transactions ---> software package vsftpd.x86_64.0.3.0.2-25.el7 Will be installed ...//Omit some content... //Installed: vsftpd.x86_64 0:3.0.2-25.el7 //Complete! [root@localhost tftpboot]# Rpm-ql vsftpd //View ftp service file list ...//Omit some content... /usr/share/man/man5/vsftpd.conf.5.gz /usr/share/man/man8/vsftpd.8.gz /var/ftp //ftp site location /var/ftp/pub [root@localhost ~]# Cd/var/ftp/ //Enter FTP service site [root@localhost ftp]# ls //View Directory pub [root@localhost ftp]# mkdir centos7 //Create directory centos7 directory Users mount mirror files [root@localhost ftp]# ls //View centos7 pub //Created successfully [root@localhost ftp]# Mount/dev/sr0/var/ftp/centos7/ //Mount the mirror file to the centos7 directory in the FTP site mount: /dev/sr0 Write protected, mounted read-only [root@localhost ftp]# Df-hT //View disk information //File System Type Capacity Used Available%Mountpoint /dev/sda2 xfs 20G 3.7G 17G 19% / devtmpfs devtmpfs 898M 0 898M 0% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs tmpfs 912M 9.0M 903M 1% /run tmpfs tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda5 xfs 10G 37M 10G 1% /home /dev/sda1 xfs 6.0G 174M 5.9G 3% /boot tmpfs tmpfs 183M 28K 183M 1% /run/user/0 /dev/sr0 iso9660 4.3G 4.3G 0 100% /var/ftp/centos7 //Mount Successfully [root@localhost ftp]# cd centos7/ //Enter centos7 directory [root@localhost centos7]# ls //View mounted image information CentOS_BuildTag EULA images LiveOS repodata RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-Testing-7 EFI GPL isolinux Packages RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 TRANS.TBL [root@localhost centos7]# cd images/ //enter images directory [root@localhost images]# ls //View directory information efiboot.img pxeboot TRANS.TBL [root@localhost images]# cd pxeboot/ //Enter pxeboot directory [root@localhost pxeboot]# ls //View directory information initrd.img TRANS.TBL vmlinuz //Compress Kernel and System Initialization Files [root@localhost pxeboot]# CP initrd.img vmlinuz/var/lib/tftpboot/ //Add compressed kernel and system initialization files to the tdtp site [root@localhost pxeboot]# Ls/var/lib/tftpboot/ //View tftp site information initrd.img pxelinux.0 vmlinuz //Successfully added compressed kernel and system initialization files
7. Add a Startup menu to the TFTP site, and when finished, turn on dhcp, tftp, ftp services, and turn off firewalls, enhanced security features
[root@localhost pxeboot]# Cd/var/lib/tftpboot/ //Enter the tftp site
[root@localhost tftpboot]# ls //View site information
initrd.img pxelinux.0 vmlinuz
[root@localhost tftpboot]# mkdir pxelinux.cfg //Add a Startup menu directory to the site, note: The directory name is not writable incorrectly
[root@localhost tftpboot]# ls //View Directory
initrd.img pxelinux.0 pxelinux.cfg vmlinuz //Successfully created Startup menu directory
