JavaScript data structure and algorithm (VII) bidirectional linked list
One way linked list and two-way linked list
Unidirectional linked list
- You can only traverse from beginning to end or from end to end (generally from beginning to end).
- The linked list connection process is one-way. The implementation principle is that there is a reference to the next node in the previous node.
- One way linked list has an obvious disadvantage: it can easily reach the next node, but it is difficult to return to the previous node. In actual development, it is often necessary to return to the previous node.
Bidirectional linked list
- You can traverse from beginning to end or from end to end.
- The process of linked list connection is two-way. The implementation principle is that a node has both a forward connected reference and a backward connected reference.
- Two way linked list can effectively solve the problems of one-way linked list.
- Disadvantages of two-way linked list:
- Each time you insert or delete a node, you need to handle four references instead of two, which is more difficult to implement.
- Compared with the one-way linked list, it occupies more memory space.
- However, compared with the convenience of two-way linked list, these shortcomings are insignificant.
double linked list
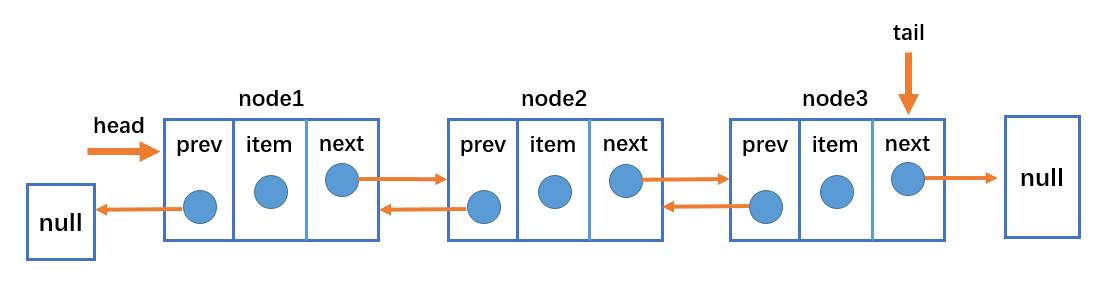
- The two-way linked list not only has a head pointer to the first node, but also a tail pointer to the last node.
- Each node consists of three parts: item stores data, prev points to the previous node, and next points to the next node.
- The prev of the first node of the bidirectional linked list points to null.
- The next of the last node of the bidirectional linked list points to null.
Common operations of bidirectional linked list
- append(element) appends a new element to the end of the linked list.
- insert(position, element) inserts a new element into the specified position of the linked list.
- getElement(position) gets the element at the specified position.
- indexOf(element) returns the index of the element in the linked list. If there is no such element in the linked list, - 1 is returned.
- update(position, element) modifies the element at the specified position.
- removeAt(position) deletes the element at the specified position from the in the linked list.
- remove(element) deletes the specified element from the linked list.
- isEmpty() returns trun if the linked list does not contain any elements, and false if the length of the linked list is greater than 0.
- size() returns the number of elements contained in the linked list, similar to the length attribute of the array.
- toString() because the linked list item uses the Node class, you need to override the default toString method inherited from the JavaScript object to output only the value of the element.
- forwardString() returns the form of a forward traversal node string.
- backwordString() returns the string form of the node traversed in reverse.
Encapsulation of bidirectional linked list
Create a two-way linked list class, DoublyLinkedList
- The DoublyNode class inherits the Node class of the one-way linked list and adds a new this.prev attribute, which is used to point to the previous Node.
- The DoublyLinkedList class inherits the LinkedList class and adds a new this.tail attribute, which points to the end node.
// Node class of bidirectional linked list (node class inheriting unidirectional linked list)
class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(element) {
super(element);
this.prev = null;
}
}
// The bidirectional linked list class inherits the unidirectional linked list class
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
}
append(element)
// append(element) appends a new element to the end of the bidirectional linked list
// Override append()
append(element) {
// 1. Create a bidirectional linked list node
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 2. Append element
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// !! Unlike a one-way linked list, there is no need to find the last node through a loop
// Cleverness
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
insert(position, element)
// insert(position, data) inserts an element
// Override insert()
insert(position, element) {
// 1. position out of bounds judgment
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 2. Create a new bidirectional linked list node
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 3. Judge multiple insertions
if (position === 0) { // Insert at position 0
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
//==Cleverness: make room for this.head and leave a newNode for assignment==//
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.perv = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // Insert in last position
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else { // Insert in the middle of 0 ~ this.length
let targetIndex = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode = null;
// Locate the node where you want to insert
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// Exchange node information
previousNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = previousNode;
newNode.next = currentNode;
currentNode.prev = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
insert(position, element)
// insert(position, data) inserts an element
// Override insert()
insert(position, element) {
// 1. position out of bounds judgment
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 2. Create a new bidirectional linked list node
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 3. Judge multiple insertions
if (position === 0) { // Insert at position 0
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
//==Cleverness: make room for this.head and leave a newNode for assignment==//
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.perv = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // Insert in last position
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else { // Insert in the middle of 0 ~ this.length
let targetIndex = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode = null;
// Locate the node where you want to insert
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// Exchange node information
previousNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = previousNode;
newNode.next = currentNode;
currentNode.prev = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
removeAt(position)
// removeAt() deletes the node at the specified location
// Override removeAt()
removeAt(position) {
// 1. position out of bounds judgment
if (position < 0 || position > this.length - 1) return null;
// 2. Delete elements according to different situations
let currentNode = this.head;
if (position === 0) { // Delete the first node
if (this.length === 1) { // There is only one node in the linked list
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else { // There are multiple nodes in the linked list
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) { // Delete the last node
currentNode = this.tail;
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
} else { // Delete nodes in 0 ~ this.length - 1
let targetIndex = 0;
let previousNode = null;
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next.perv = previousNode;
}
this.length--;
return currentNode.data;
}
update(position, data)
// update(position, data) modifies the node at the specified location
// Override update()
update(position, data) {
// 1. Delete node at position
const result = this.removeAt(position);
// 2. Insert element in position
this.insert(position, data);
return result;
}
forwardToString()
// forwardToString() linked list data is returned in string form from front to back
forwardToString() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let result = '';
// Traverse all nodes and splice them into strings until the node is null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + '--';
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return result;
}
backwardString()
// backwardString() the linked list data is returned as a string from back to front
backwardString() {
let currentNode = this.tail;
let result = '';
// Traverse all nodes and splice them into strings until the node is null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + '--';
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
return result;
}
Implementation of other methods
Other methods of two-way linked list are realized by inheriting one-way linked list.
