Label
PostgreSQL, HTAP, OLTP, OLAP, Scenario and Performance Testing
background
PostgreSQL is a database with a long history, which can be traced back to 1973. It was first awarded by the 2014 Computer Turing Prize winner and the originator of relational database. Michael_Stonebraker PostgreSQL has similar functions, performance, architecture and stability as Oracle.
The PostgreSQL community has many contributors, from all walks of life around the world. Over the years, PostgreSQL releases a large version every year, known for its enduring vitality and stability.
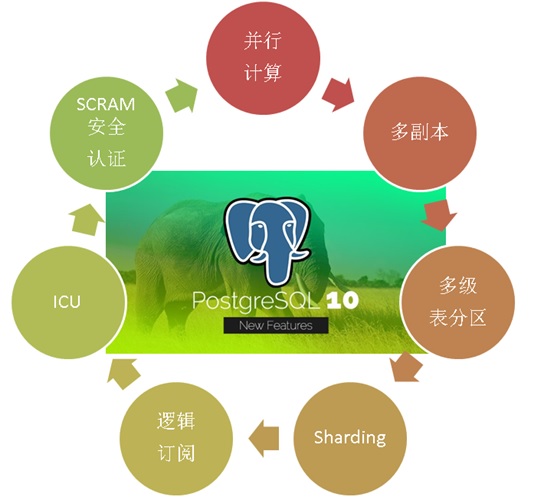
In October 2017, PostgreSQL released version 10, which carries many amazing features. The goal is to meet the requirements of mixed HTAP scenarios of OLAP and OLTP:
PostgreSQL 10 features, the most popular HTAP database for developers
1. Multi-core Parallel Enhancement
2. fdw aggregation push-down
3. Logical Subscription
4, zoning
5. Multi-copies at the financial level
6. json, jsonb full-text retrieval