[root@localhost tftpboot]# cd pxelinux.cfg/ //Enter the created Startup menu directory
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# vim default //Edit Startup Menu File
default auto //Default mode
prompt 1 //Wait time 1 second
//Write Profile Template
label auto
kernel vmlinuz //Kernel Information
append initrd=initrd.img method=ftp://192.168.100.100/centos7
//Load system initialization file in ftp mode with centos7
label linux text
kernel vmlinuz
append text initrd=initrd.img method=ftp://192.168.100.100/centos7
label linux rescue //Enter first aid mode
kernel vmlinuz
append rescue initrd=initrd.img method=ftp://192.168.100.100/centos7
~
~
:wq //Save Exit After Writing Complete
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# systemctl start dhcpd //start dhcp service
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# systemctl start tftp //start tftp service
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# systemctl start vsftpd //start ftp service
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# systemctl stop firewalld.service //turn off firewall functionality
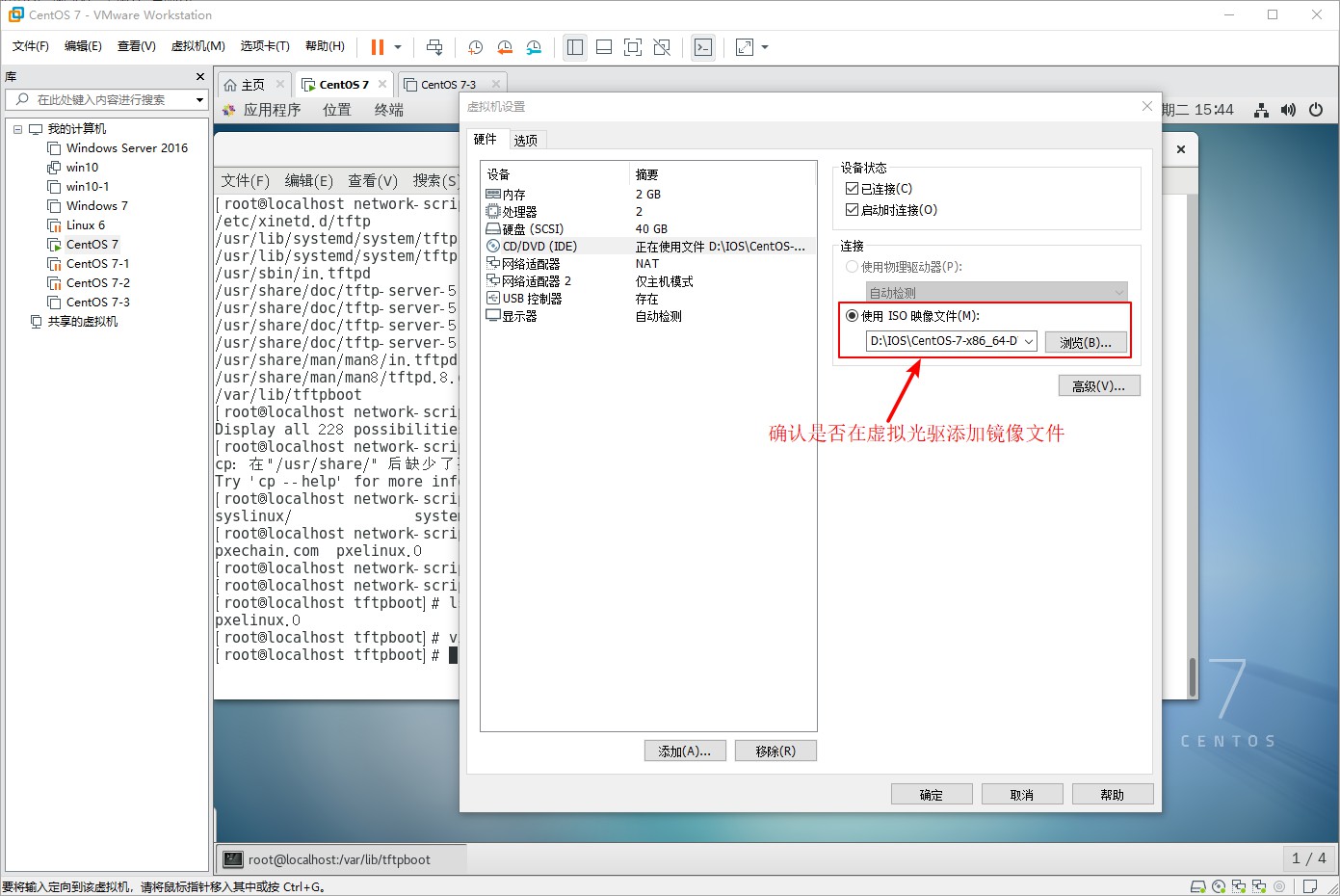
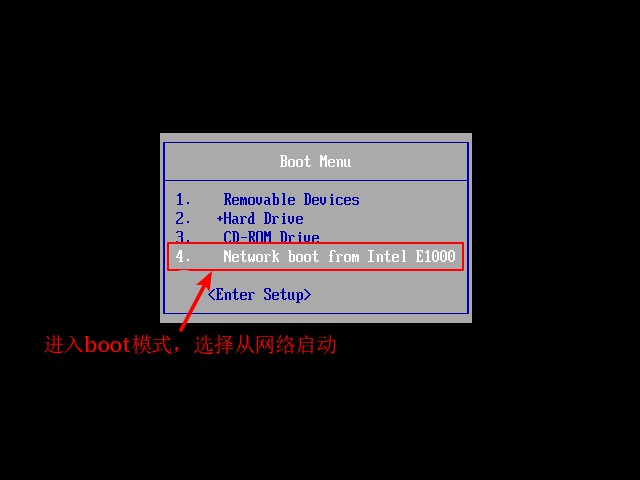
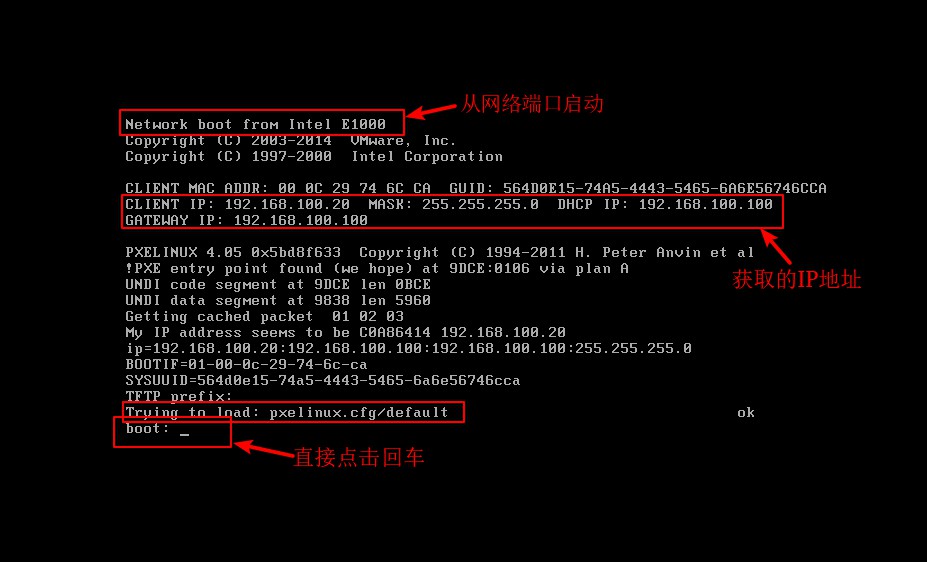
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# setenforce 0 //Turn off enhanced security features8. Verify the installation of PXE network deployment, open the configured virtual machine, press ESC key in the boot interface, enter boot mode, and choose to start from the network

About kickstart
kickstart unattended Technology
- Create an answer file that predefines various installation settings
- Fully automatic installation without interactive setup
- Complete various post-installation configuration operations by adding the%post script
Demo
1. Install kickstart service software in CentOS 7
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# Yum install system-config-kickstart-y //install kickstart software //Plugins loaded: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.163.com * extras: mirrors.huaweicloud.com * updates: mirrors.huaweicloud.com //Resolving dependencies --> Checking transactions ---> software package system-config-kickstart.noarch.0.2.9.7-1.el7 Will be installed ...//Omit some content... //Installed: system-config-kickstart.noarch 0:2.9.7-1.el7 //Installed as a dependency: gnome-python2.x86_64 0:2.28.1-14.el7 gnome-python2-canvas.x86_64 0:2.28.1-14.el7 libart_lgpl.x86_64 0:2.3.21-10.el7 libgnomecanvas.x86_64 0:2.30.3-8.el7 rarian.x86_64 0:0.8.1-11.el7 rarian-compat.x86_64 0:0.8.1-11.el7 system-config-date.noarch 0:1.10.6-3.el7.centos system-config-date-docs.noarch 0:1.0.11-4.el7 system-config-keyboard.noarch 0:1.4.0-5.el7 system-config-keyboard-base.noarch 0:1.4.0-5.el7 system-config-language.noarch 0:1.4.0-9.el7 usermode-gtk.x86_64 0:1.111-5.el7 //Complete!
