Last article A Brief Talk on redis cluster Cluster The advantages of redis cluster architecture, the comparison between redis cluster and redis replication + sentinal, and the data fragmentation algorithm of redis cluster are mainly explained. The original hash algorithm and consistency hash algorithm + virtual nodes are also briefly introduced. From the title point of view, you know that this article mainly explains redis cluster cluster building, less gossip, we directly open up!
Environmental preparation:
centos6.5 minimal
redis-3.2.8
3 * Node
Note: The redis cluster cluster needs at least three master nodes, a highly available and robust distributed cluster. Each master recommends at least one slave, six machines for formal environment and at least three machines. In order to simulate cluster building, three virtual machines are used to build six instances of redis cluster.
redis installation
Install redis on each node (not here, refer to the blogger's previous comments) redis installation)
Introduction to redis cluster configuration
cluster-enabled <yes/no> //Whether to start redis cluster cluster cluster
cluster-config-file <filename> //Specify a file, the cluster redis instance holds the location of the cluster state, and the file mainly holds the information of other machines in the cluster, such as the upper and lower bounds of nodes, failover; this is what redis itself maintains.
cluster-node-timeout <milliseconds> //Node survival time-out, more than milliseconds time, the cluster thinks that the node downtime, master downtime will trigger the master-standby switch, slave downtime will not provide services.
redis cluster cluster cluster construction
Define 6 redis instance configuration files: 7001.conf, 7002.conf, 7003.conf, 7004.conf, 7005.conf, 7006.conf
redis cluster configuration
On each node redis performs the following operations, taking 7001 as an example
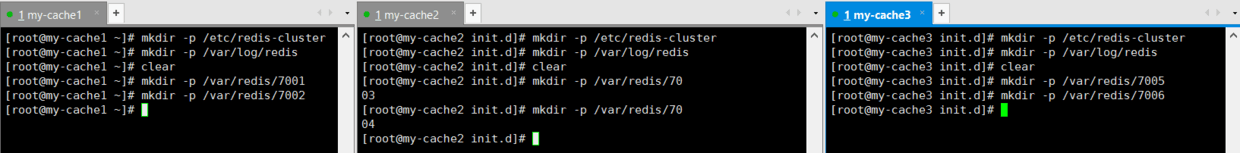
mkdir -p /etc/redis-cluster //Unified Catalogue for Cluster Information Preservation
mkdir -p /var/log/redis //Unified Storage Catalogue of Log Information
mkdir -p /var/redis/7001 // Persistence file of redis
Copy redis.conf under redis-3.2.8 to / etc/redis directory and rename it 7001.conf. The configuration information is modified as follows:
cd /usr/local/redis-3.2.8 && cp redis.conf /etc/redis/7001.conf
port 7001 cluster-enabled yes cluster-config-file /etc/redis-cluster/node-7001.conf cluster-node-timeout 15000 daemonize yes pidfile /var/run/redis_7001.pid dir /var/redis/7001 logfile /var/log/redis/7001.log bind 192.168.43.16 appendonly yes
Modify redis instance startup script
- Under / etc/init.d, put six startup scripts: redis_7001, redis_7002, redis_7003, redis_7004, redis_7005, redis_7006.
cd redis-3.2.8 && cp utils/redis_init_script /etc/init.d/redis_7001 && chmod 777 /etc/init.d/redis_*
- In each startup script, modify the corresponding port number
vim redis_7001
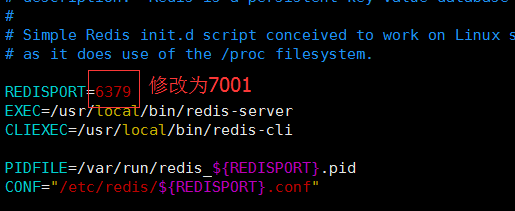
Other 7002, 7003, 7004, 7005, 7006 repeat the above operations
Node-redis instance correspondence:
192.168.43.16 7001
192.168.43.16 7002
192.168.43.17 7003
192.168.43.17 7004
192.168.43.18 7005
192.168.43.18 7006
Creating Clusters
Start six redis instances, respectively
cd /etc/init.d/ && ./redis_7001 start
cd /etc/init.d/ && ./redis_7002 start
cd /etc/init.d/ && ./redis_7003 start
cd /etc/init.d/ && ./redis_7004 start
cd /etc/init.d/ && ./redis_7005 start
cd /etc/init.d/ && ./redis_7006 start
Create redis cluster through redis-trib.rb
redis-trib.rb requires a ruby environment, so you need to install ruby, just install it in a node, which is installed on 192.168.43.16 machine.