7. There are also some features of plug-in form, such as vector computing, JIT, SQL graph computing, SQL stream computing, distributed parallel computing, time series processing, gene sequencing, chemical analysis, image analysis, etc.
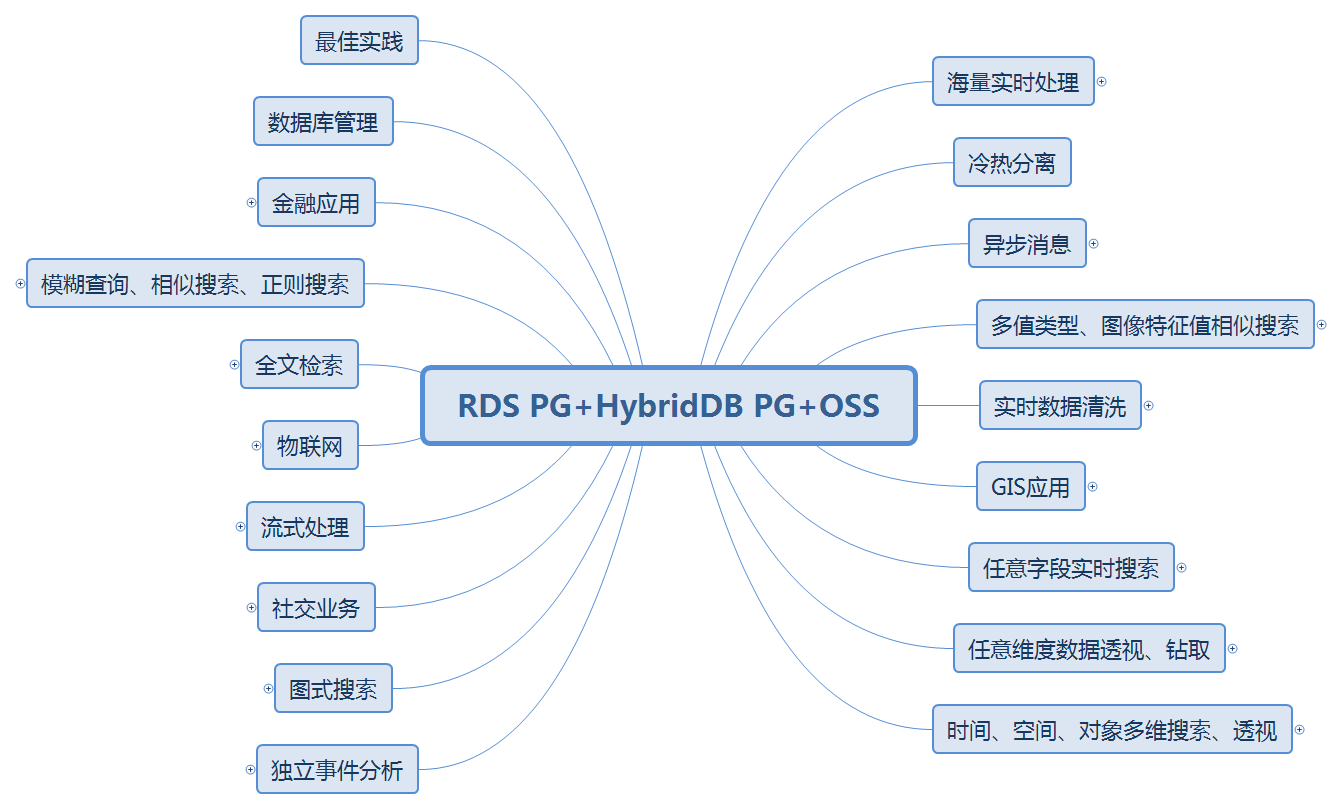
PostgreSQL can be seen in various application scenarios:
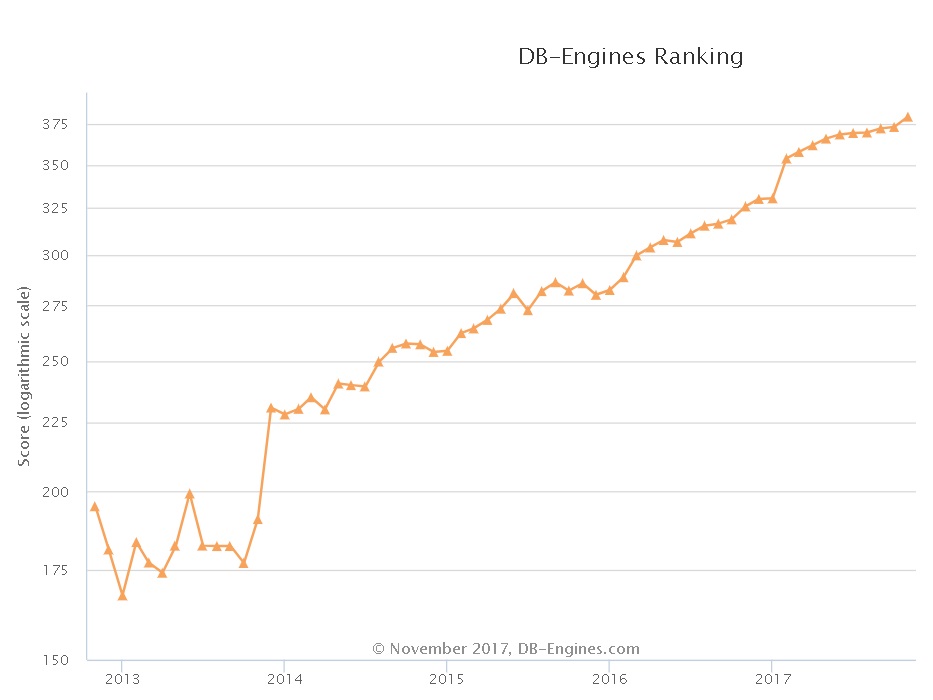
PostgreSQL has developed very rapidly in recent years. From the database scoring trend of dbranking, a well-known database evaluation website, we can see the upward trend of PostgreSQL:
From the annual community meetings held in PostgreSQL China, we can see the same trend. More and more companies are participating, more and more companies are sharing, and more and more subjects are shared. They span traditional enterprises, Internet, medical, financial, state-owned enterprises, logistics, e-commerce, social networking, vehicle networking, sharing XX, cloud, game, public transport, aviation, railway, military, training. Training, consulting services, etc.
The next series of articles will introduce various application scenarios and corresponding performance indicators of PostgreSQL.
