re:
- Introduction: Modules for Regular Expressions
- Regular expression characters:
More: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%AD%A3%E5%88%99%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F/1700215?fr=aladdin
Commonly used optional flags:
re.S: Make. Match all characters including newlines
re.I:) Matching ignores case and case
If you want to use multiple tokens at the same time, you need to use |:
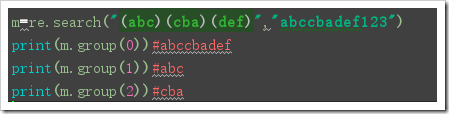
groups and group s:
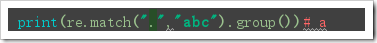
The return results of match and search matches are all objects. To get the corresponding string, you need to use group(num) or groups():
group(num=0):
The direct call returns the entire matching result.
If there are parameters in group: group(0) represents the whole matching result, group(1) lists the first grouping matching part, group(2) lists the second grouping matching part, group(3) lists the third grouping matching part, and so on.
groups()
Returns all grouped matched characters in tuples
Additional:
- The start([group]) method is used to get the starting position (index of the first character of the substring) of the grouped matched substring in the whole string. The default value of the parameter is 0.
- The end([group]) method is used to get the end position of the grouped matched substring in the whole string (index + 1 of the last character of the substring), and the default parameter is 0.
- The span([group]) method returns (start (group), end (group).
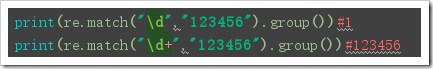
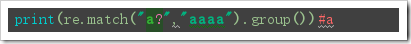
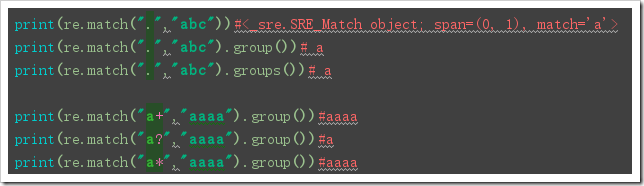
re.match(pattern, string, flags=0):
Function: re.match matches from scratch and returns None if the beginning of the string does not match.
Introduction of parameters:
- pattern: Matched regular expressions
- String: The string to match.
- flags: flags: flags that control how regular expressions are matched, such as case-sensitive, multi-line matching, and so on.
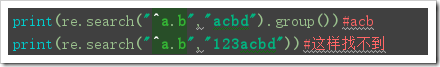
re.search(pattern, string, flags=0):
Function: re.search searches the entire string and returns the first matching result
Introduction of parameters:
pattern: matching regular expression
String: The string to match.
Flags: flags that control how regular expressions are matched
re.sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0):
Function: re.sub. For replacing matches in strings, specify the number of replacements
Introduction of parameters:
Pattern: A pattern string in a regular.
Reply: Replaced strings can also be a function.
String: The original string to be replaced is found.
count: The maximum number of substitutions after pattern matching. The default 0 is to replace all matches.
Usage:
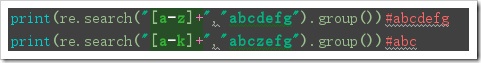
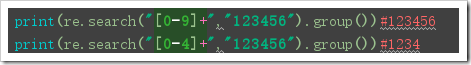
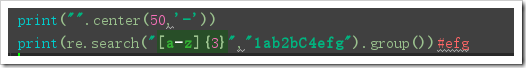
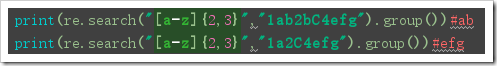
import re print(re.sub("abc","ABC","123abc123"))#123ABC123 print(re.sub("abc","ABC","123abc123abc123abc",2))#123ABC123ABC123abc print(re.sub("abc","ABC","123abc123abc123abc",2))#123ABC123ABC123abc def func(x): x=int(x.group())+1 return str(x) print(re.sub("123",lambda x:str(int(x.group())+1),"123abc123"))#124abc124 print(re.sub("123",func,"123abc123"))#124abc124
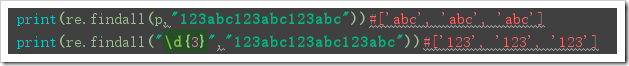
re.findall(string[, pos[, endpos]]):
Function: re.findall searches the entire string and returns all matched strings as elements in the list
Introduction of parameters:
- String: The string to be matched.
- pos: Optional parameter, specifying the starting position of the string, defaulting to 0.
- endpos: An optional parameter specifying the end position of the string, defaulting to the length of the string.
Usage:
re.compile function
- The compile function is used to compile regular expressions and generate a Pattern object.
- Note: It can only be used by match() and search().
import re print(".".center(50,'-')) print(re.match(".","abc"))#<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 1), match='a'> print(re.match(".","abc").group())# a print(re.match(".","abc").groups())# a print("+".center(50,'-')) print(re.match("a+","aaaa").group())#aaaa print("?".center(50,'-')) print(re.match("a?","aaaa").group())#a print("*".center(50,'-')) print(re.match("a*","aaaa").group())#aaaa print("^".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("^a.b","acbd").group())#acb print(re.match("^a.+","abc").group()) print(re.search("^a.b","123acbd"))#So I can't find it. print(re.search("a.+d$","acbd").group())#acbd print(re.search("a.+d$","acbdc"))#So I can't find it. print("".center(50,'-')) print("\d".center(50,'-')) print(re.match("\d","123456").group())#1 print(re.match("\d+","123456").group())#123456 print("\D".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("\D","123456b").group())#b print(re.search("\D","a123456").group())#a print("\s".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("a\sb","123a b456").group())#a b print("[]".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("[a-z]+","abcdefg").group())#abcdefg print(re.search("[a-k]+","abczefg").group())#abc print(re.search("[0-9]+","123456").group())#123456 print(re.search("[0-4]+","123456").group())#1234 print(re.search("[a-zA-Z0-9]+","1a2bC456ef").group())#1a2bC456ef print("".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("[a-z]+|[A-Z]+","1ab2bC4ef").group())#ab print(re.search("([a-z]|[A-Z])+","1ab2bC4ef").group())#ab print("{n}{n,m}".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("[a-z]{3}","1ab2bC4efg").group())#efg print(re.search("[a-z]{2,3}","1ab2bC4efg").group())#ab print(re.search("[a-z]{2,3}","1a2C4efg").group())#efg print(re.search("[a-z]{2,}","1a2C4efgaaaa").group())#efgaaaa print("Packet matching".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("([a-z]|[A-Z])+","1ab2bC4ef").group())#ab print(re.search("([a-z]|[A-Z])+","1ab2bC4ef").group())#ab print("group groups".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("(\d[a-z]\d){3}","1x11a32a465").group())#1x11a32a4 print(re.search("(abc){3}","abcabcabc123").group())#abcabcabc print(re.search("(abc)","abcabcabc123").groups())#('abc',) m=re.search("(abc)(cba)(def)","abccbadef123") print(m.groups())#('abc', 'cba', 'def') print(m.group(0))#abccbadef print(m.group(1))#abc print(m.group(2))#cba print("findall".center(50,'-')) print(re.findall("(abc)","abcabcabc123"))#['abc', 'abc', 'abc'] print("flag".center(50,'-')) print(re.search("a.b","a\nb",re.S).group())#Printed in two lines a b print(re.search("a.b","A\nb",re.S|re.I).group())#Printed in two lines A b print(re.search("ab","Ab",re.I).group())#Ab