The article started with me Personal Blog
Preface
Last article: ' Chrome Dinosaur Game Source Exploration Seven--Alternating Day and Night Modes In this article, the following will be achieved: 1. Drawing of small dinosaurs 2. Keyboard control of small dinosaurs 3. Page defocusing will reset the state of small dinosaurs
Draw static Dinosaurs
Define small dinosaurs:
/** * Small Dinosaurs * @param {HTMLCanvasElement} canvas canvas * @param {Object} spritePos Picture coordinates in Sprite */ function Trex(canvas, spritePos) { this.canvas = canvas; this.ctx = canvas.getContext('2d'); this.spritePos = spritePos; this.xPos = 0; this.yPos = 0; this.groundYPos = 0; // y-coordinate of a small dinosaur on the ground this.currentFrame = 0; // Current animation frame this.currentAnimFrames = []; // Stores the x-coordinate of the animated frame in the current state on the Sprite chart this.blinkDelay = 0; // Time between blinks (random) this.blinkCount = 0; // blink response this.animStartTime = 0; // Start time of the little dinosaur blink animation this.timer = 0; // timer this.msPerFrame = 1000 / FPS; // frame rate this.status = Trex.status.WAITING; // Current status this.config = Trex.config; this.jumping = false; // Whether to skip this.ducking = false; // Whether to dodge (lean down) this.jumpVelocity = 0; // The speed of the jump this.reachedMinHeight = false; // Is minimum height reached this.speedDrop = false; // Whether to accelerate the decline this.jumpCount = 0; // Number of skips this.jumpspotX = 0; // x-coordinate of jump point this.init(); }
Related configuration parameters:
Trex.config = { GRAVITY: 0.6, // gravitation WIDTH: 44, // Width when standing HEIGHT: 47, WIDTH_DUCK: 59, // Width at bend HEIGHT_DUCK: 25, MAX_JUMP_HEIGHT: 30, // Maximum Jump Height MIN_JUMP_HEIGHT: 30, // Minimum Jump Height SPRITE_WIDTH: 262, // Total width of a standing dinosaur in a sprite map DROP_VELOCITY: -5, // Falling speed INITIAL_JUMP_VELOCITY: -10, // Initial Jump Speed SPEED_DROP_COEFFICIENT: 3, // Acceleration factor when falling (the larger the falling the faster) INTRO_DURATION: 1500, // Time of opening animation START_X_POS: 50, // The x-coordinate of the dinosaur on canvas after the opening animation }; Trex.BLINK_TIMING = 7000; // Maximum time between blinks // The state of small dinosaurs Trex.status = { CRASHED: 'CRASHED', // Hit an obstacle DUCKING: 'DUCKING', // Avoiding (leaning down) JUMPING: 'JUMPING', // Jumping RUNNING: 'RUNNING', // Running WAITING: 'WAITING', // Waiting (no game started) }; // Configure different animation frames for different states Trex.animFrames = { WAITING: { frames: [44, 0], msPerFrame: 1000 / 3 }, RUNNING: { frames: [88, 132], msPerFrame: 1000 / 12 }, CRASHED: { frames: [220], msPerFrame: 1000 / 60 }, JUMPING: { frames: [0], msPerFrame: 1000 / 60 }, DUCKING: { frames: [264, 323], msPerFrame: 1000 / 8 }, };
To supplement some of the data used in this article:
Runner.config = { // ... BOTTOM_PAD: 10, // Distance of small dinosaurs from the bottom of canvas MAX_BLINK_COUNT: 3, // Maximum Number of Blinks of Little Dinosaurs }; Runner.spriteDefinition = { LDPI: { // ... TREX: {x: 848, y: 2}, // Small Dinosaurs }, };
Then look at the methods on the Trex prototype chain.Let's start by drawing small, static dinosaurs:
Trex.prototype = { init: function() { // Getting y-coordinates of a small dinosaur standing on the ground this.groundYPos = Runner.defaultDimensions.HEIGHT - this.config.HEIGHT - Runner.config.BOTTOM_PAD; this.yPos = this.groundYPos; // y-coordinate initialization of small dinosaurs this.draw(0, 0); // Draw the first picture of a small dinosaur }, /** * Draw Little Dinosaurs * @param {Number} x The x-coordinate of the current frame relative to the first frame * @param {Number} y y-coordinate of current frame relative to first frame */ draw: function(x, y) { // Coordinates in Sprite var sourceX = x + this.spritePos.x; var sourceY = y + this.spritePos.y; // Width and height in Sprite var sourceWidth = this.ducking && this.status != Trex.status.CRASHED ? this.config.WIDTH_DUCK : this.config.WIDTH; var sourceHeight = this.config.HEIGHT; // Height when drawn on canvas var outputHeight = sourceHeight; // Avoidance state. if (this.ducking && this.status != Trex.status.CRASHED) { this.ctx.drawImage( Runner.imageSprite, sourceX, sourceY, sourceWidth, sourceHeight, this.xPos, this.yPos, this.config.WIDTH_DUCK, outputHeight ); } else { // Hit an obstacle while dodging if (this.ducking && this.status == Trex.status.CRASHED) { this.xPos++; } // Running Status this.ctx.drawImage( Runner.imageSprite, sourceX, sourceY, sourceWidth, sourceHeight, this.xPos, this.yPos, this.config.WIDTH, outputHeight ); } this.ctx.globalAlpha = 1; }, };
In the previous chapter into arcade mode, you used data from the Trex class and temporarily defined the Trex class, so don't forget to delete it.
