Introduction to LAMP Architecture
LAMP is the abbreviation of Linux Apache MySQL PHP; linux is the operating system, Apache is a web service software, mysql database software, and PHP is a scripting language (currently many websites are written in PHP language, google, Baidu, Taobao, ape class forum, etc.).
LAMP is to install Apache, mysql and PHP on Linux system; we can install Apache and PHP on one machine, mysql on another machine, or three software on the same machine. But Apache and PHP need to be on the same machine because PHP exists as a module of Apache and they must be together.
The relationship between Apache and php
Apache and php are a whole. php is a module form combined with apache. Apache can not interact directly with mysql. Apache can only get data from MySQL through php module. php can get data and then give it to apache. Apache can give it to users.
Php is connected to mysql, and the operation of fetching data is called dynamic request.
How does httpd, PHP and MySQL work
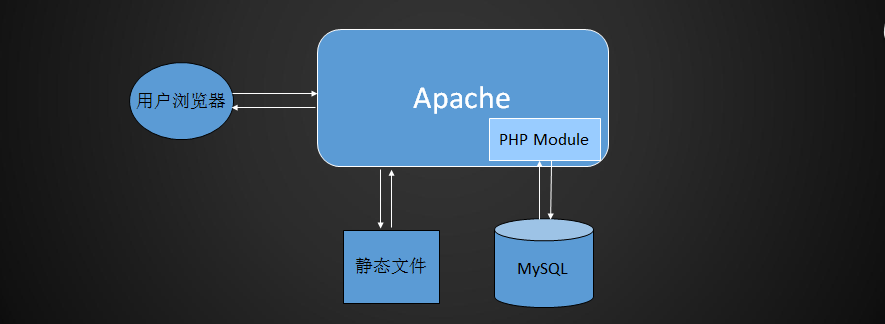
Introduction to MySQL/Mariadb
MySQL is a relational database developed by mysql ab, which was acquired by sun in 2008 (1 billion knives) and oracle in 2009 (7.4 billion knives). MySQL official website https://www.mysql.com Latest version 5.7GA/8.0DMR MySQL 5.6 has changed a lot and 5.7 performance has improved a lot. Mariadb is a branch of MySQL, the official website https://mariadb.com/latest version 10.2 MariaDB is maintained mainly by SkySQL (now renamed MariaDB), which was founded by the original author of MySQL and led by most of the original staff. Mariadb 5.5 corresponds to MySQL 5.5, 10.0 corresponds to MySQL 5.6 Community Version, Enterprise Version, GA (General Available) refers to the generic version used in production environment, DMR (Development Milestone Release) development milestone release, RC (Release Candidate) release candidate version, Beta open test version, Alpha internal test version.
Installation of Mysql
Several commonly used installation packages of MySQL: rpm, source code, binary compiler-free
- Mysql's source installation is different from apache's c make. Check the installation documentation specifically.
- Rpm package installation can not customize the installation path;
- Binary: Before publishing, compile on a linux server, then re-arrange the compiled files into a directory, pack and compress them and publish them. The advantage is that it doesn't take too much time to compile, decompress them directly and use them. If you want to install more accurately and perfectly, you can use the source code installation, usually use the binary installation.
Binary packages are platform-specific. Previous versions of centos7 distinguish between 32-bit and 64-bit, and centos7 directly selects 64-bit installation.
[root@linux-128 src]# uname - i // / See how many bits linux is x86_64
Download the source package:
[root@linux-128 ~]# cd /usr/local/src // / Recommends that all packages be placed in this directory
Download address to r.aminglinux.com for the latest download
[root@linux-128 src]# wget http://mirrors.sohu.com/mysql/MySQL-5.6/mysql-5.6.35-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz
Initialization
- decompression
[root@linux-128 src]# tar zxvf mysql-5.6.35-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz
- Rename
[root@linux-128 src]# mv mysql-5.6.35-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64 /usr/local/mysql [root@linux-128 ~]# cd /usr/local/mysql [root@linux-128 mysql]# ls bin data include man README share support-files COPYING docs lib mysql-test scripts sql-bench
- Create a mysql user because that user is required to start mysql
[root@linux-128 mysql]# useradd -s /sbin/nologin mysql
- Create directories to store database directories
[root@linux-128 mysql]# mkdir /data
- Initialization
[root@linux-128 mysql]# / scripts / mysql_install_db -- user = MySQL -- datadir=/data/mysql /- user = MySQL runs as user mysql, and -- datadir=/data/mysql stores the directory of the database ERROR: please install the following Perl modules before executing ./scripts/mysql_install_db: Data::Dumper //There was an error because of the lack of packages perl-Module-Install //You can use yum list to view missing packages [root@linux-128 mysql]# yum list |grep perl |grep -i dumper Repodata is over 2 weeks old. Install yum-cron? Or run: yum makecache fast perl-Data-Dumper.x86_64 2.145-3.el7 base perl-Data-Dumper-Concise.noarch 2.020-6.el7 epel perl-Data-Dumper-Names.noarch 0.03-17.el7 epel perl-XML-Dumper.noarch 0.81-17.el7 base //Install the perl-Data-Dumper package [root@linux-128 mysql]# yum install -y perl-Data-Dumper
Then execute it once.