yum install -y ruby
yum install -y rubygems
gem install redis
cp /usr/local/redis-3.2.8/src/redis-trib.rb /usr/local/bin //Creating Soft Connections
Creating Clusters
redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.43.16:7001 192.168.43.16:7002 192.168.43.17:7003 192.168.43.17:7004 192.168.43.18:7005 192.168.43.18:7006
--replicas indicate how many slave s are allocated per master
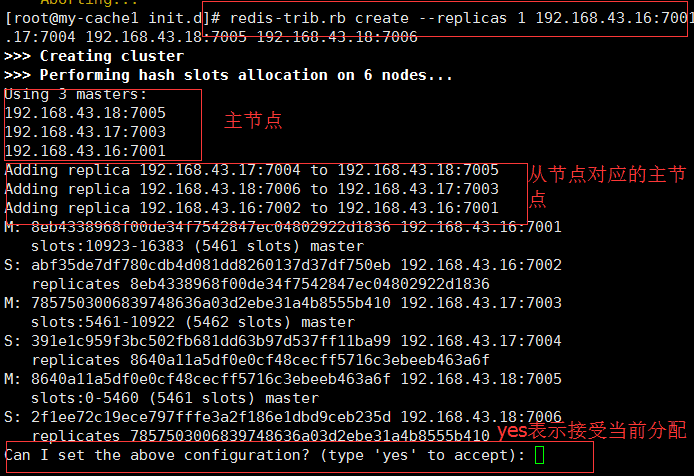
Figure yes confirms that receiving the current allocation continues to complete cluster creation
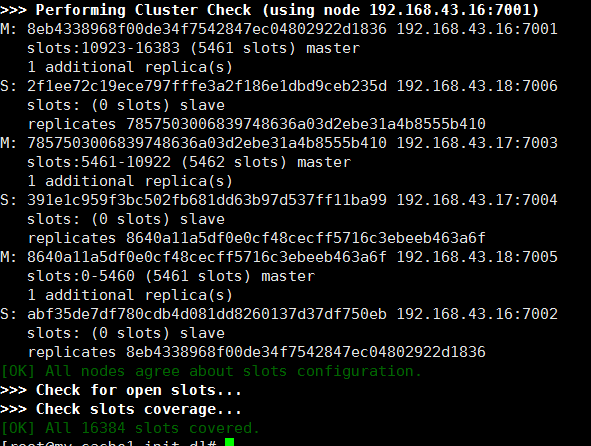
Check cluster information
redis-trib.rb check 192.168.43.16:7001
Re-create the cluster
- Close all redis instances
pkill redis
- Clear Cluster Information Save Files
cd /etc/redis-cluster && rm -rf *
- Clear redis persistent data files
cd /var/redis/7001 && rm -rf *
- Recreate using the redis-trib.rb create --replicas command described above
redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.43.16:7001 192.168.43.16:7002 192.168.43.17:7003 192.168.43.17:7004 192.168.43.18:7005 192.168.43.18:7006
Well, that's all for redis cluster cluster deployment in this chapter.
Above is the content of this chapter. If there is something wrong, please give more advice. Thank you.
For the convenience of those in need, all the software in this series is available. https://pan.baidu.com/s/1qYsJZfY
Chapter 2: Preview of redis cluster cluster
Author: Secret Pursuer (reprinted please indicate the source)