Next, you need to call the Trex class through the Runner class.Add attributes to store instances of small dinosaurs:
function Runner(containerSelector, opt_config) { // ... + this.tRex = null; // Small Dinosaurs }
Initialize small dinosaurs:
Runner.prototype = { init: function () { // ... // Loading small dinosaurs + this.tRex = new Trex(this.canvas, this.spriteDef.TREX); }, };
This draws a static dinosaur when the game is initialized, as shown in the following figure:

To achieve blinking effect
When the game is initialized, the little dinosaurs blink randomly.The default is to blink at most three times.This effect will be achieved below.
Add a way to update the dinosaurs:
Trex.prototype = { /** * Update Little Dinosaurs * @param {Number} deltaTime Interval Time * @param {String} opt_status The state of small dinosaurs */ update: function(deltaTime, opt_status) { this.timer += deltaTime; // Parameters to update status if (opt_status) { this.status = opt_status; this.currentFrame = 0; this.msPerFrame = Trex.animFrames[opt_status].msPerFrame; this.currentAnimFrames = Trex.animFrames[opt_status].frames; if (opt_status == Trex.status.WAITING) { this.animStartTime = getTimeStamp(); // Set the time at which the blink animation begins this.setBlinkDelay(); // Set the time between blinks } } if (this.status == Trex.status.WAITING) { // Little Dinosaur Blinking this.blink(getTimeStamp()); } else { // Draw animation frames this.draw(this.currentAnimFrames[this.currentFrame], 0); } if (this.timer >= this.msPerFrame) { // Update the current animation frame, if at the last frame, to the first frame, otherwise to the next frame this.currentFrame = this.currentFrame == this.currentAnimFrames.length - 1 ? 0 : this.currentFrame + 1; // Reset timer this.timer = 0; } }, // Set the time between blinks setBlinkDelay: function() { this.blinkDelay = Math.ceil(Math.random() * Trex.BLINK_TIMING); }, // Little Dinosaur Blinking blink: function (time) { var deltaTime = time - this.animStartTime; // The interval is longer than the randomly obtained blink interval to blink if (deltaTime >= this.blinkDelay) { this.draw(this.currentAnimFrames[this.currentFrame], 0); // Blinking if (this.currentFrame == 1) { console.log('Blink'); this.setBlinkDelay(); // Reset blink interval time this.animStartTime = time; // Update the start time of blink animation this.blinkCount++; // Blinks plus one } } }, };
Then the baby dinosaurs are initially updated to wait:
Trex.prototype = { init: function () { // ... this.update(0, Trex.status.WAITING); // Initially in a waiting state }, };
Finally, in Runner's update method, Trex's update method is called to blink the little dinosaur:
Runner.prototype = { update: function () { // ... // The game starts or the little dinosaur hasn't blinked three times - if (this.playing) { + if (this.playing || (!this.activated && + this.tRex.blinkCount < Runner.config.MAX_BLINK_COUNT)) { + this.tRex.update(deltaTime); // Make the next update this.scheduleNextUpdate(); } }, };
The results are as follows:

You can see that the code logic for blinking triggered three times, but the actual dinosaur blinked only once.That's what we said before. By default, small dinosaurs can only blink up to three times.The specific reasons are as follows:
Let's start with this code in Trex's update method:
if (this.timer >= this.msPerFrame) { // Update the current animation frame, if at the last frame, to the first frame, otherwise to the next frame this.currentFrame = this.currentFrame == this.currentAnimFrames.length - 1 ? 0 : this.currentFrame + 1; // Reset timer this.timer = 0; }
This code keeps the current animation frame updated to the next frame.For small dinosaurs, the two frames of open and close eyes are constantly switched.If the current frame is "open eyes", then the little dinosaur will still be open after the blink function is executed, that is, the actual little dinosaur did not blink; similarly, only when the current frame is "closed eyes", will the little dinosaur blink truly.
