What is a stretched geometry
Stretching means that we have a two-dimensional graphic that is transformed into a three-dimensional graphic by stretching on the z-axis.For example, if we stretch THREE.CircleGeometry, we get a cylindrical-like figure; if we stretch THREE.PlaneGeometry, we get a cube.Here's a description of the commonly used THREE.ExtrudeGeometry
Introduction to THREE.ExtrudeGeometry
THREE.ExtrudeGeometry can create a three-dimensional graphic from a two-dimensional graphic.
Simple use
var geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(shapes, options);- shapes stretch geometries by providing one or more graphics (THREE.Shape objects).Look at the previous section
- options is a write that configures the THREE.PlaneGeometry configuration item with:
| attribute | Is it necessary | describe |
|---|---|---|
| amount | no | This property specifies how high (deep) the graph can be.Default value is 100 |
| bevelThickness | no | This property specifies the depth of the bevel.The bevel is the chamfer between the front and back and the stretch body.This value defines the depth at which the diagonal angle enters the graph.Default value is 6 |
| bevelSize | no | This property specifies the height of the bevel.This height is added to the normal height of the graphic.The default value is bevelThickness - 2 |
| bevelSegments | no | This property defines the number of segments at an angle.The more segments there are, the smoother the curve will be.Default value is 3 |
| bevelEnabled | no | If this property is set to true, there will be an oblique angle.Default value is true |
| curveSegments | no | This property specifies how many segments the stretch body is divided along the depth direction.The default value is 1.The larger the value, the more individual faces |
| steps | no | This property specifies how many segments the stretch body is divided along the depth direction.The default value is 1.The larger the value, the more individual faces. |
| extrudePath | no | This property specifies the path along which the graph is stretched (THREE.CurvePath).If not specified, the graph is stretched along the z-axis |
| material | no | This property defines the index of the material used before and after.If you want to use separate materials for the front and back, you can use the THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject function to create the grid |
