I. deploy the master node
1.1 master node service
The kubernetes master node runs the following components:
- kube-apiserver
- kube-scheduler
- kube-controller-manager
- kube-nginx
Kube apiserver, Kube scheduler and Kube controller manager all run in multi instance mode:
Kube scheduler and Kube controller manager will automatically elect a leader instance. Other instances are in blocking mode. When the leader is hung, a new leader will be re elected to ensure service availability.
Kube API server is stateless, and proxy access through Kube nginx is needed to ensure service availability.
1.2 install Kubernetes
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# wget https://dl.k8s.io/v1.14.2/kubernetes-server-linux-amd64.tar.gz 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# tar -xzvf kubernetes-server-linux-amd64.tar.gz 4 [root@k8smaster01 work]# cd kubernetes 5 [root@k8smaster01 kubernetes]# tar -xzvf kubernetes-src.tar.gz
1.3 distribute Kubernetes
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# for master_ip in ${MASTER_IPS[@]} 4 do 5 echo ">>> ${master_ip}" 6 scp kubernetes/server/bin/{apiextensions-apiserver,cloud-controller-manager,kube-apiserver,kube-controller-manager,kube-proxy,kube-scheduler,kubeadm,kubectl,kubelet,mounter} root@${master_ip}:/opt/k8s/bin/ 7 ssh root@${master_ip} "chmod +x /opt/k8s/bin/*" 8 done
II. Deploy highly available Kube API server
2.1 introduction to high availability apserver
In this experiment, we deploy a three instance Kube API server cluster. They use Kube nginx for proxy access to ensure service availability.
2.2 create Kubernetes certificate and private key
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# cat > kubernetes-csr.json <<EOF 3 { 4 "CN": "kubernetes", 5 "hosts": [ 6 "127.0.0.1", 7 "172.24.8.71", 8 "172.24.8.72", 9 "172.24.8.73", 10 "${CLUSTER_KUBERNETES_SVC_IP}", 11 "kubernetes", 12 "kubernetes.default", 13 "kubernetes.default.svc", 14 "kubernetes.default.svc.cluster", 15 "kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local." 16 ], 17 "key": { 18 "algo": "rsa", 19 "size": 2048 20 }, 21 "names": [ 22 { 23 "C": "CN", 24 "ST": "Shanghai", 25 "L": "Shanghai", 26 "O": "k8s", 27 "OU": "System" 28 } 29 ] 30 } 31 EOF 32 #Create CA certificate request file for Kubernetes
Interpretation:
The hosts field specifies the list of IP and domain names authorized to use the certificate. The IP and domain names of the master node and kubernetes service are listed here;
kubernetes service IP is automatically created by apiserver, which is generally the first IP of the network segment specified by the service cluster IP range parameter. You can obtain it later by the following command:
1 # kubectl get svc kubernetes1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# cfssl gencert -ca=/opt/k8s/work/ca.pem \ 3 -ca-key=/opt/k8s/work/ca-key.pem -config=/opt/k8s/work/ca-config.json \ 4 -profile=kubernetes kubernetes-csr.json | cfssljson -bare kubernetes #Generate CA key (CA key. PEM) and certificate (ca.pem)
2.3 distribute certificate and private key
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# for master_ip in ${MASTER_IPS[@]} 4 do 5 echo ">>> ${master_ip}" 6 ssh root@${master_ip} "mkdir -p /etc/kubernetes/cert" 7 scp kubernetes*.pem root@${master_ip}:/etc/kubernetes/cert/ 8 done
2.4 create encryption profile
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# cat > encryption-config.yaml <<EOF 4 kind: EncryptionConfig 5 apiVersion: v1 6 resources: 7 - resources: 8 - secrets 9 providers: 10 - aescbc: 11 keys: 12 - name: key1 13 secret: ${ENCRYPTION_KEY} 14 - identity: {} 15 EOF
2.5 distribute encryption profile
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# for master_ip in ${MASTER_IPS[@]} 4 do 5 echo ">>> ${master_ip}" 6 scp encryption-config.yaml root@${master_ip}:/etc/kubernetes/ 7 done
2.6 create audit policy file