2. Open kickstart service software in graphical interface after installation
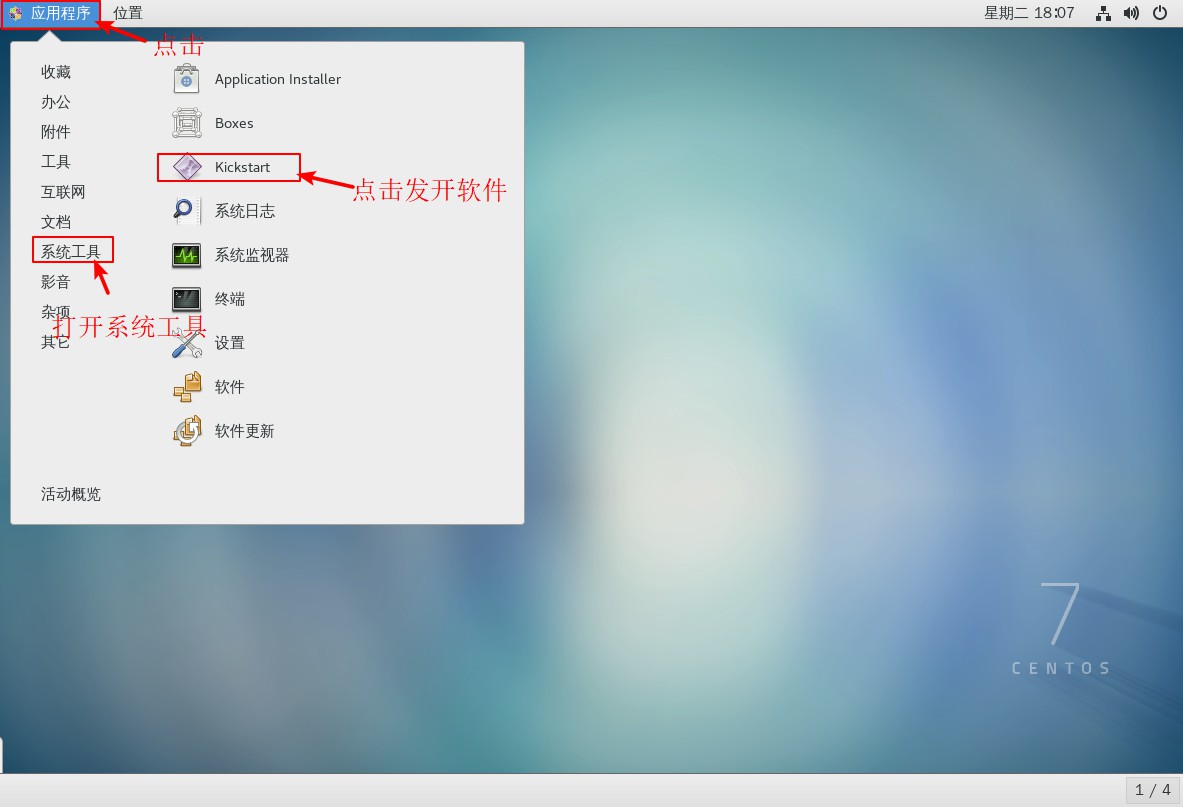
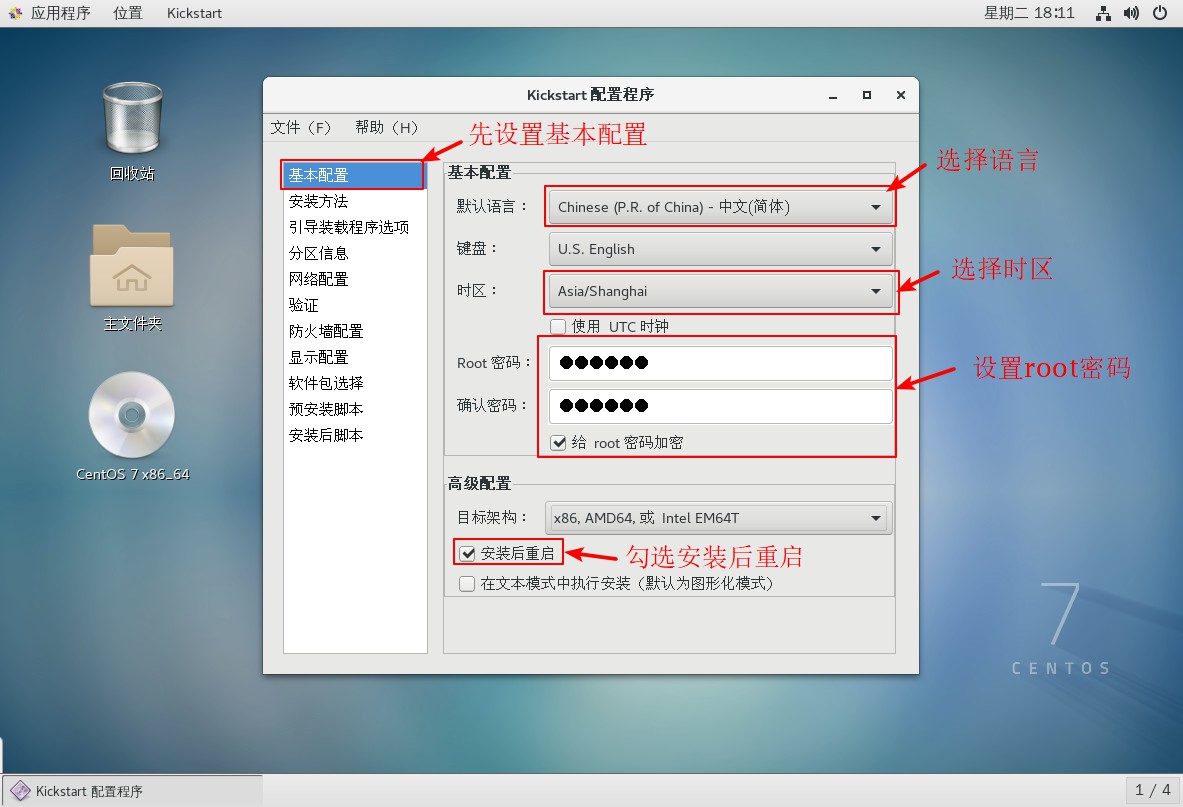
3. Set up the basic configuration after opening the software