As for the purpose, it is to prevent the small dinosaurs from blinking.For example, modify the blink function to:
// Little Dinosaur Blinking blink: function () { this.draw(this.currentAnimFrames[this.currentFrame], 0); },
So the little dinosaurs keep blinking.So you need to restrict it, here's what the Chrome developers do: set an interval to allow a small dinosaur to blink when the interval between blinks is longer than this and the current animation frame is "closed eyes".Then after each blink, the random blinks of the dinosaurs were achieved by resetting the blink interval (default set to 0-7 seconds).
Starting animation of a small dinosaur
Here's how the little dinosaur responds to keyboard keystrokes.
First, when the game egg is triggered, the little dinosaur jumps once and moves 50 pixels to the right (the default setting is 50 pixels).
Add a way for the little dinosaurs to start jumping:
Trex.prototype = { // Start jumping startJump: function(speed) { if (!this.jumping) { // Update Little Dinosaurs to Jump this.update(0, Trex.status.JUMPING); // Adjust the speed of the jump according to the speed of the game this.jumpVelocity = this.config.INITIAL_JUMP_VELOCITY - (speed / 10); this.jumping = true; this.reachedMinHeight = false; this.speedDrop = false; } }, };
To invoke:
Runner.prototype = { onKeyDown: function (e) { if (!this.crashed && !this.paused) { if (Runner.keyCodes.JUMP[e.keyCode]) { e.preventDefault(); // ... // Start jumping + if (!this.tRex.jumping && !this.tRex.ducking) { + this.tRex.startJump(this.currentSpeed); + } } } }, };
In this way, the little dinosaur will remain stationary on the ground after pressing the space bar.Next, the animation frame needs to be updated to animate the little dinosaur running.
Add a way to update the animation frame of a small dinosaur:
Trex.prototype = { // Update the animation frame of a small dinosaur jumping updateJump: function(deltaTime) { var msPerFrame = Trex.animFrames[this.status].msPerFrame; // Get the frame rate of the current state var framesElapsed = deltaTime / msPerFrame; // Accelerated drop if (this.speedDrop) { this.yPos += Math.round(this.jumpVelocity * this.config.SPEED_DROP_COEFFICIENT * framesElapsed); } else { this.yPos += Math.round(this.jumpVelocity * framesElapsed); } // The speed of the jump is influenced by gravity, decreasing upwards and then reversing this.jumpVelocity += this.config.GRAVITY * framesElapsed; // Minimum allowed jump height reached if (this.yPos < this.minJumpHeight || this.speedDrop) { this.reachedMinHeight = true; } // The maximum allowable jump height has been reached if (this.yPos < this.config.MAX_JUMP_HEIGHT || this.speedDrop) { this.endJump(); // End Jump } // Return to the ground, jump complete if (this.yPos > this.groundYPos) { this.reset(); // Reset the status of the baby dinosaurs this.jumpCount++; // Number of jumps plus one } }, // End of Jump endJump: function() { if (this.reachedMinHeight && this.jumpVelocity < this.config.DROP_VELOCITY) { this.jumpVelocity = this.config.DROP_VELOCITY; // Drop Speed Reset to Default } }, // Reset Little Dinosaur State reset: function() { this.yPos = this.groundYPos; this.jumpVelocity = 0; this.jumping = false; this.ducking = false; this.update(0, Trex.status.RUNNING); this.speedDrop = false; this.jumpCount = 0; }, };
The attribute value of minJumpHeight is:
Trex.prototype = { init: function() { // Minimum Jump Height + this.minJumpHeight = this.groundYPos - this.config.MIN_JUMP_HEIGHT; // ... }, }
Then make a call:
Runner.prototype = { update: function () { // ... if (this.playing) { this.clearCanvas(); + if (this.tRex.jumping) { + this.tRex.updateJump(deltaTime); + } this.runningTime += deltaTime; var hasObstacles = this.runningTime > this.config.CLEAR_TIME; // this.playingIntro was not defined at first! this.playingIntro is true - if (!this.playingIntro) { + if (this.tRex.jumpCount == 1 && !this.playingIntro) { this.playIntro(); // Perform opening animation } // ... } // ... }, };
This way, after pressing the space bar, the little dinosaur will jump once and run animation.Figure:

Here's how it works: After the first jump, the little dinosaur moves 50 pixels to the right.