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# cat > audit-policy.yaml <<EOF 4 apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1beta1 5 kind: Policy 6 rules: 7 # The following requests were manually identified as high-volume and low-risk, so drop them. 8 - level: None 9 resources: 10 - group: "" 11 resources: 12 - endpoints 13 - services 14 - services/status 15 users: 16 - 'system:kube-proxy' 17 verbs: 18 - watch 19 20 - level: None 21 resources: 22 - group: "" 23 resources: 24 - nodes 25 - nodes/status 26 userGroups: 27 - 'system:nodes' 28 verbs: 29 - get 30 31 - level: None 32 namespaces: 33 - kube-system 34 resources: 35 - group: "" 36 resources: 37 - endpoints 38 users: 39 - 'system:kube-controller-manager' 40 - 'system:kube-scheduler' 41 - 'system:serviceaccount:kube-system:endpoint-controller' 42 verbs: 43 - get 44 - update 45 46 - level: None 47 resources: 48 - group: "" 49 resources: 50 - namespaces 51 - namespaces/status 52 - namespaces/finalize 53 users: 54 - 'system:apiserver' 55 verbs: 56 - get 57 58 # Don't log HPA fetching metrics. 59 - level: None 60 resources: 61 - group: metrics.k8s.io 62 users: 63 - 'system:kube-controller-manager' 64 verbs: 65 - get 66 - list 67 68 # Don't log these read-only URLs. 69 - level: None 70 nonResourceURLs: 71 - '/healthz*' 72 - /version 73 - '/swagger*' 74 75 # Don't log events requests. 76 - level: None 77 resources: 78 - group: "" 79 resources: 80 - events 81 82 # node and pod status calls from nodes are high-volume and can be large, don't log responses for expected updates from nodes 83 - level: Request 84 omitStages: 85 - RequestReceived 86 resources: 87 - group: "" 88 resources: 89 - nodes/status 90 - pods/status 91 users: 92 - kubelet 93 - 'system:node-problem-detector' 94 - 'system:serviceaccount:kube-system:node-problem-detector' 95 verbs: 96 - update 97 - patch 98 99 - level: Request 100 omitStages: 101 - RequestReceived 102 resources: 103 - group: "" 104 resources: 105 - nodes/status 106 - pods/status 107 userGroups: 108 - 'system:nodes' 109 verbs: 110 - update 111 - patch 112 113 # deletecollection calls can be large, don't log responses for expected namespace deletions 114 - level: Request 115 omitStages: 116 - RequestReceived 117 users: 118 - 'system:serviceaccount:kube-system:namespace-controller' 119 verbs: 120 - deletecollection 121 122 # Secrets, ConfigMaps, and TokenReviews can contain sensitive & binary data, 123 # so only log at the Metadata level. 124 - level: Metadata 125 omitStages: 126 - RequestReceived 127 resources: 128 - group: "" 129 resources: 130 - secrets 131 - configmaps 132 - group: authentication.k8s.io 133 resources: 134 - tokenreviews 135 # Get repsonses can be large; skip them. 136 - level: Request 137 omitStages: 138 - RequestReceived 139 resources: 140 - group: "" 141 - group: admissionregistration.k8s.io 142 - group: apiextensions.k8s.io 143 - group: apiregistration.k8s.io 144 - group: apps 145 - group: authentication.k8s.io 146 - group: authorization.k8s.io 147 - group: autoscaling 148 - group: batch 149 - group: certificates.k8s.io 150 - group: extensions 151 - group: metrics.k8s.io 152 - group: networking.k8s.io 153 - group: policy 154 - group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io 155 - group: scheduling.k8s.io 156 - group: settings.k8s.io 157 - group: storage.k8s.io 158 verbs: 159 - get 160 - list 161 - watch 162 163 # Default level for known APIs 164 - level: RequestResponse 165 omitStages: 166 - RequestReceived 167 resources: 168 - group: "" 169 - group: admissionregistration.k8s.io 170 - group: apiextensions.k8s.io 171 - group: apiregistration.k8s.io 172 - group: apps 173 - group: authentication.k8s.io 174 - group: authorization.k8s.io 175 - group: autoscaling 176 - group: batch 177 - group: certificates.k8s.io 178 - group: extensions 179 - group: metrics.k8s.io 180 - group: networking.k8s.io 181 - group: policy 182 - group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io 183 - group: scheduling.k8s.io 184 - group: settings.k8s.io 185 - group: storage.k8s.io 186 187 # Default level for all other requests. 188 - level: Metadata 189 omitStages: 190 - RequestReceived 191 EOF
2.7 distribution strategy document
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# for master_ip in ${MASTER_IPS[@]} 4 do 5 echo ">>> ${master_ip}" 6 scp audit-policy.yaml root@${master_ip}:/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml 7 done
2.8 create a certificate and key to access metrics server
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# cat > proxy-client-csr.json <<EOF 3 { 4 "CN": "aggregator", 5 "hosts": [], 6 "key": { 7 "algo": "rsa", 8 "size": 2048 9 }, 10 "names": [ 11 { 12 "C": "CN", 13 "ST": "Shanghai", 14 "L": "Shanghai", 15 "O": "k8s", 16 "OU": "System" 17 } 18 ] 19 } 20 EOF 21 #Create CA certificate request file for metrics server
Interpretation:
The CN name needs to be in the -- requestheader allowed names parameter of the Kube apiserver, otherwise, you will be prompted for insufficient permissions when accessing metrics later.