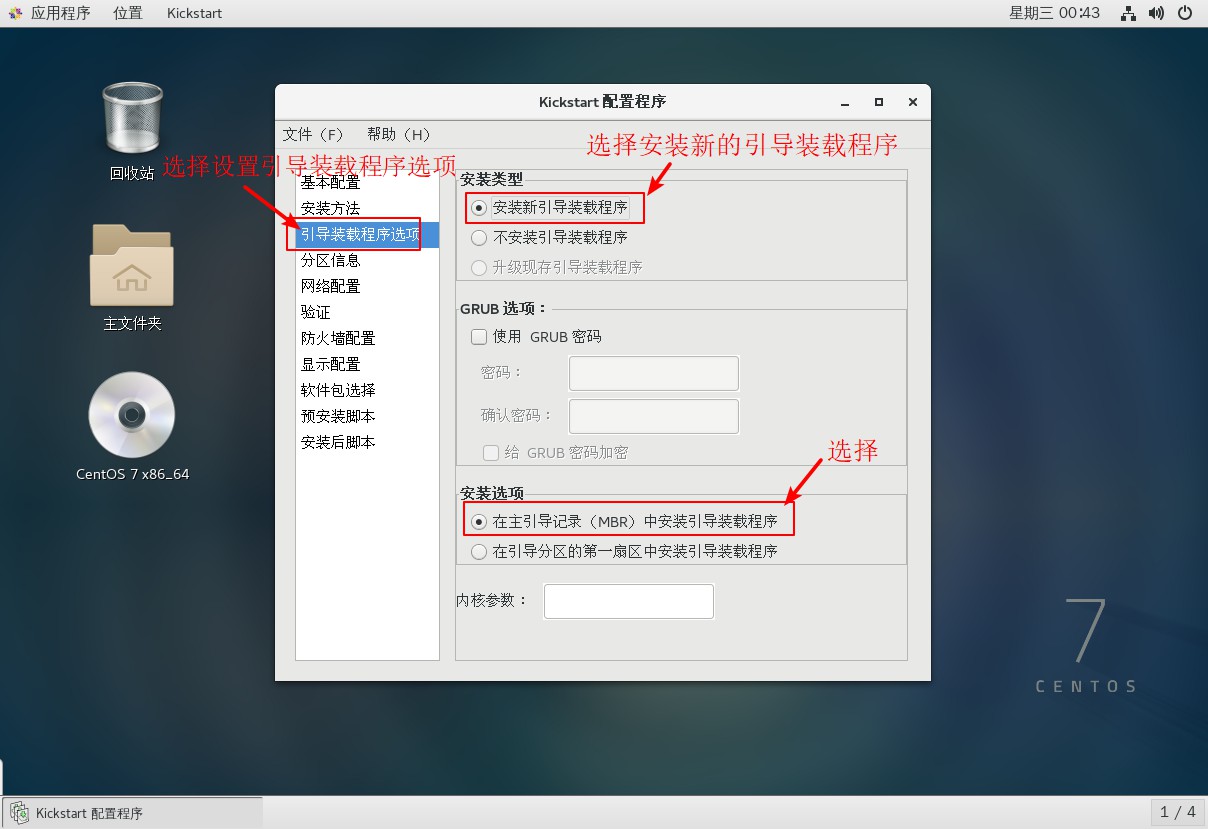
4. Set installation method and boot loader options

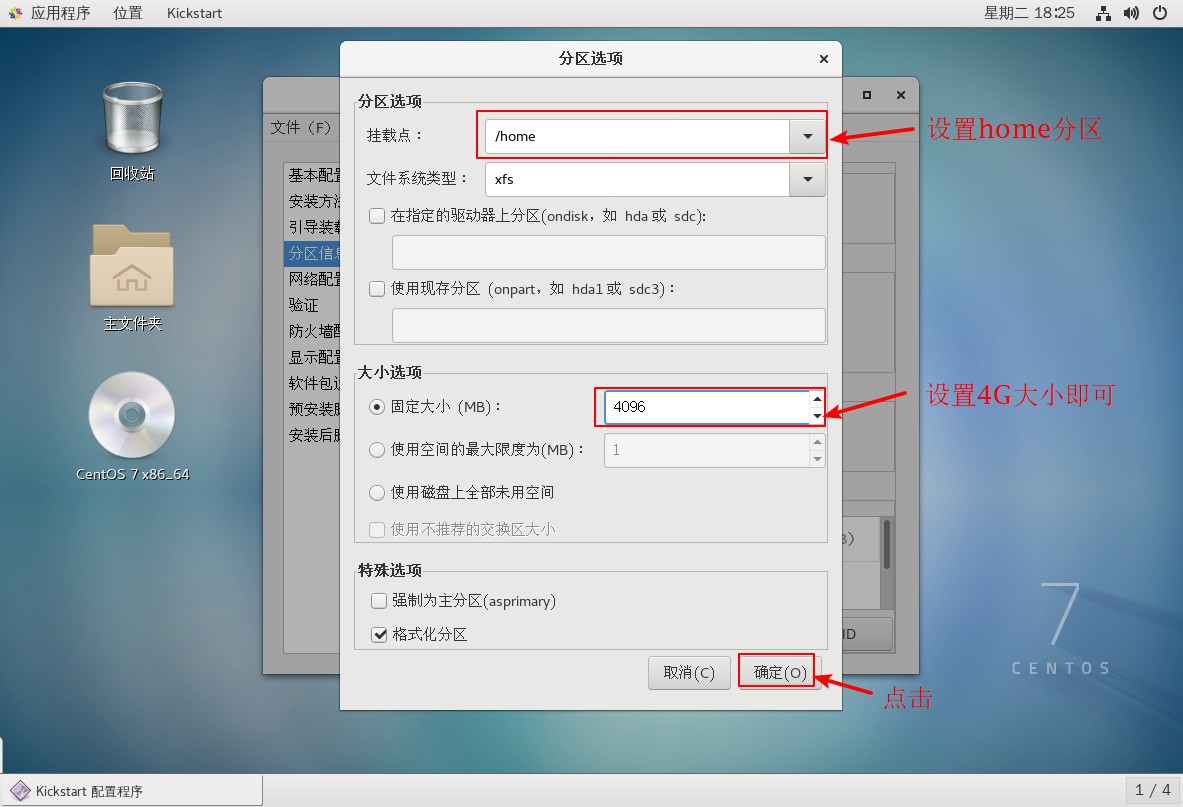
5. Set up partition information


