I found a calculator program written in college, and a graphical interface, which can graphically display the expression syntax tree, ha ha;)
There are only 200 lines of Java code, which can not only calculate addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, but also match parentheses~
Code comments:
From simple interface color matching to simple and easy to understand error prompt, all of them embody the design concept of "user experience" supremacy; code exception handling is comprehensive and reasonable, water tight, code indenting is elegant and generous, variable naming is intuitive and easy to understand; combined with notes of moderate and simple length, the program as a whole gives a fresh and refined feeling. It's not hard to see the author's love for learning and demanding for design behind it. The craftsman spirit can be seen. It's really a model for university data structure learning to apply!
For the dry goods of data structure, please refer to the blogger's Deep understanding of Java collection framework series You must not be disappointed.
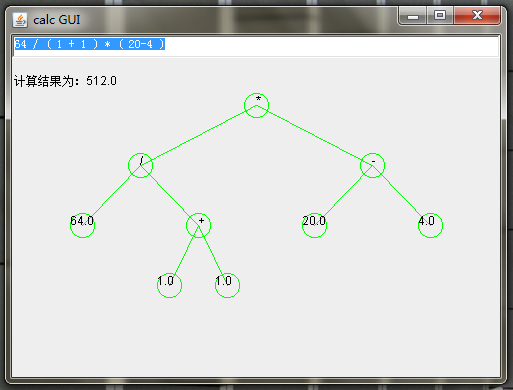
The implementation algorithm refers to Chapter 3 "stack and queue" of Yan Weimin's "data structure (C Language Edition)" and section 3.2.5 "expression evaluation".
import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Graphics; import java.awt.Point; import java.awt.TextField; import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter; import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; import java.util.Stack; import javax.swing.JFrame; /** * The calculator program of graphical interface can only calculate addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, * There can be parentheses in the formula. Numbers can be decimals */ public class CalcGUI extends JFrame{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private TreeNode resultTree; private String textFieldString; private boolean calcSuccess = true; private char ops[][] = { {'>', '>', '<', '<', '<', '>', '>'}, {'>', '>', '<', '<', '<', '>', '>'}, {'>', '>', '>', '>', '<', '>', '>'}, {'>', '>', '>', '>', '<', '>', '>'}, {'<', '<', '<', '<', '<', '=', 'E'}, {'E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E'}, {'<', '<', '<', '<', '<', 'E', '='}, }; Stack<TreeNode> nodesStack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); Stack<Character> opsStack = new Stack<Character>(); public static void main(String[] args) { CalcGUI gui = new CalcGUI(); gui.userGUI(); } public void userGUI(){ this.setLayout(new BorderLayout()); TextField tf = new TextField("Please enter an expression and press Enter Start calculation~", 40); tf.selectAll(); tf.getText(); tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter(){ public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){ if(e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_ENTER){ textFieldString = ((TextField)e.getComponent()).getText(); calcSuccess = true; resultTree = null; try{ resultTree = calc(textFieldString + "#"); }catch(Exception e1){ calcSuccess = false; } CalcGUI.this.repaint(); } } }); this.add(tf, BorderLayout.NORTH); this.setSize(500, 500); this.setTitle("calc GUI"); this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); this.setResizable(true); this.setVisible(true); } private int levelHeight = 60; private int diameter = 25; public void paint(Graphics g){ super.paint(g); if(calcSuccess){ if(resultTree != null){ g.drawString("The calculation results are as follows:" + resultTree.value, 10, 80); int rootBeginX = this.getWidth() / 2; int rootBeginY = 100; Point p = new Point(rootBeginX, rootBeginY); drawTree(g, resultTree, p, this.getWidth() / 2 - 20, p); } }else{ g.setColor(Color.RED); g.drawString("Incorrect expression syntax!", 10, 80); } } private void drawCircle(Graphics g, Point p, int r){ g.drawOval(p.x - r, p.y - r, r * 2, r * 2); } private void drawTree(Graphics g, TreeNode node, Point pme, int width, Point pfather){ if(node == null) return; // System.out.println("in drawTree, node.value=" + node.value + ",node.op=" + node.op); g.setColor(Color.GREEN); this.drawCircle(g, pme, diameter / 2); g.drawLine(pme.x, pme.y, pfather.x, pfather.y); if(node.op != 'E'){ g.setColor(Color.BLACK); g.drawString(String.valueOf(node.op), pme.x, pme.y); }else{ g.setColor(Color.BLACK); g.drawString(String.valueOf(node.value), pme.x - diameter / 2, pme.y); } drawTree(g, node.lft, new Point(pme.x - width / 2, pme.y + levelHeight), width / 2, pme); drawTree(g, node.rt, new Point(pme.x + width / 2, pme.y + levelHeight), width / 2, pme); } public TreeNode calc(String inStr) throws Exception{ opsStack.push('#'); StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(); int i = 0; while(i < inStr.length()){ if(Character.isDigit(inStr.charAt(i)) || inStr.charAt(i) == '.'){// number buf.delete(0, buf.length()); while(i < inStr.length() && (Character.isDigit(inStr.charAt(i)) || inStr.charAt(i) == '.')) buf.append(inStr.charAt(i++)); Double number = Double.parseDouble(buf.toString()); nodesStack.push(new TreeNode(number)); }else if(inStr.charAt(i) == ' '){ i++; continue; }else{// operation char op = inStr.charAt(i); int subNew = getSub(op); boolean goOn = true; while(goOn){ if(opsStack.isEmpty()) throw new Exception("Too few operators!"); char opFormer = opsStack.peek(); int subFormer = getSub(opFormer); switch(ops[subFormer][subNew]){ case '=': goOn = false; opsStack.pop(); break; case '<': goOn = false; opsStack.push(op); break; case '>': goOn = true; TreeNode n1 = nodesStack.pop(); TreeNode n0 = nodesStack.pop(); double rs = doOperate(n0.value, n1.value, opFormer); nodesStack.push(new TreeNode(rs, opFormer, n0, n1)); opsStack.pop(); break; default: throw new Exception("No matching operators:" + op); } } i++; } } return nodesStack.pop(); } private double doOperate(double n0, double n1, char op) throws Exception{ switch(op){ case '+': return n0 + n1; case '-': return n0 - n1; case '*': return n0 * n1; case '/': return n0 / n1; default: throw new Exception("Illegal operator:" + op); } } private int getSub(char c){ switch(c){ case '+': return 0; case '-': return 1; case '*': return 2; case '/': return 3; case '(': return 4; case ')': return 5; case '#': return 6; default : return -1; } } } class TreeNode{ public double value; public char op = 'E'; public TreeNode lft; public TreeNode rt; public TreeNode(double value){ this.value = value; } public TreeNode(double value, char op, TreeNode lft, TreeNode rt){ this.value = value; this.op = op; this.lft = lft; this.rt = rt; } StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(); public String toString(){ out(this); return buf.toString(); } private void out(TreeNode node){ if(node == null) return; out(node.lft); if(node.op != 'E') buf.append(node.op); else buf.append(node.value); out(node.rt); } }