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# cfssl gencert -ca=/opt/k8s/work/ca.pem \ 3 -ca-key=/opt/k8s/work/ca-key.pem -config=/opt/k8s/work/ca-config.json \ 4 -profile=kubernetes proxy-client-csr.json | cfssljson -bare proxy-client #Generate CA key (CA key. PEM) and certificate (ca.pem)
2.9 distributing certificates and private keys
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# for master_ip in ${MASTER_IPS[@]} 4 do 5 echo ">>> ${master_ip}" 6 scp proxy-client*.pem root@${master_ip}:/etc/kubernetes/cert/ 7 done
2.10 create the system D of Kube API server
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# cat > kube-apiserver.service.template <<EOF 4 [Unit] 5 Description=Kubernetes API Server 6 Documentation=https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/kubernetes 7 After=network.target 8 9 [Service] 10 WorkingDirectory=${K8S_DIR}/kube-apiserver 11 ExecStart=/opt/k8s/bin/kube-apiserver \\ 12 --advertise-address=##MASTER_IP## \\ 13 --default-not-ready-toleration-seconds=360 \\ 14 --default-unreachable-toleration-seconds=360 \\ 15 --feature-gates=DynamicAuditing=true \\ 16 --max-mutating-requests-inflight=2000 \\ 17 --max-requests-inflight=4000 \\ 18 --default-watch-cache-size=200 \\ 19 --delete-collection-workers=2 \\ 20 --encryption-provider-config=/etc/kubernetes/encryption-config.yaml \\ 21 --etcd-cafile=/etc/kubernetes/cert/ca.pem \\ 22 --etcd-certfile=/etc/kubernetes/cert/kubernetes.pem \\ 23 --etcd-keyfile=/etc/kubernetes/cert/kubernetes-key.pem \\ 24 --etcd-servers=${ETCD_ENDPOINTS} \\ 25 --bind-address=##MASTER_IP## \\ 26 --secure-port=6443 \\ 27 --tls-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/cert/kubernetes.pem \\ 28 --tls-private-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/cert/kubernetes-key.pem \\ 29 --insecure-port=0 \\ 30 --audit-dynamic-configuration \\ 31 --audit-log-maxage=15 \\ 32 --audit-log-maxbackup=3 \\ 33 --audit-log-maxsize=100 \\ 34 --audit-log-mode=batch \\ 35 --audit-log-truncate-enabled \\ 36 --audit-log-batch-buffer-size=20000 \\ 37 --audit-log-batch-max-size=2 \\ 38 --audit-log-path=${K8S_DIR}/kube-apiserver/audit.log \\ 39 --audit-policy-file=/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml \\ 40 --profiling \\ 41 --anonymous-auth=false \\ 42 --client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/cert/ca.pem \\ 43 --enable-bootstrap-token-auth \\ 44 --requestheader-allowed-names="aggregator" \\ 45 --requestheader-client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/cert/ca.pem \\ 46 --requestheader-extra-headers-prefix="X-Remote-Extra-" \\ 47 --requestheader-group-headers=X-Remote-Group \\ 48 --requestheader-username-headers=X-Remote-User \\ 49 --service-account-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/cert/ca.pem \\ 50 --authorization-mode=Node,RBAC \\ 51 --runtime-config=api/all=true \\ 52 --enable-admission-plugins=NodeRestriction \\ 53 --allow-privileged=true \\ 54 --apiserver-count=3 \\ 55 --event-ttl=168h \\ 56 --kubelet-certificate-authority=/etc/kubernetes/cert/ca.pem \\ 57 --kubelet-client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/cert/kubernetes.pem \\ 58 --kubelet-client-key=/etc/kubernetes/cert/kubernetes-key.pem \\ 59 --kubelet-https=true \\ 60 --kubelet-timeout=10s \\ 61 --proxy-client-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/cert/proxy-client.pem \\ 62 --proxy-client-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/cert/proxy-client-key.pem \\ 63 --service-cluster-ip-range=${SERVICE_CIDR} \\ 64 --service-node-port-range=${NODE_PORT_RANGE} \\ 65 --logtostderr=true \\ 66 --v=2 67 Restart=on-failure 68 RestartSec=10 69 Type=notify 70 LimitNOFILE=65536 71 72 [Install] 73 WantedBy=multi-user.target 74 EOF