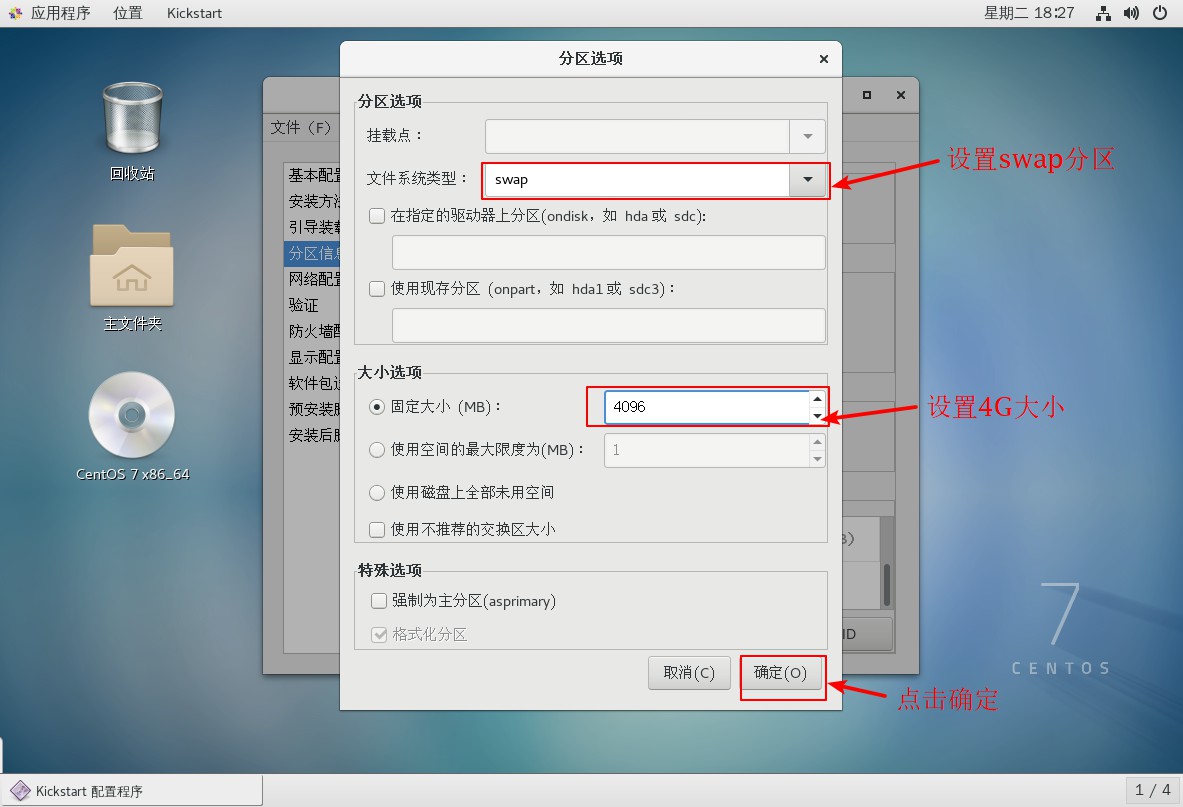
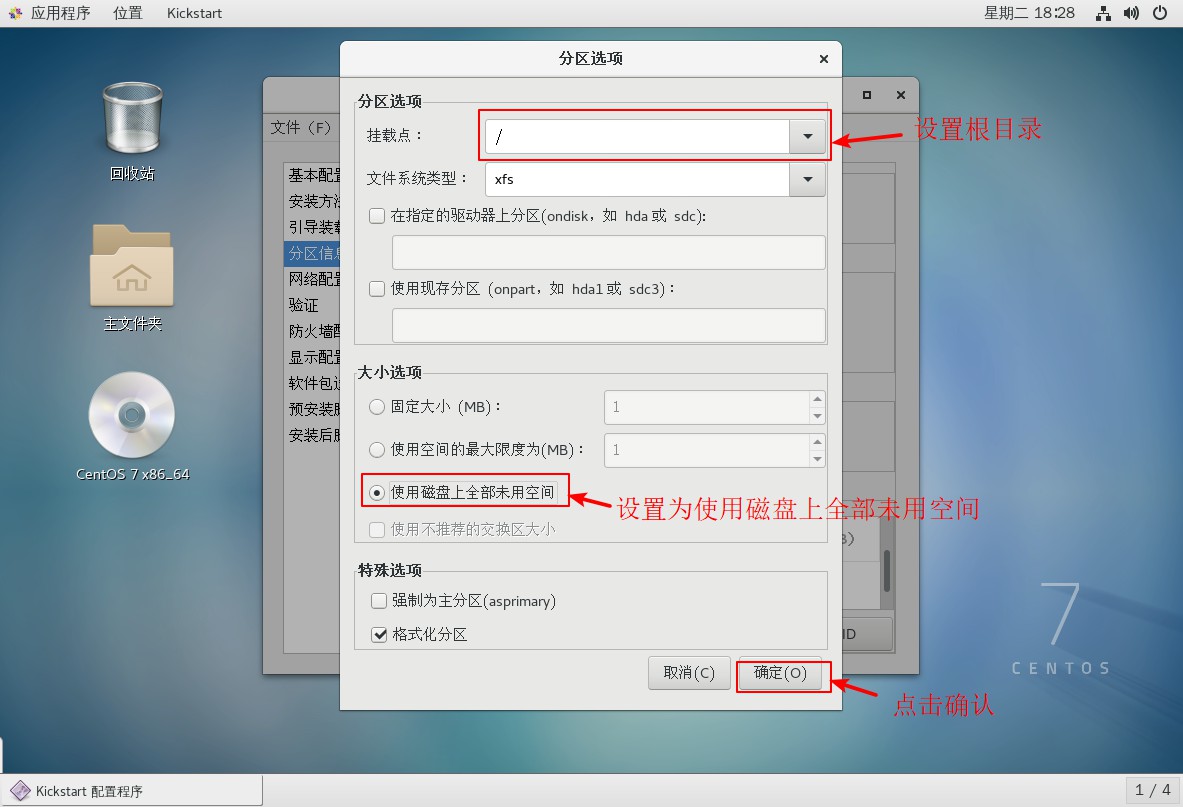
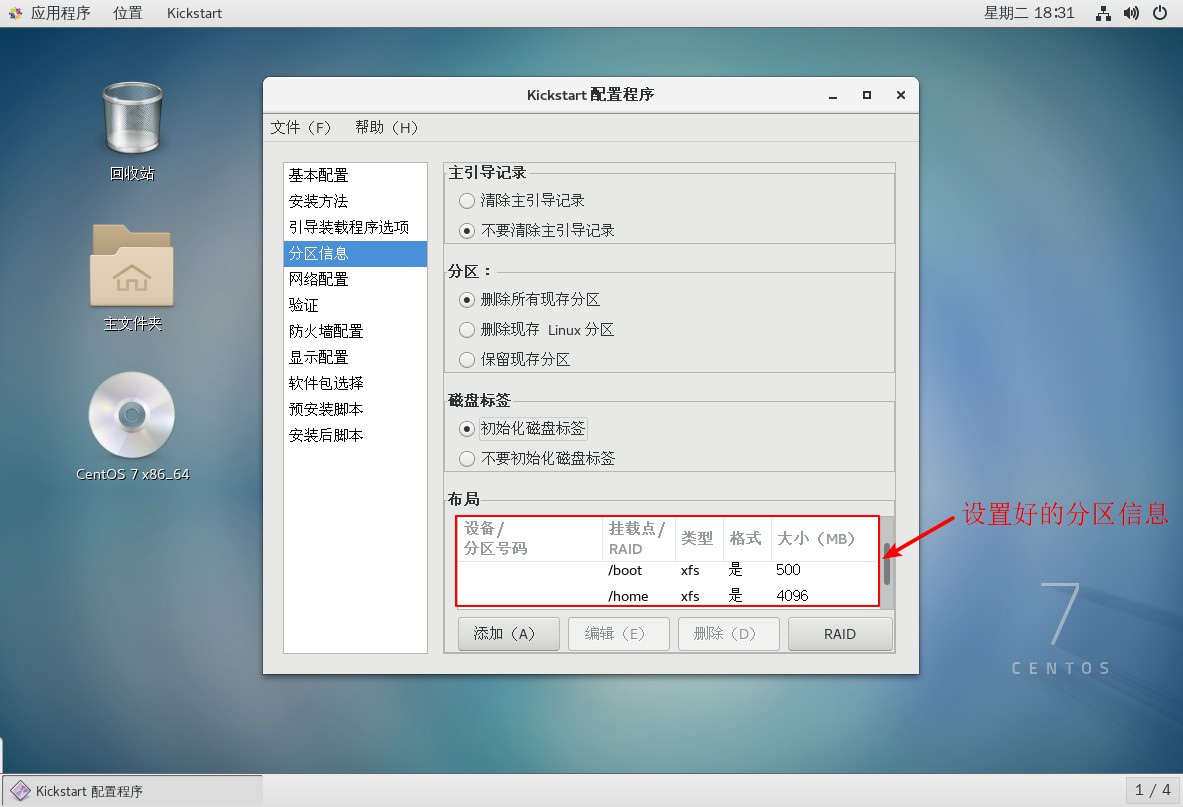
6. Set up network card configuration

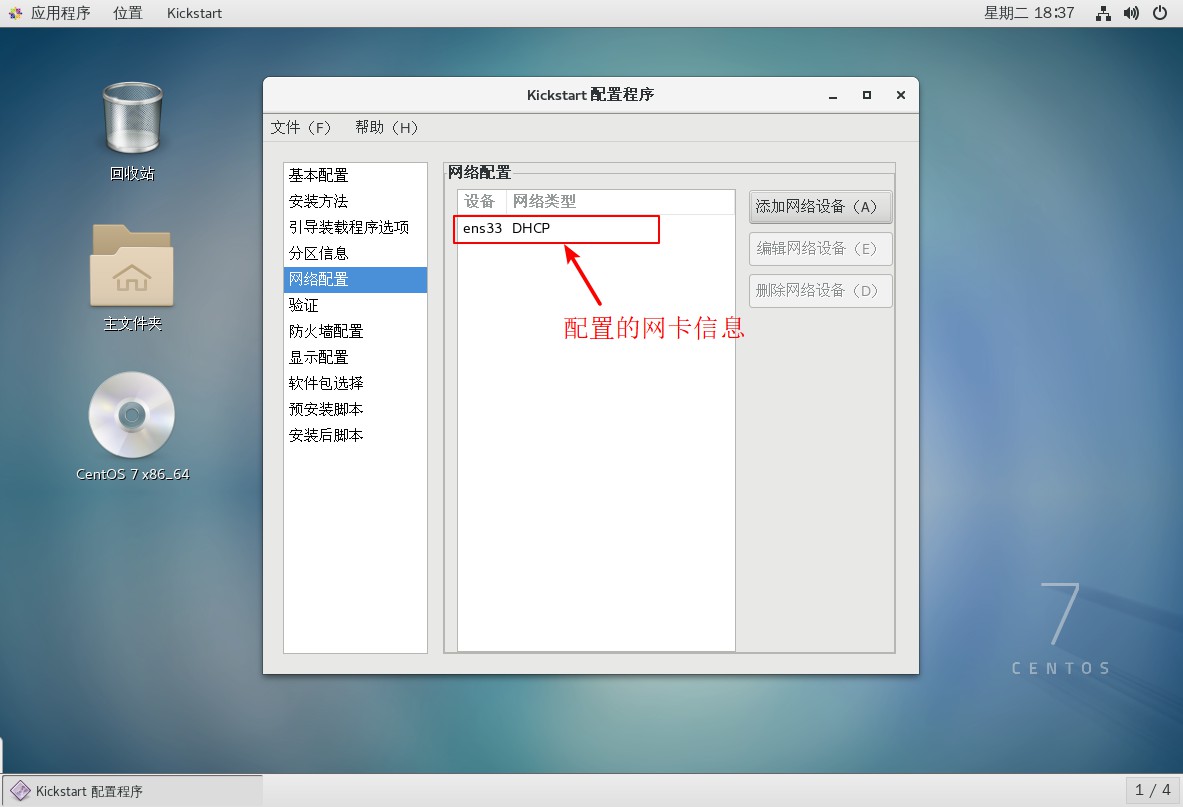
