Example:
First, create a new table and insert values:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table_score_one;
CREATE TABLE table_score_one (
id INT (10) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
student_no VARCHAR (10) NOT NULL,
student_name VARCHAR (10) NOT NULL,
class_no VARCHAR (10) NOT NULL,
class_name VARCHAR (10) NOT NULL,
score INT (10) NOT NULL
) DEFAULT CHARSET='utf8';
INSERT INTO `table_score_one` VALUES ('1', '201601', 'Zhang San', '0001', 'Mathematics', '98');
INSERT INTO `table_score_one` VALUES ('2', '201601', 'Zhang San', '0002', 'Chinese', '66');
INSERT INTO `table_score_one` VALUES ('3', '201602', 'Li Si', '0001', 'Mathematics', '60');
INSERT INTO `table_score_one` VALUES ('4', '201602', 'Li Si', '0003', 'English?', '78');
INSERT INTO `table_score_one` VALUES ('5', '201603', 'Wang Wu', '0001', 'Mathematics', '99');
INSERT INTO `table_score_one` VALUES ('6', '201603', 'Wang Wu', '0002', 'Chinese', '99');
INSERT INTO `table_score_one` VALUES ('7', '201603', 'Wang Wu', '0003', 'English?', '98');Where auto_increment represents the sequential generation of values. The default starts from 1.
The table is as follows: 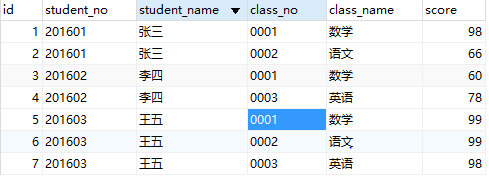
The second step updates the value:
update table_score_one set class_name ='Mathematics' , class_no = '0001' where id = 6;As shown in the picture: 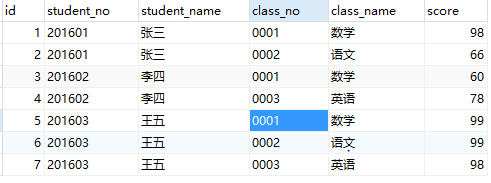
The third step:
Delete all the same data except the id.
delete table_test_one where id not in (select min(id) from table_test_one group by student_no, student_name, class_no, class_name, score);The above statement means: first, by grouping according to student_no, student_name, class_no, class_name and score, we can find the smallest id of each group, and then delete the id that is not in the result of the query.
But there will be a mistake:
You can't specify target table 'table_score_one' for update in FROM clause
Meaning: You can't query some values in the same sql statement first and modify the table.
Solution: The result of select is selected more than once through an intermediate table.
DELETE
FROM
table_score_one
WHERE
id NOT IN (
SELECT
a.min_id
FROM
(
SELECT
min(id) AS min_id
FROM
table_score_one
GROUP BY
student_no,
class_no,
class_name,
score
) a
);Aliases should be established for the results.
Reference resources: http://blog.csdn.net/u013142781/article/details/50836476