Interpretation:
- --Advertisement address: the IP notified by apiserver (kubernetes service back-end node IP);
- --Default - * - tolerance seconds: set the threshold related to node exceptions;
- --Max - * - requests inflight: the maximum threshold value related to the request;
- --Etcd - *: Certificate to access etcd and etcd server address;
- --Experimental encryption provider config: Specifies the configuration used to encrypt secret in etcd;
- --Bind address: the IP monitored by https cannot be 127.0.0.1, otherwise the external world cannot access its security port 6443;
- --Secret port: https listening port;
- --Insecure port = 0: turn off listening to http insecure port (8080);
- --tls-*-file: Specifies the certificate, private key and CA file used by apiserver;
- --Audit - *: configure parameters related to audit policy and audit log file;
- --Client CA file: verify the certificate brought by the client (Kue controller manager, Kube scheduler, kubelet, Kube proxy, etc.) request;
- --Enable bootstrap token auth: enable the token authentication of kubelet bootstrap;
- --requestheader - *: the configuration parameters related to the aggregator layer of Kube API server, which need to be used by proxy client & HPA;
- --Requestheader client CA file: used to sign the certificate specified by -- proxy client cert file and -- proxy client key file; used when metric aggregator is enabled;
- --Requestheader allowed names: cannot be empty. The value is the CN name of the comma separated -- proxy client cert file certificate. Here it is set to "aggregator";
- --Service account key file: the public key file that signs the ServiceAccount Token, and the -- service account private key file that Kube controller manager specifies. The two files are used in pairs;
- --Runtime config = API / all = true: enable all versions of APIs, such as autoscaling/v2alpha1;
- --Authorization mode = Node, RBAC, -- anonymous-auth=false: enable Node and RBAC authorization modes, and reject unauthorized requests;
- --Enable admission plugins: enable some plugins that are closed by default;
- --Allow privileged: the container to run and execute the privileged permission;
- --Apiserver count = 3: Specifies the number of apiserver instances;
- --Event TTL: Specifies the save time of events;
- --Kubelet - *: if specified, use https to access kubelet APIs; you need to define RBAC rules for the user corresponding to the certificate (the user of kubernetes*.pem certificate above is kubernetes), otherwise, when accessing the kubelet API, you will be prompted that you are not authorized;
- --Proxy client - *: the certificate used by apiserver to access metrics server;
- --Service Cluster IP range: Specifies the Service Cluster IP address segment;
- --Service node port range: Specifies the port range of the NodePort.
Tip: if the Kube API server machine is not running Kube proxy, you need to add the -- enable aggregator routing = true parameter.
