1.1.usage of urlopen function
#encoding:utf-8 from urllib import request res = request.urlopen("https://www.cnblogs.com/") print(res.readlines()) #urlopen Parameters #def urlopen(url, data=None, timeout=socket._GLOBAL_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT, # *, cafile=None, capath=None, cadefault=False, context=None):
1.2.urlretrieve function
Save files on Web pages locally
#coding:utf-8 from urllib import request res = request.urlretrieve("https://www.cnblogs.com/",'cnblog.html') #urlretrieve parameter #def urlretrieve(url, filename=None, reporthook=None, data=None):
1.3. Parameter encoding and decoding functions
urlencode function for encoding Chinese and special characters
#urlencode function # Simple usage #from urllib import parse # data = {'name':'Derrick','age':100} # qs = parse.urlencode(data) # print(qs) #name=%E5%BE%B7%E7%91%9E%E5%85%8B&age=100 #Actual use cases from urllib import request,parse url = "http://www.baidu.com/s" params = {"wd":"Blog Garden"} qs = parse.urlencode(params) url = url + "?" + qs res = request.urlopen(url) print(res.read())
The parse ﹣ QS function is used to decode the encoded url parameter.
from urllib import parse qs = "name=%E5%BE%B7%E7%91%9E%E5%85%8B&age=100" print(parse.parse_qs(qs)) #{'name': ['Derrick'], 'age': ['100']}
1.4.urlparse and urlplit function usage
urlparse and urlplit are used to segment the components of url. The only difference is that urlplit does not have the attribute "params"
from urllib import request,parse url = "https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=cnblog#2" result = parse.urlparse(url) print(result) #ParseResult(scheme='https', netloc='www.baidu.com', path='/s', params='', query='wd=cnblog', fragment='2') print('scheme:',result.scheme) #Agreement print('netloc:',result.netloc) #domain name print('path:',result.path) #Route print('query:',result.query) #Query parameters #Result #scheme: https # netloc: www.baidu.com # path: /s # query: wd=cnblog
1.5.Request crawls to the position information of the network
Parameters of the Request class
class Request: def __init__(self, url, data=None, headers={}, origin_req_host=None, unverifiable=False, method=None):
Position information of climbing to hook net
The position information of lagoon is in Ajax.json
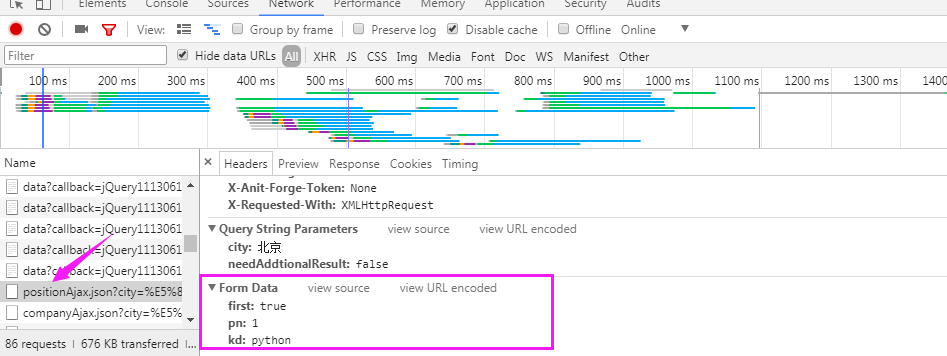
Code:
#utilize Request Position information of class A from urllib import request,parse url = "https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json?city=%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC&needAddtionalResult=false" #Request header headers = { "User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/64.0.3282.140 Safari/537.36", "Referer":"https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python?city=%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC&cl=false&fromSearch=true&labelWords=&suginput=" } #post Request data to be submitted data = { 'first':'true', 'pn':1, 'kd':'python' } #post Requested data Data must be encoded byte type req = request.Request(url,headers=headers,data=parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8'),method='POST') #Create a request object res = request.urlopen(req) #The acquired information is byte type and needs to be decoded print(res.read().decode('utf-8'))
Proxyhandler agent
Principle of proxy: before requesting the destination website, first request the proxy server, then ask the proxy server to request the destination website, obtain the data, and then return it to us.
#Use of agents from urllib import request url = "https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=cnblog" #1.Use ProxyHandler The incoming agent builds a handler # handler = request.ProxyHandler({'http':'115.210.31.236.55:9000'}) handler = request.ProxyHandler({'http':'115.210.31.236.55:9000'}) #2.Use created handler Construct a opener opener = request.build_opener(handler) #3.Use opener To send a request res = opener.open(url) print(res.read())