| extrudeMaterial | no | This property specifies the index of the material used for the bevels and stretches.If you want to use separate materials for the front and back, you can use the THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject function to create the grid |
| uvGenerator | no | When you use textures for a material, the UV map determines which part of the texture is used for a particular surface.Using the UVGenerator property, you can pass in your own object that will create UV settings for the faces created by the incoming graphics.If not specified, THREE.ExtrudeGeometry.WorldUVGenerator is used |
| frames | no | frenet frames are used for tangents, normals, and sub-normals of spline curves.This property is used when stretching a geometry along an extrude path.You don't need to specify it, because Three.js provides a way to do it - THREE.TubeGeometry.FrenetFrames, which is also used as a default value. |
Case Code
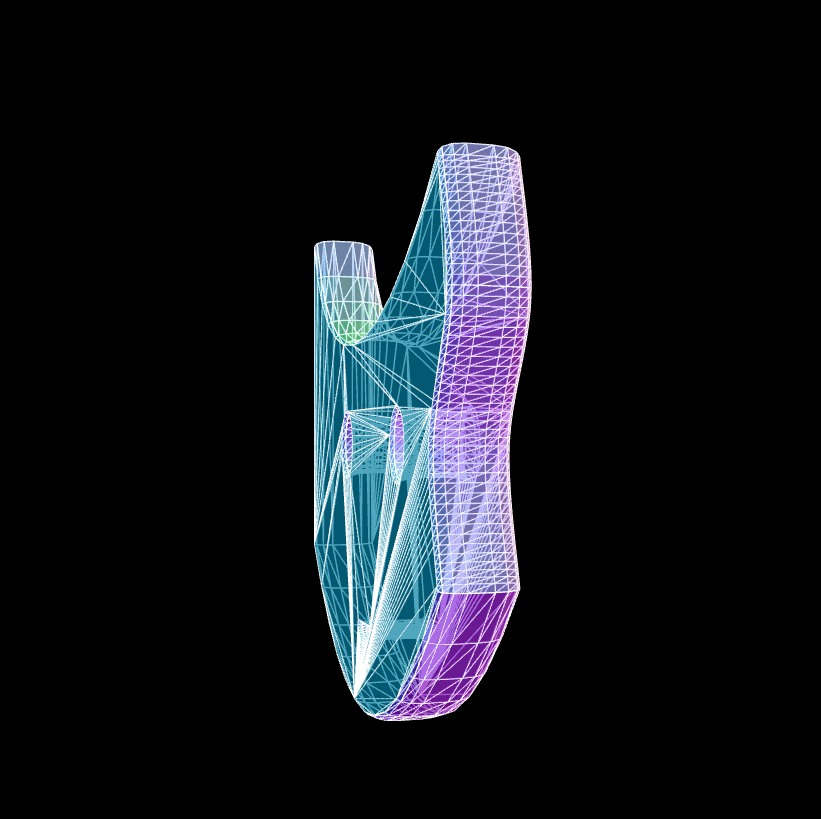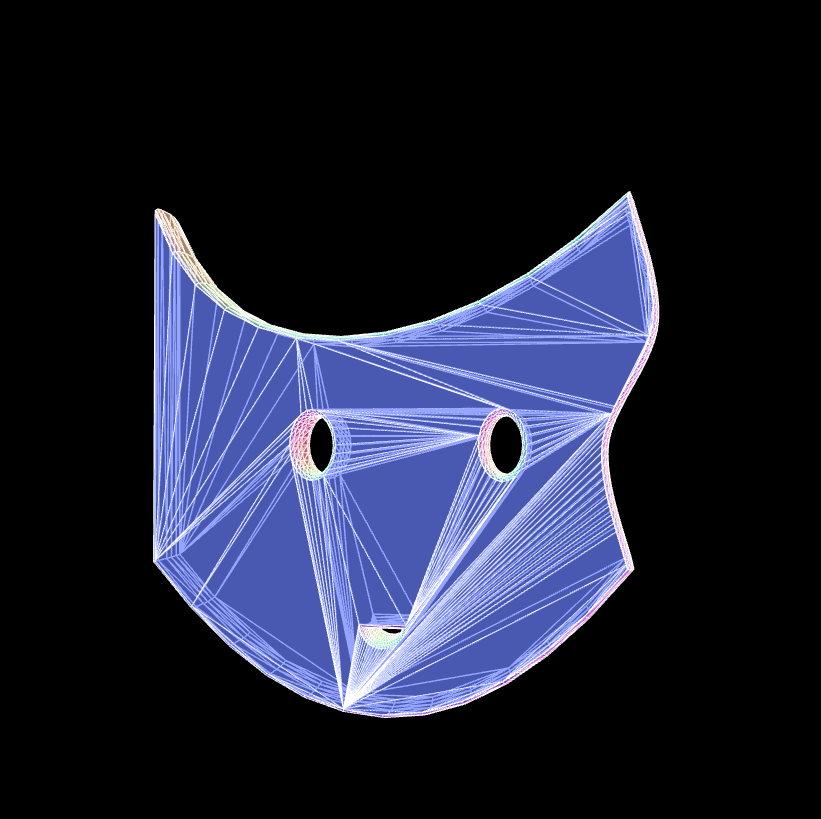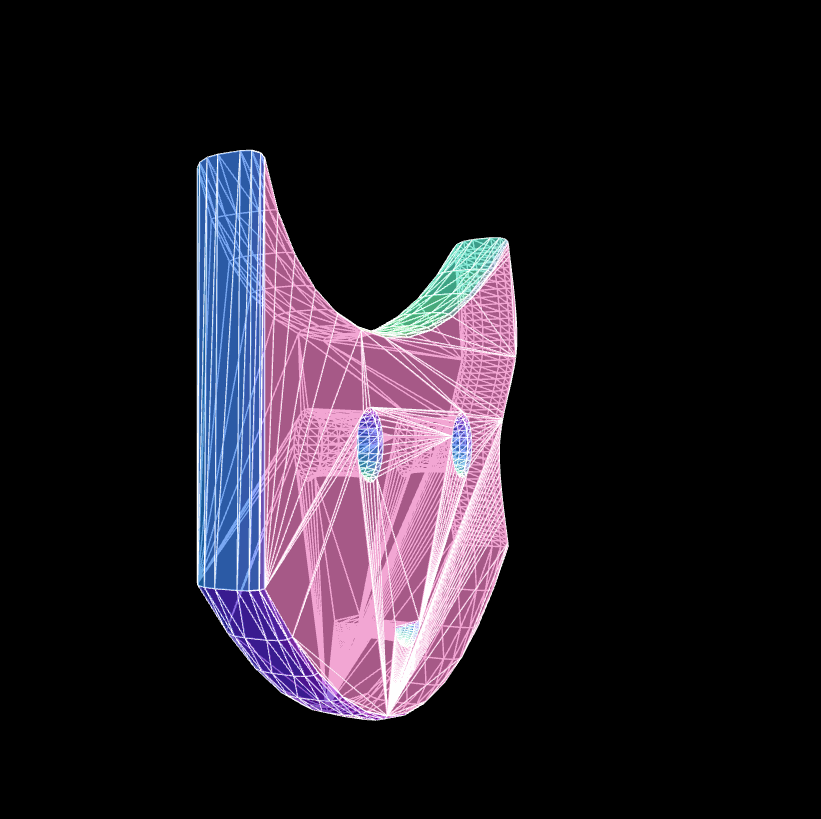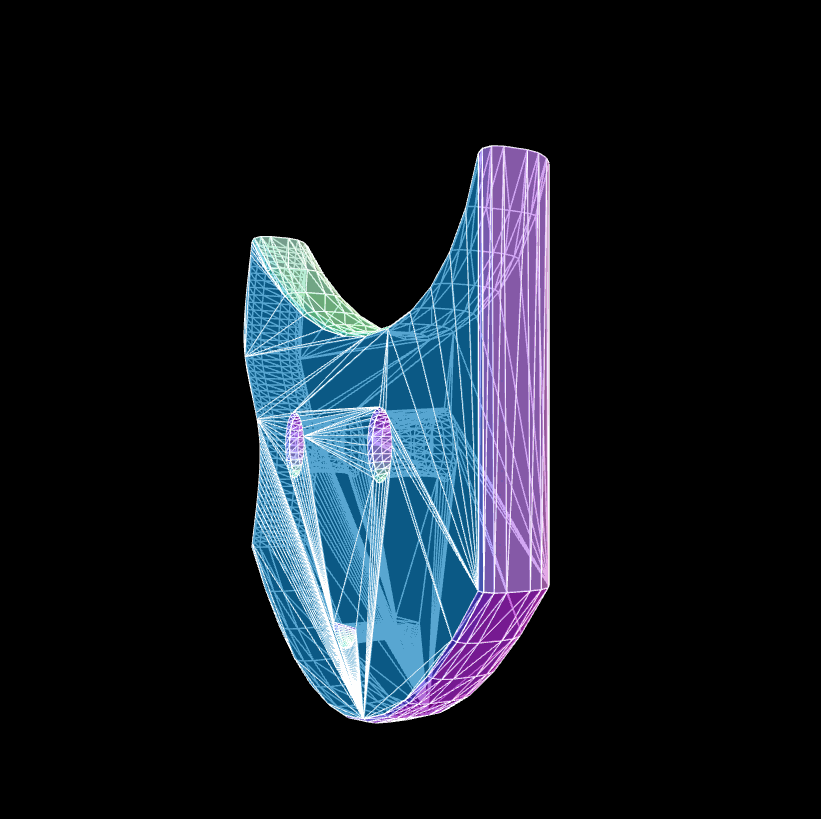
The whole code is below, so you can copy it and run it yourself
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style type="text/css">
html, body {
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
}
canvas {
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body onload="draw();">
</body>
<script src="https://johnson2heng.github.io/three.js-demo/lib/three.js"></script>
<script src="https://johnson2heng.github.io/three.js-demo/lib/js/QuickHull.js"></script>
<script src="https://johnson2heng.github.io/three.js-demo/lib/js/geometries/ConvexGeometry.js"></script>
<script src="https://johnson2heng.github.io/three.js-demo/lib/js/controls/OrbitControls.js"></script>
<script src="https://johnson2heng.github.io/three.js-demo/lib/js/libs/stats.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://johnson2heng.github.io/three.js-demo/lib/js/libs/dat.gui.min.js"></script>
<script>
var renderer;
function initRender() {
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({antialias:true});
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
}
var camera;
function initCamera() {
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth/window.innerHeight, 1, 10000);
camera.position.set(0, 0, 100);
}
var scene;
function initScene() {
scene = new THREE.Scene();
}
var light;
function initLight() {
scene.add(new THREE.AmbientLight(0x404040));
light = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff);