Note: the CA certificate specified by requestheader client CA file must have client auth and server auth;
If the -- requestheader allowed names is empty, or the CN name of the -- proxy client cert file certificate is not in the allowed names, the subsequent view of node s or pods' metrics fails, indicating:
1 [root@zhangjun-k8s01 1.8+]# kubectl top nodes 2 Error from server (Forbidden): nodes.metrics.k8s.io is forbidden: User "aggregator" cannot list resource "nodes" in API group "metrics.k8s.io" at the cluster scope 3
2.11 distribute systemd
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 2 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 3 [root@k8smaster01 work]# for (( i=0; i < 3; i++ )) 4 do 5 sed -e "s/##MASTER_NAME##/${MASTER_NAMES[i]}/" -e "s/##MASTER_IP##/${MASTER_IPS[i]}/" kube-apiserver.service.template > kube-apiserver-${MASTER_IPS[i]}.service 6 done 7 [root@k8smaster01 work]# ls kube-apiserver*.service #Replace the corresponding IP 8 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# cd /opt/k8s/work 9 [root@k8smaster01 work]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 10 [root@k8smaster01 work]# for master_ip in ${MASTER_IPS[@]} 11 do 12 echo ">>> ${master_ip}" 13 scp kube-apiserver-${master_ip}.service root@${master_ip}:/etc/systemd/system/kube-apiserver.service 14 done #Distribute systemd
III. start and verify
3.1 start the Kube API server service
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 2 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# for master_ip in ${MASTER_IPS[@]} 3 do 4 echo ">>> ${master_ip}" 5 ssh root@${master_ip} "mkdir -p ${K8S_DIR}/kube-apiserver" 6 ssh root@${master_ip} "systemctl daemon-reload && systemctl enable kube-apiserver && systemctl restart kube-apiserver" 7 done
3.2 check Kube API server service
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 2 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# for master_ip in ${MASTER_IPS[@]} 3 do 4 echo ">>> ${master_ip}" 5 ssh root@${master_ip} "systemctl status kube-apiserver |grep 'Active:'" 6 done
3.3 view the data written to etcd by Kube API server
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# source /opt/k8s/bin/environment.sh 2 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl \ 3 --endpoints=${ETCD_ENDPOINTS} \ 4 --cacert=/opt/k8s/work/ca.pem \ 5 --cert=/opt/k8s/work/etcd.pem \ 6 --key=/opt/k8s/work/etcd-key.pem \ 7 get /registry/ --prefix --keys-only
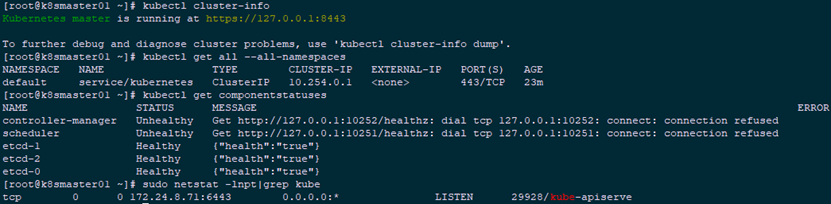
3.4 checking cluster information
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# kubectl cluster-info 2 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# kubectl get all --all-namespaces 3 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# kubectl get componentstatuses 4 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# sudo netstat -lnpt|grep kube #Check the port on which Kube API server listens
Tips:
If the following error information is output when executing the kubectl command, the ~ /. kube/config file used is incorrect. Please switch to the correct account before executing the command:
The connection to the server localhost:8080 was refused - did you specify the right host or port?
When executing the kubectl get componentstatuses command, apiserver sends a request to 127.0.0.1 by default. When controller manager and scheduler are running in cluster mode, they may not be on the same machine as Kube API server. At this time, the status of controller manager or scheduler is Unhealthy, but in fact, they work normally;
6443: the secure port for receiving https requests, authenticating and authorizing all requests;
Because the insecure port is closed, the 8080 is not monitored.
3.5 authorization
Kube apiserver is granted access to the kubelet API.
When kubectl exec, run, logs and other commands are executed, the apiserver will forward the request to the https port of kubelet. This experiment defines RBAC rules and authorizes the certificate (kubernetes.pem) user name (CN: kuberntes) used by apiserver to access the kubelet API
1 [root@k8smaster01 ~]# kubectl create clusterrolebinding kube-apiserver:kubelet-apis --clusterrole=system:kubelet-api-admin --user kubernetes