Articles Catalogue
Introduction to OpenResty
OpenResty (also known as ngx_openresty) is a scalable Web platform based on NGINX, initiated by Chinese Zhang Yichun, which provides many high-quality third-party modules.
OpenResty is a powerful Web application server. Web developers can use Lua scripting language to mobilize all kinds of C and Lua modules supported by Nginx. More importantly, in terms of performance, OpenResty can quickly construct ultra-high performance Web application systems that are capable of concurrent connection response over 10K.
Analog cache forward
- 1. nginx services opened under lnmp architecture before closing
nginx -s stop
- 2. Decompress and compile the original package of OpenResty downloaded from the official website
Note: The compilation and installation of OpenResty uses gmake
tar zxf openresty-1.13.6.1.tar.gz cd openresty-1.13.6.1 ./configure gmake && gmake install
- 3. Copy the two php files used by memcache for testing to the default release directory of OpenResty's Nginx
cp /usr/local/lnmp/nginx/html/example.php /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html cp /usr/local/lnmp/nginx/html/memcache.php /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html
- 4. Edit the nginx configuration file for openresty
vim /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
Write in:
http {
upstream memcache { ##All requests are forwarded to the memcache cache cache service
server localhost:11211; ##The memcache service is on port 11211 of this machine
keepalive 512;
}
location /memc { ##Setting up access and storage of memcache
internal; ##Only internal
memc_connect_timeout 100ms; #Define connection sending and its timeout
memc_send_timeout 100ms;
memc_read_timeout 100ms;
set $memc_key $query_string; #memcache is stored as key-value pairs
set $memc_exptime 300;
memc_pass memcache;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
set $key $uri$args;
srcache_fetch GET /memc $key;
srcache_store PUT /memc $key;
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
#fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi.conf; ##Define files identified when nginx is connected to php
}
The parameters of the configuration file are detailed as follows:
- upstream module interface
Essentially, upstream belongs to handler, but it does not produce its own content, but gets the content by requesting the back-end server, so it is called upstream. The whole process of requesting and obtaining the response content has been encapsulated in nginx, so upstream module only needs to develop several callback functions to complete the specific work of constructing the request and analyzing the response.
All requests operate on memcache through location, and memc-nginx-module accesses memcache based on http method semantics
The GET method of http is used to represent get, the PUT method is used to represent set, and the caching method of memcache is set to accept internal access only.
memc_key denotes what is the key, query_string is used as the key in the file, and $memc_exptime denotes the cache expiration time in seconds.
- 5. Check the configuration file for errors and open the service
[root@LNMPserver1 html]# /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
- 6. Open the service and view the port
[root@LNMPserver1 html]# /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx [root@LNMPserver1 html]# netstat -tnlp Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:11211 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6843/memcached tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 15320/nginx tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5089/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 962/master tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6748/php-fpm tcp 0 0 :::11211 :::* LISTEN 6843/memcached tcp 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 5089/sshd tcp 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 962/master tcp 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 31925/mysqld
- 7. Browser View
So far, combined with OpenResty's cache forward has been done, let's summarize and analyze it.
Analysis
The main thing we have done here is to specify upstream memcache in OpenResty's nginx configuration file, which is why we use OpenResty because it integrates modules such as memcache. We can clearly understand from its configuration file that all requests will go through port 11211 of the local memcache. And
location ~ \.php$ {
set $key $uri$args;
srcache_fetch GET /memc $key;
srcache_store PUT /memc $key;
All pages accessing the end of.php are specified here, which are fetched from / memc and saved if not. So, we're going to move memcache forward to where Nginx accepts requests.
Stress testing
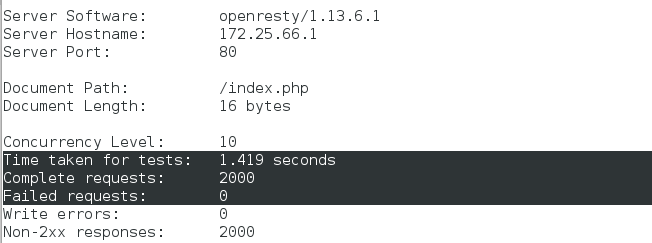
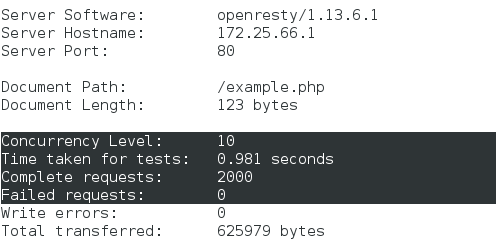
We tested it again on real hosts:
ab -c 10 -n 2000 http://172.25.66.1/index.php ab -c 10 -n 2000 http://172.25.66.1/example.php
It can be found that the response time and accuracy of both pages have been improved qualitatively. The example.php page with two-level memcache is faster.