light.position.set(1,1,1);
scene.add(light);
}
function initModel() {
var shape = new THREE.ShapeGeometry(drawShape());
var material = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({color:0xff00ff});
material.side = THREE.DoubleSide;//Set to be visible on both sides
var mesh = new THREE.Mesh(shape,material);
scene.add(mesh);
/*This method is used to create two textures
* var shape = new THREE.ShapeGeometry(drawShape());
var mesh = createMesh(shape);
scene.add(mesh);
* */
}
//Generate 2d Graphics
function drawShape() {
// Instantiate shape object
var shape = new THREE.Shape();
// Set the position of the starting point
shape.moveTo(20, 10);
// Draw a straight line from the starting point to the current position
shape.lineTo(20, 40);
//Set a curve to 3040
shape.bezierCurveTo(15, 25, -5, 25, -20, 40);
// Set a smooth curve through all current vertices
shape.splineThru(
[
new THREE.Vector2(-22, 30),
new THREE.Vector2(-18, 20),
new THREE.Vector2(-20, 10)
]
);
// Set the curve back to its vertex
shape.quadraticCurveTo(0, -15, 20, 10);
// Add First Eye
var hole1 = new THREE.Path();
hole1.absellipse(6, 20, 2, 3, 0, Math.PI * 2, true);
shape.holes.push(hole1);
// Add a second eye
var hole2 = new THREE.Path();
hole2.absellipse(-10, 20, 2, 3, 0, Math.PI * 2, true);
shape.holes.push(hole2);
// Add mouth, half circle
var hole3 = new THREE.Path();
hole3.absarc(0, 5, 2, 0, Math.PI, true);
shape.holes.push(hole3);
// Return shape
return shape;
}
//Generate model
function createMesh(geom) {
//Sets the current model matrix to be offset 20 along the negative y-axis
geom.applyMatrix(new THREE.Matrix4().makeTranslation(0, -20, 0));
// Create Normal Texture
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({
flatShading: THREE.FlatShading,
transparent: true,
opacity: 0.7
});
// Create a wireframe texture
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
// Create a model
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial,wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
//Initialize Performance Plug-in
var stats;
function initStats() {
stats = new Stats();
document.body.appendChild(stats.dom);
}
//User Interaction Plugin Left Mouse Press and Hold Rotation, Right Mouse Press and Hold Pan, Roller Zoom
var controls;
function initControls() {
controls = new THREE.OrbitControls( camera, renderer.domElement );
// Delete this function if the animate method is used
//controls.addEventListener( 'change', render );