[root@linux-128 mysql]# ./scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --datadir=/data/mysql If you see two OK instructions that are executed correctly, or echo $? The result of 0 also indicates that the execution is correct. [root@linux-128 mysql]# echo $? 0
Configure Mysql
Mysql's configuration file is my-default.cnf in the / usr/local/mysql/support-files/directory. It's msyql's template configuration file.
- Copy configuration files
[root@linux-128 mysql]# cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/my-default.cnf /etc/my.cnf cp: Is it covered?"/etc/my.cnf"? y //The file my.cnf already exists here, which was left by the previous system rpm installation. We can see which package it was installed in. [root@linux-128 mysql]# rpm -qf /etc/my.cnf mariadb-libs-5.5.52-1.el7.x86_64
Let's just press "y" to cover it here.
- Modify configuration files
[root@linux-128 mysql]# vim /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] # Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data # For advice on how to change settings please see # http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/server-configuration-defaults.html # *** DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE. It's a template which will be copied to the # *** default location during install, and will be replaced if you # *** upgrade to a newer version of MySQL. [mysqld] # Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data # For advice on how to change settings please see # http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/server-configuration-defaults.html # *** DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE. It's a template which will be copied to the # *** default location during install, and will be replaced if you # *** upgrade to a newer version of MySQL. [mysqld] # Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data # cache in MySQL. Start at 70% of total RAM for dedicated server, else 10%. # innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M # Remove leading # to turn on a very important data integrity option: logging # changes to the binary log between backups. # log_bin # These are commonly set, remove the # and set as required. basedir = /usr/local/mysql //Installation directory of mysql datadir = /data/mysql //Catalogues for storing databases port = 3306 //port # Ser_id =.... // mysql ID number, used as master and slave socket = /tmp/mysql.sock //The suite word address that mysql service monitors is also used for communication. # Remove leading # to set options mainly useful for reporting servers. # The server defaults are faster for transactions and fast SELECTs. # Adjust sizes as needed, experiment to find the optimal values. # join_buffer_size = 128M # sort_buffer_size = 2M # read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
Startup script
- Copy startup script
[root@linux-128 mysql]# cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
- Modify the startup script
[root@linux-128 mysql]# vim /etc/init.d/mysqld basedir=/usr/local/mysql datadir=/data/mysql
- Modify authority
[root@linux-128 mysql]# chmod 755 /etc/init.d/mysqld
- Add mysqld service to the list of system services
[root@linux-128 mysql]# chkconfig --add mysqld
- Set up boot start
[root@linux-128 mysql]# chkconfig mysqld on
- Startup service
[root@linux-128 mysql]# service mysqld start Starting MySQL.Logging to '/data/mysql/linux-128.err'. . SUCCESS!
If you can't start, go to the / data/mysql / directory to see the error log, which is usually the host name. err
- View the mysql process
[root@linux-128 mysql]# ps aux |grep mysqld root 2808 0.0 0.0 11776 1572 pts/0 S 23:56 0:00 /bin/sh /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --datadir=/data/mysql --pid-file=/data/mysql/linux-128.pid mysql 2970 1.5 23.9 973064 449420 pts/0 Sl 23:56 0:01 /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/data/mysql --plugin-dir=/usr/local/mysql/lib/plugin --user=mysql --log-error=/data/mysql/linux-128.err --pid-file=/data/mysql/linux-128.pid --socket=/tmp/my.sock --port=3306 root 2998 0.0 0.0 112676 972 pts/0 S+ 23:58 0:00 grep --color=auto mysqld
- View the port mysql listens on
[root@linux-128 mysql]# netstat -lnp |grep mysqld tcp6 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 2970mysqld unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 33024 2970/mysqld /tmp/my.sock
If we don't know the startup file for mysql, we can also use the command line method to start MySQL Open mysql before closing
[root@linux-128 mysql]# service mysqld stop Shutting down MySQL.. SUCCESS!
Execute command line
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf --user=mysql --datadir=/data/mysql &