Modify Trex's update method.Move the little dinosaur when you know the opening animation is being performed:
Trex.prototype = { update: function(deltaTime, opt_status) { this.timer += deltaTime; // Parameters to update status if (opt_status) { // ... } // Performing opening animation, moving the little dinosaur 50 pixels to the right + if (this.playingIntro && this.xPos < this.config.START_X_POS) { + this.xPos += Math.round((this.config.START_X_POS / + this.config.INTRO_DURATION) * deltaTime); + } // ... }, };
You can see that when the playingIntro attribute is true, the small dinosaurs move to the right.So control the movement of the small dinosaurs after their first jump by controlling the value of this property.
Modify the playIntro method on Runner to mark the small dinosaurs as performing the opening animation:
Runner.prototype = { playIntro: function () { if (!this.activated && !this.crashed) { + this.tRex.playingIntro = true; // Small Dinosaurs Perform Opening Animations // ... } }, };
Then you need to end the opening animation of the little dinosaur after you start the game, that is, when you execute the startGame method:
Runner.prototype = { startGame: function () { this.setArcadeMode(); // Enter arcade mode + this.tRex.playingIntro = false; // The opening animation of a small dinosaur ends // ... }, };
The results are as follows:

It is clear that the little dinosaur moved a distance to the right after its first jump (the default is 50 pixels).
Keyboard control of small dinosaurs
In this game, when the_key is pressed, if the small dinosaur is jumping, it will fall down quickly. If the small dinosaur is on the ground, it will enter a dodging state, to achieve these effects below.
Accelerated drop:
Trex.prototype = { // Set the little dinosaur to drop faster and cancel the current jump immediately setSpeedDrop: function() { this.speedDrop = true; this.jumpVelocity = 1; }, };
Set whether the little dinosaurs are dodging:
Trex.prototype = { // Set up whether the little dinosaurs are dodging while running setDuck: function(isDucking) { if (isDucking && this.status != Trex.status.DUCKING) { // Dodge state this.update(0, Trex.status.DUCKING); this.ducking = true; } else if (this.status == Trex.status.DUCKING) { // Running Status this.update(0, Trex.status.RUNNING); this.ducking = false; } }, };
Called in the onKeyDown method:
Runner.prototype = { onKeyDown: function () { if (!this.crashed && !this.paused) { if (Runner.keyCodes.JUMP[e.keyCode]) { // ... + } else if (this.playing && Runner.keyCodes.DUCK[e.keyCode]) { + e.preventDefault(); + + if (this.tRex.jumping) { + this.tRex.setSpeedDrop(); // Accelerated drop + } else if (!this.tRex.jumping && !this.tRex.ducking) { + this.tRex.setDuck(true); // Enter dodging state + } + } } }, };
This achieves the effect mentioned above.But when the little dinosaur dodges, it doesn't get up again if it releases the key.Because there is no defined event to respond when keyboard keys are released.Define it below:
Runner.prototype = { onKeyUp: function(e) { var keyCode = String(e.keyCode); if (Runner.keyCodes.DUCK[keyCode]) { // Avoidance state this.tRex.speedDrop = false; this.tRex.setDuck(false); } }, };
Then call to modify the handleEvent method:
Runner.prototype = { handleEvent: function (e) { return (function (eType, events) { switch (eType) { // ... + case events.KEYUP: + this.onKeyUp(e); + break; default: break; } }.bind(this))(e.type, Runner.events); }, };
The results are as follows:
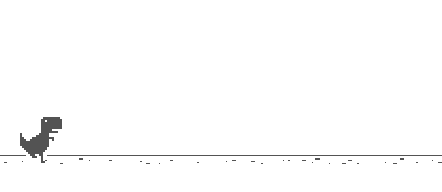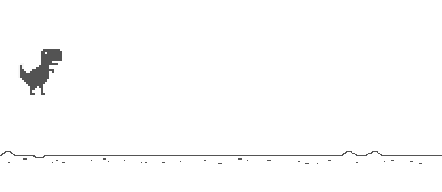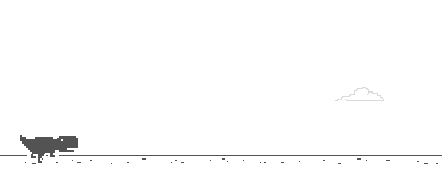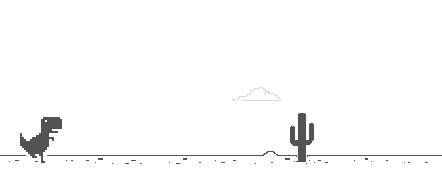
The first jump is a normal fall, the second is an accelerated fall
Handle the jumps of small dinosaurs
Small dinosaur jumps are divided into big jumps and small jumps, as shown in the figure:

To achieve this effect, you only need to end the jump of the small dinosaur as soon as the_key is released.