7. Configure post-installation script information

8. Save the configured file information to the FTP site after completion
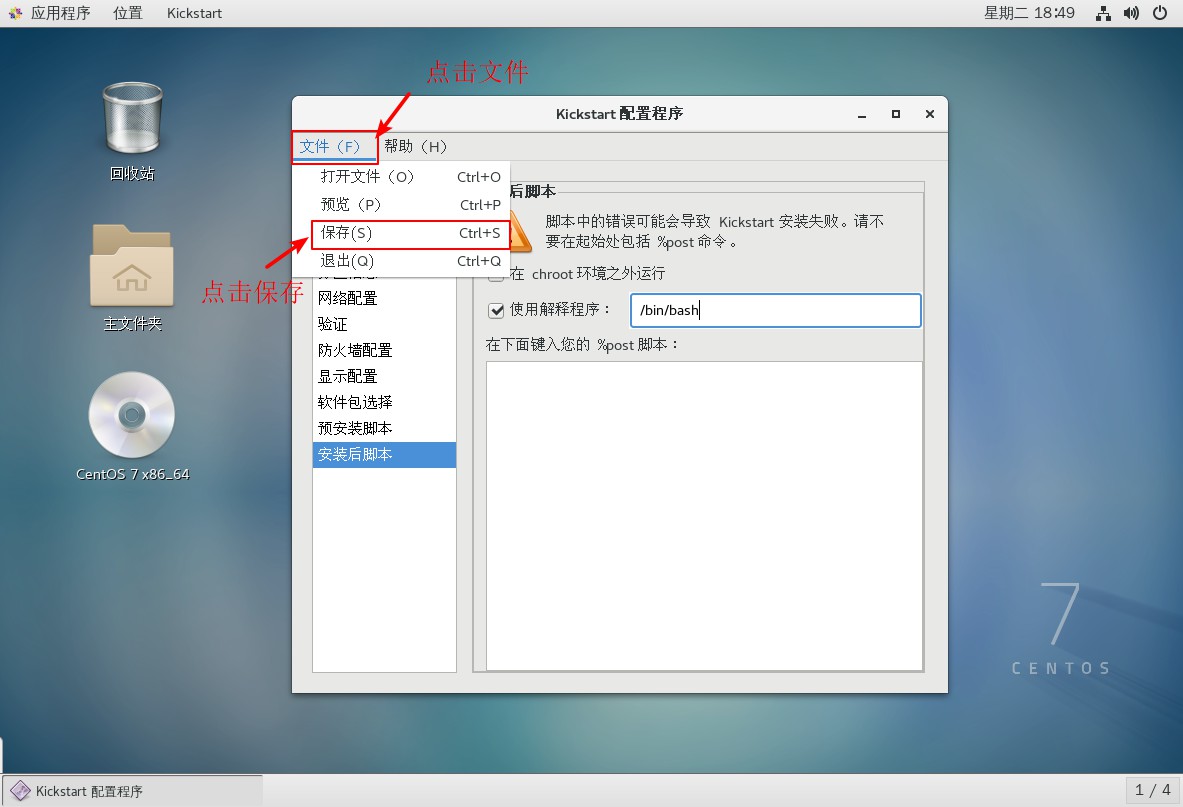
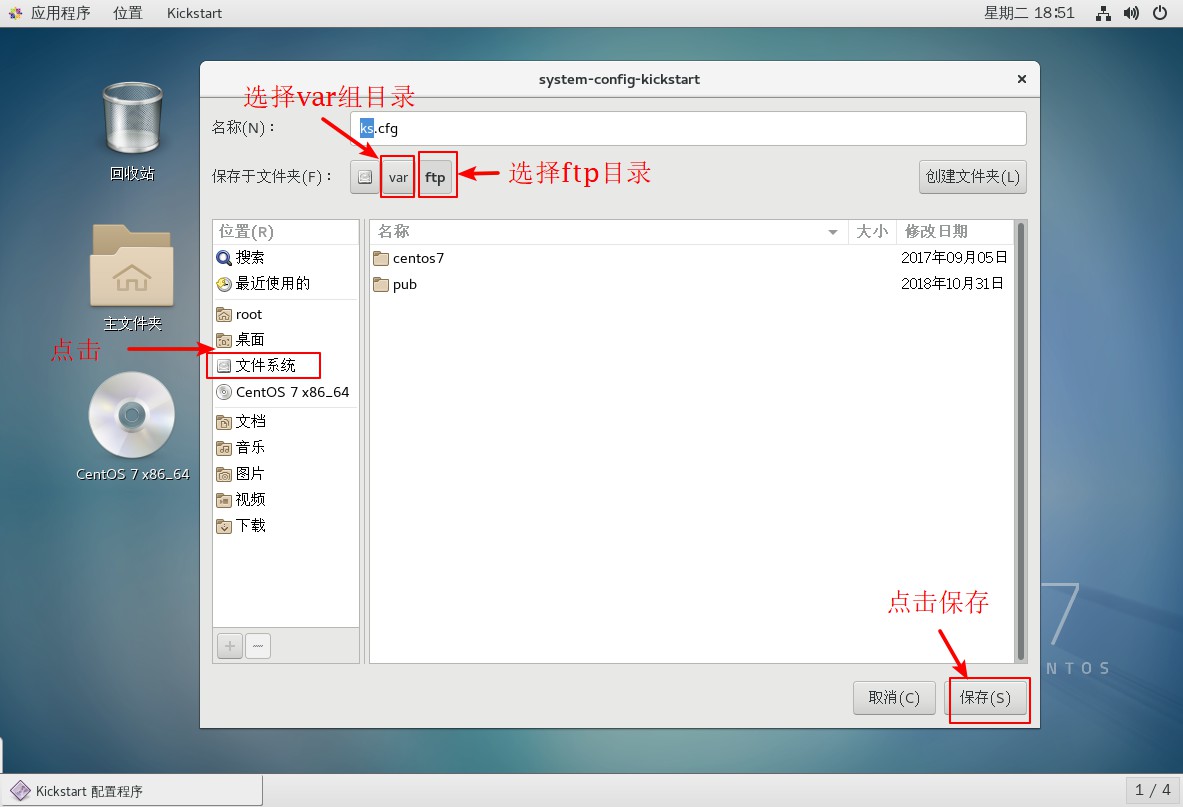
9. Close the software after saving, open the terminal, go to the ftp site to view the saved file, go to view the file, and add the required component installation package to the template.