Complete implementation
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
// ------------Common operations of linked list ------------//
// append(element) appends a new element to the end of the bidirectional linked list
// Override append()
append(element) {
// 1. Create a bidirectional linked list node
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 2. Append element
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// !! Unlike a one-way linked list, there is no need to find the last node through a loop
// Cleverness
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
// insert(position, data) inserts an element
// Override insert()
insert(position, element) {
// 1. position out of bounds judgment
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 2. Create a new bidirectional linked list node
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 3. Judge multiple insertions
if (position === 0) {
// Insert at position 0
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
//==Cleverness: make room for this.head and leave a newNode for assignment==//
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.perv = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
} else if (position === this.length) {
// Insert in last position
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// Insert in the middle of 0 ~ this.length
let targetIndex = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode = null;
// Locate the node where you want to insert
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// Exchange node information
previousNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = previousNode;
newNode.next = currentNode;
currentNode.prev = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
// getData() inherits one-way linked list
getData(position) {
return super.getData(position);
}
// indexOf() inherits one-way linked list
indexOf(data) {
return super.indexOf(data);
}
// removeAt() deletes the node at the specified location
// Override removeAt()
removeAt(position) {
// 1. position out of bounds judgment
if (position < 0 || position > this.length - 1) return null;
// 2. Delete elements according to different situations
let currentNode = this.head;
if (position === 0) {
// Delete the first node
if (this.length === 1) {
// There is only one node in the linked list
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
// There are multiple nodes in the linked list
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) {
// Delete the last node
currentNode = this.tail;
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
} else {
// Delete nodes in 0 ~ this.length - 1
let targetIndex = 0;
let previousNode = null;
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next.perv = previousNode;
}
this.length--;
return currentNode.data;
}
// update(position, data) modifies the node at the specified location
// Override update()
update(position, data) {
// 1. Delete node at position
const result = this.removeAt(position);
// 2. Insert element in position
this.insert(position, data);
return result;
}
// remove(data) deletes the node where the specified data is located (inherits the one-way linked list)
remove(data) {
return super.remove(data);
}
// isEmpty() determines whether the linked list is empty
isEmpty() {
return super.isEmpty();
}
// size() gets the length of the linked list
size() {
return super.size();
}
// forwardToString() linked list data is returned in string form from front to back
forwardToString() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let result = "";
// Traverse all nodes and splice them into strings until the node is null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + "--";
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return result;
}
// backwardString() the linked list data is returned as a string from back to front
backwardString() {
let currentNode = this.tail;
let result = "";
// Traverse all nodes and splice them into strings until the node is null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + "--";
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
return result;
}
}
Code test
const doublyLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList();
// append() test
doublyLinkedList.append("ZZ");
doublyLinkedList.append("XX");
doublyLinkedList.append("CC");
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// insert() test
doublyLinkedList.insert(0, "00");
doublyLinkedList.insert(2, "22");
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// getData() test
console.log(doublyLinkedList.getData(1)); //--> ZZ
// indexOf() test
console.log(doublyLinkedList.indexOf("XX")); //--> 3
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// removeAt() test
doublyLinkedList.removeAt(0);
doublyLinkedList.removeAt(1);
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// update() test
doublyLinkedList.update(0, "111111");
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// remove() test
console.log(doublyLinkedList.remove("111111"));
console.log(doublyLinkedList.remove("22222"));
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// forwardToString() test
console.log(doublyLinkedList.forwardToString());
// backwardString() test
console.log(doublyLinkedList.backwardString());
/–> 3
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
//removeAt() test
doublyLinkedList.removeAt(0);
doublyLinkedList.removeAt(1);
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
//update() test
doublyLinkedList.update(0, "111111");
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
//remove() test
console.log(doublyLinkedList.remove("111111"));
console.log(doublyLinkedList.remove("22222"));
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
//forwardToString() test
console.log(doublyLinkedList.forwardToString());
//backwardString() test
console.log(doublyLinkedList.backwardString());