Modify the onKeyUp method:
Runner.prototype = { onKeyUp: function(e) { var keyCode = String(e.keyCode); + var isjumpKey = Runner.keyCodes.JUMP[keyCode]; + if (this.isRunning() && isjumpKey) { // jump + this.tRex.endJump(); } else if (Runner.keyCodes.DUCK[keyCode]) { // Avoidance state this.tRex.speedDrop = false; this.tRex.setDuck(false); } }, };
The isRunning method is defined as follows:
Runner.prototype = { // Is the game in progress isRunning: function() { return !!this.raqId; }, };
This allows the small dinosaurs to do big and small jumps.
Finally, the effect is that if the page is out of focus and the little dinosaur is jumping, it resets its state (that is, it immediately returns to the ground).This effect is easy to achieve by calling the reset method defined earlier:
Runner.prototype = { play: function () { if (!this.crashed) { // ... + this.tRex.reset(); } }, };
The results are as follows:
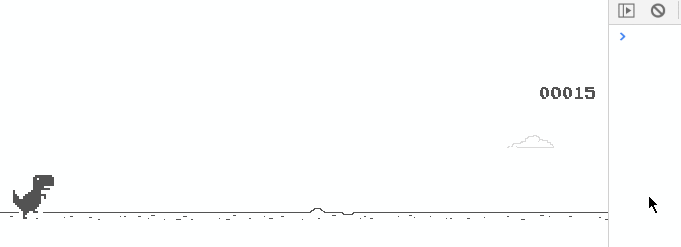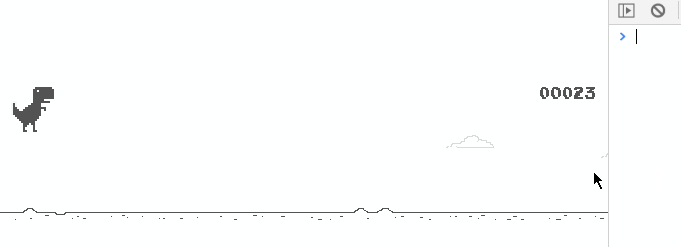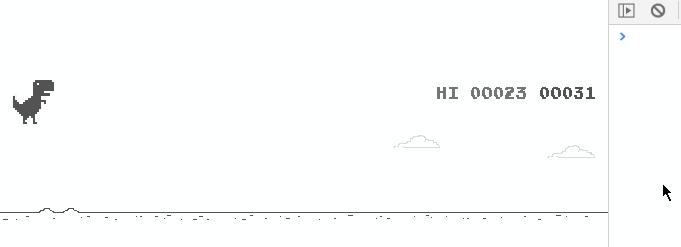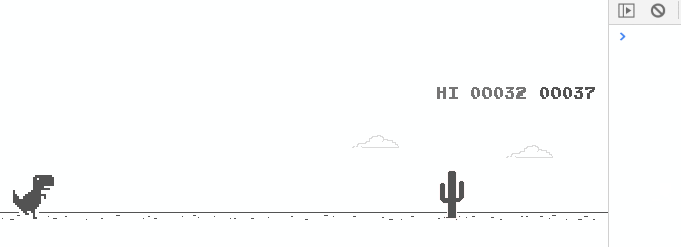
View the added code, Stamp here
Demo experience address: https://liuyib.github.io/pages/demo/games/google-dino/dino-gogogo/
| Previous | Next | Chrome Dinosaur Game Source Exploration Seven--Alternating Day and Night Modes | TODO |