[root@localhost ~]# Cd/var/ftp //Enter FTP site [root@localhost ftp]# ls //View directory information centos7 ks.cfg pub [root@localhost ftp]# vim ks.cfg //Enter edit mode to view saved template information platform=x86, AMD64, or Intel EM64T #version=DEVEL # Install OS instead of upgrade install # Keyboard layouts keyboard 'us' # Root password rootpw --iscrypted $1$QnfXQpTo$2SWg34gaOZQoLWy.bGlmd/ //root user key template # Use network installation url --url="ftp://192.168.100.100/centos7 "//Installation Path Template # System language lang zh_CN //Set Keyboard Mode # Firewall configuration firewall --disabled # System authorization information auth --useshadow --passalgo=sha512 # Use graphical install graphical firstboot --disable # SELinux configuration selinux --enforcing # Network information network --bootproto=dhcp --device=ens33 //Setup Network Card Information # Reboot after installation reboot # System timezone timezone Asia/Shanghai # System bootloader configuration bootloader --location=none # Partition clearing information clearpart --all --initlabel # Disk partitioning information part /boot --fstype="xfs" --size=500 //Disk Partition Setup Template part /home --fstype="xfs" --size=4096 part swap --fstype="swap" --size=4096 part / --fstype="xfs" --grow --size=1 :q //Exit Template [root@localhost ftp]# Cd/root//enter root user home directory [root@localhost ~]# ls //View Home Directory Information anaconda-ks.cfg Public Video Document Music //Find the anaconda-ks.cfg template initial-setup-ks.cfg Template Picture Download Desktop [root@localhost ~]# vim anaconda-ks.cfg //Enter editing anaconda-ks.cfg template ...//Omit some content... %packages @^gnome-desktop-environment @base @core @desktop-debugging @dial-up @directory-client @fonts @gnome-desktop @guest-agents //Find this part of the information and copy it @guest-desktop-agents @input-methods @internet-browser @java-platform @multimedia @network-file-system-client @networkmanager-submodules @print-client @x11 chrony kexec-tools %end ...//Omit some content... :q //Sign out [root@localhost ~]# Vim/var/ftp/ks.cfg //Enter FTP site, edit ks.cfg file part /boot --fstype="xfs" --size=500 part /home --fstype="xfs" --size=4096 part swap --fstype="swap" --size=4096 part / --fstype="xfs" --grow --size=1 %packages @^gnome-desktop-environment @base @core @desktop-debugging @dial-up @directory-client @fonts //Paste this section below @gnome-desktop @guest-agents @guest-desktop-agents @input-methods @internet-browser @java-platform @multimedia @network-file-system-client @networkmanager-submodules @print-client @x11 chrony kexec-tools %end ~ :wq //Save Exit
10. Add ks.cfg file boot entries to the tftp site boot menu file.
[root@localhost ~]# Cd/var/lib/tftpboot/ //Enter the tftp site
[root@localhost tftpboot]# ls //View site information
initrd.img pxelinux.0 pxelinux.cfg vmlinuz
[root@localhost tftpboot]# cd pxelinux.cfg/ //Enter directory
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# ls
default
[root@localhost pxelinux.cfg]# vim default //Enter Edit Startup Menu File
default auto
prompt 1
label auto
kernel vmlinuz //Add ks=ftp://192.168.100.100/ks.cfg entry so that the ks.cfg template content can be read by the system at installation time
append initrd=initrd.img method=ftp://192.168.100.100/centos7 ks=ftp://192.168.100.100/ks.cfg
label linux text
kernel vmlinuz
append text initrd=initrd.img method=ftp://192.168.100.100/centos7
label linux rescue
kernel vmlinuz
append rescue initrd=initrd.img method=ftp://192.168.100.100/centos7
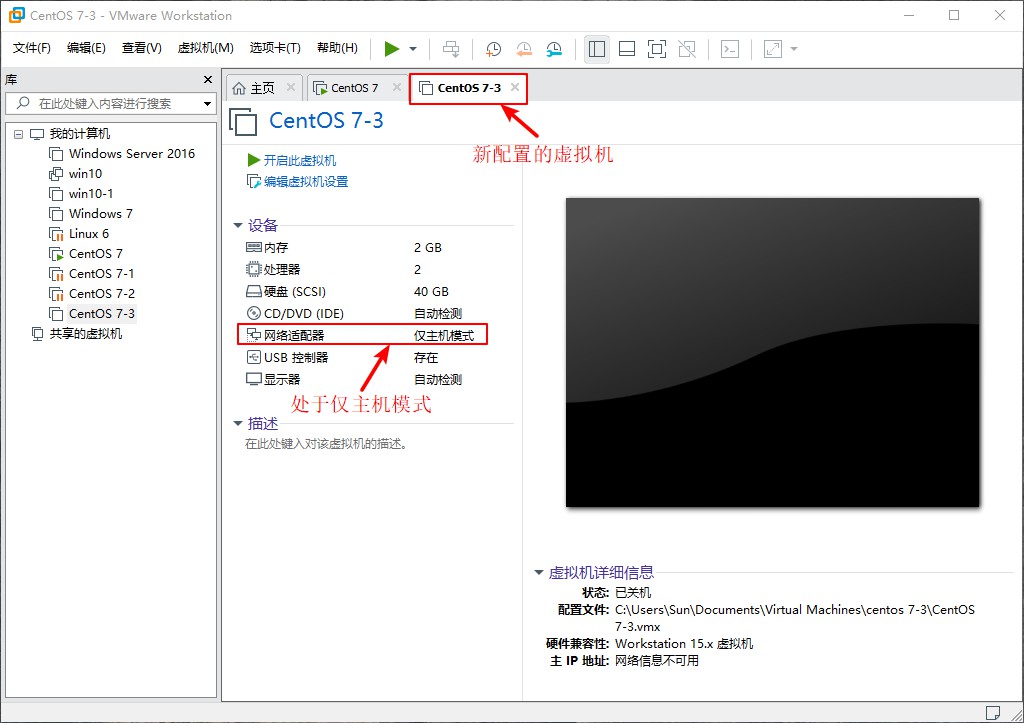
:wq //Save Exit11. Configure a new virtual machine, set the network card to host-only mode, and then verify the PXE deployment setup + kickstart unattended setup.