// Whether damping or spinning means inertia when animating loops
controls.enableDamping = true;
//Dynamic Damping Factor is Mouse Drag Rotation Sensitivity
//controls.dampingFactor = 0.25;
//Is it scalable
controls.enableZoom = true;
//Whether to rotate automatically
controls.autoRotate = false;
//Set the camera's farthest distance from the origin
controls.minDistance = 20;
//Set the camera's farthest distance from the origin
controls.maxDistance = 160;
//Whether to turn on right-click dragging
controls.enablePan = true;
}
//Generate gui settings configuration item
var gui,shape;
function initGui() {
//Declare an object that holds relevant data for modifications to requirements
gui = {
amount:2,
bevelThickness:2,
bevelSize:0.5,
bevelEnabled:true,
bevelSegments:3,
curveSegments:12,
steps:1,
asGeom:function () {
// Delete old model
scene.remove(shape);
// Create a new
var options = {
amount: gui.amount,
bevelThickness: gui.bevelThickness,
bevelSize: gui.bevelSize,
bevelSegments: gui.bevelSegments,
bevelEnabled: gui.bevelEnabled,
curveSegments: gui.curveSegments,
steps: gui.steps
};
shape = createMesh(new THREE.ExtrudeGeometry(drawShape(), options));
// Add model to scene
scene.add(shape);
}
};
var datGui = new dat.GUI();
//Add setting properties to gui, gui.add (object, property, minimum, maximum)
datGui.add(gui, 'amount', 0, 20).onChange(gui.asGeom);
datGui.add(gui, 'bevelThickness', 0, 10).onChange(gui.asGeom);
datGui.add(gui, 'bevelSize', 0, 10).onChange(gui.asGeom);
datGui.add(gui, 'bevelSegments', 0, 30).step(1).onChange(gui.asGeom);
datGui.add(gui, 'bevelEnabled').onChange(gui.asGeom);
datGui.add(gui, 'curveSegments', 1, 30).step(1).onChange(gui.asGeom);
datGui.add(gui, 'steps', 1, 5).step(1).onChange(gui.asGeom);
//Call to generate a graph once
gui.asGeom();
}
function render() {
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
//Functions triggered by window changes
function onWindowResize() {
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
render();
renderer.setSize( window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight );
}
function animate() {
//Update Controller
controls.update();
render();
//Update Performance Plug-in
stats.update();
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}
function draw() {
initRender();
initScene();
initCamera();
initLight();
//initModel();
initControls();
initStats();
initGui();
animate();
window.onresize = onWindowResize;
}
</script>
</html>