Environmental Science
Reference to Environmental Deployment Method:
Aliyun ECS: 56 core, 224G, 1.5TB*2 SSD cloud disk.
Operating System: CentOS 7.4 x64
Database version: PostgreSQL 10
PS: The CPU and IO performance of ECS is discounted by physical opportunity, and can be estimated by one-fold performance decline. Running physical mainframe can be estimated by multiplying the performance tested here by 2.
Scenario-Full Text Retrieval-Indexed Real-Time Writing (OLTP)
1, background
String search is a very common business requirement, which includes:
1. Prefix + Fuzzy Query. (b-tree index can be used)
2. Suffix + Fuzzy Query. (b-tree index can be used)
3. Fuzzy query before and after. (You can use pg_trgm and gin indexes)
4. Full-text retrieval. (Full-text search types and gin or rum indexes can be used)
5. Regular query. (You can use pg_trgm and gin indexes)
6. Similar query. (You can use pg_trgm and gin indexes)
Generally speaking, the database does not have the ability to speed up after 3 years, but PostgreSQL is very powerful, it can perfectly support the acceleration of such queries. (Refers to queries and writes that do not conflict, and the index BUILD is real-time.)
Users do not need to synchronize data to search engines, and then query, and search engines can only do full-text retrieval, and you do not do regular, similar, ambiguous these requirements.
PostgreSQL can greatly simplify the user's architecture, cost of development, and ensure the absolute real-time data query.
2, design
Five million words are randomly extracted from a thesaurus, 64 words are randomly extracted, and a 64-word word segmentation string is formed (refer to the Tathagata Palm at the end of the actual scene for the use of word segmentation, the main purpose of this paper is to test the performance). schemaless is written to the full-text search field in a single point.
Including full-text search GIN index, this CASE mainly embodies the ability to write data while BUILD full-text index.
3. Preparing test sheets
create table t_fts( id int, ts tsvector ); create index idx_t_fts_ts on t_fts using gin (ts) with (gin_pending_list_limit = 65535, fastupdate=on) tablespace tbs1; alter table t_fts set (toast.autovacuum_enabled =off); alter table t_fts set (autovacuum_enabled =off); do language plpgsql $$ declare begin for i in 0..1024 loop execute 'create table t_fts_'||i||' (like t_fts including all) inherits(t_fts)'; execute 'alter table t_fts_'||i||' set (toast.autovacuum_enabled =off)'; execute 'alter table t_fts_'||i||' set (autovacuum_enabled =off)'; end loop; end; $$;
4. Preparing test functions (optional)
create or replace function gen_rand_tsvector(int,int) returns tsvector as $$ select array_to_tsvector(array_agg((random()*$1)::int::text)) from generate_series(1,$2); $$ language sql strict; create or replace function ins_t_fts(int) returns void as $$ declare begin execute 'insert into t_fts_'||$1||' values (1, gen_rand_tsvector(5000000, 64))'; end; $$ language plpgsql strict;
5. Preparing test data
6. Preparing test scripts
vi test.sql \set suffix random(0,1024) select ins_t_fts(:suffix);
7, test
CONNECTS=56 TIMES=300 export PGHOST=$PGDATA export PGPORT=1999 export PGUSER=postgres export PGPASSWORD=postgres export PGDATABASE=postgres pgbench -M prepared -n -r -f ./test.sql -P 5 -c $CONNECTS -j $CONNECTS -T $TIMES
8. Test results
transaction type: ./test.sql scaling factor: 1 query mode: prepared number of clients: 56 number of threads: 56 duration: 300 s number of transactions actually processed: 28190260 latency average = 0.596 ms latency stddev = 1.695 ms tps = 93946.251980 (including connections establishing) tps = 93955.787059 (excluding connections establishing) script statistics: - statement latencies in milliseconds: 0.002 \set suffix random(0,1024) 0.594 select ins_t_fts(:suffix);
TPS: 93955
Average response time: 0.596 milliseconds
Reference resources
PostgreSQL, Greenplum Application Case Book "Tathagata Palm" - Catalogue
"Database Selection - Elephant Eighteen Touches - To Architects and Developers"
PostgreSQL uses pgbench to test sysbench related case s